Import Liberty Collectives
Importing a WebSphere® Liberty collective creates a Liberty-Collective Kubernetes custom resource to represent the collective. Application Navigator automatically discovers applications that are deployed on the collective and creates Liberty-App Kubernetes custom resources to represent those applications. Application Navigator periodically polls the collective to keep the state of the Liberty-Collective resources and Liberty-App resources synchronized with the collective.
About this task
You can import an existing WebSphere Liberty collective into IBM Application Navigator to establish visibility and access to the collective. A collective can be imported into Application Navigator with the ‘Liberty Collectives’ page in Application Navigator or the Kubernetes kubectl command.
Procedure
Import the WebSphere Liberty collective using the ‘Liberty Collectives’ page
-
Open the WebSphere Liberty collective page and launch create dialog.
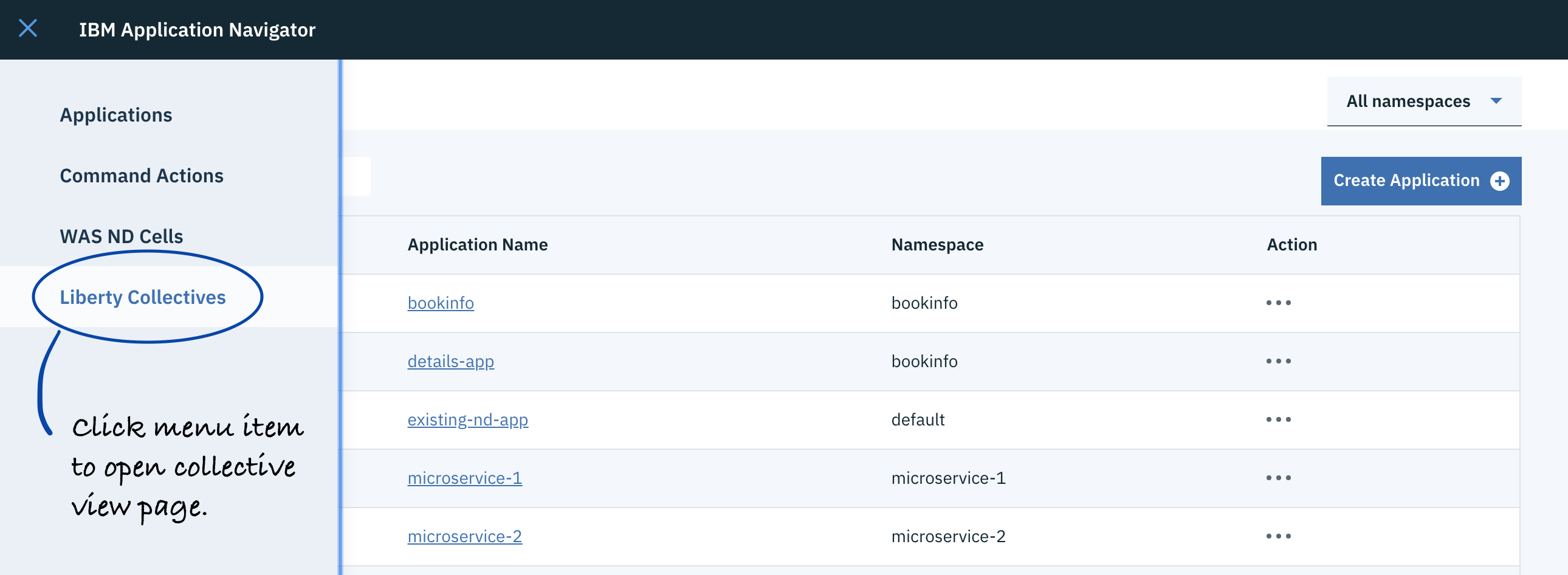
-
Enter details and create the collective.
-
Under the General details tab, enter a name for the collective.
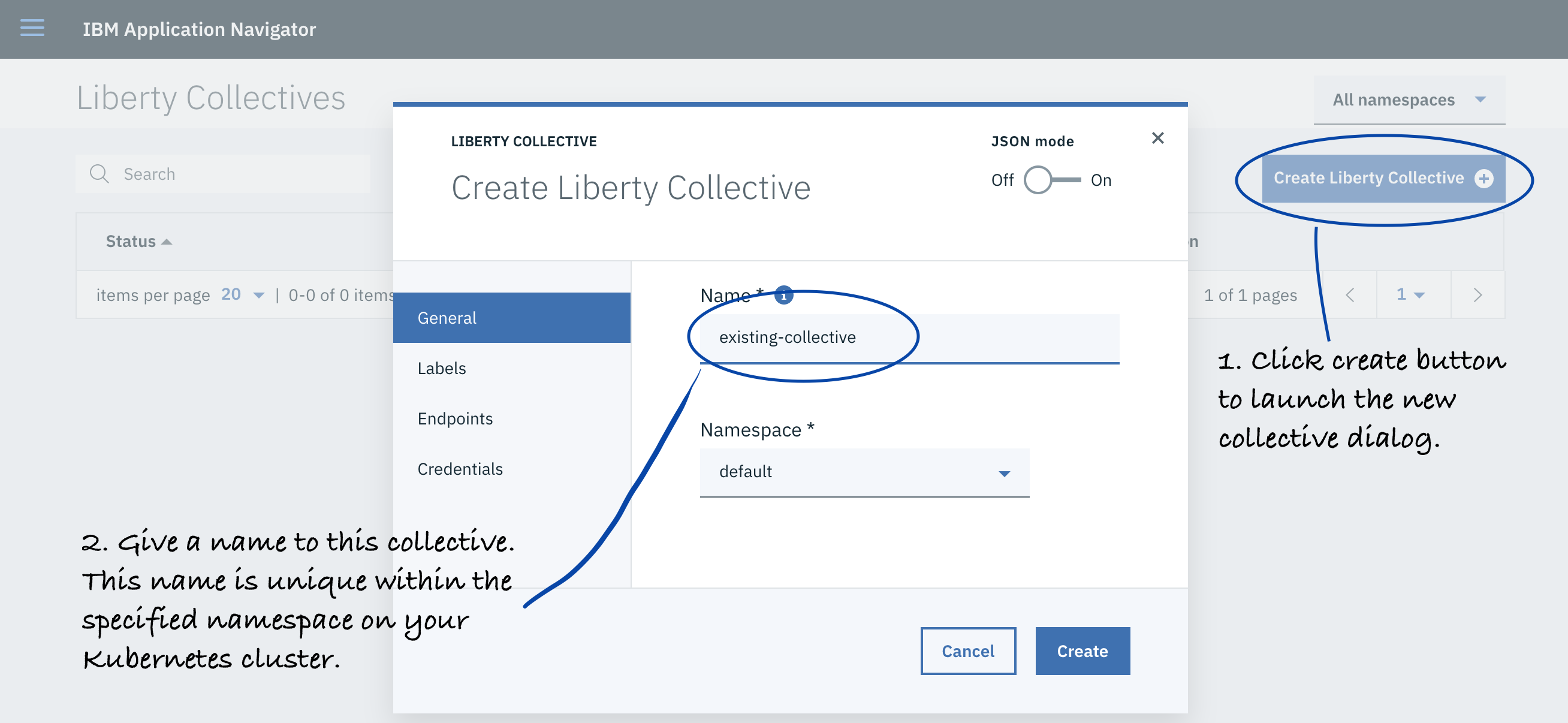
-
Click Endpoints and enter your host name, and adjust any port values (defaults are provided).
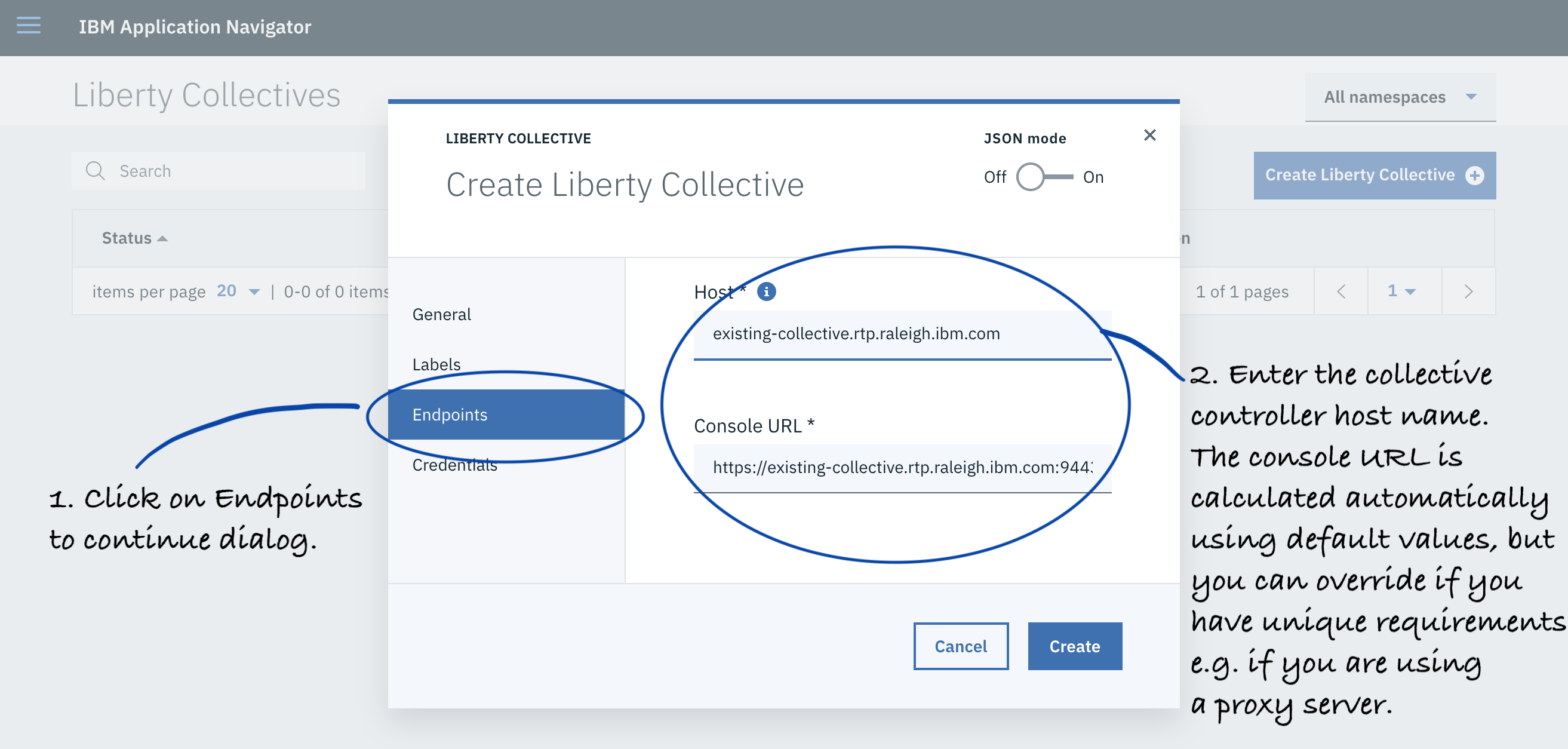
-
Click Credentials and enter a Kubernetes secret name, user name, and password to log in to your collective.
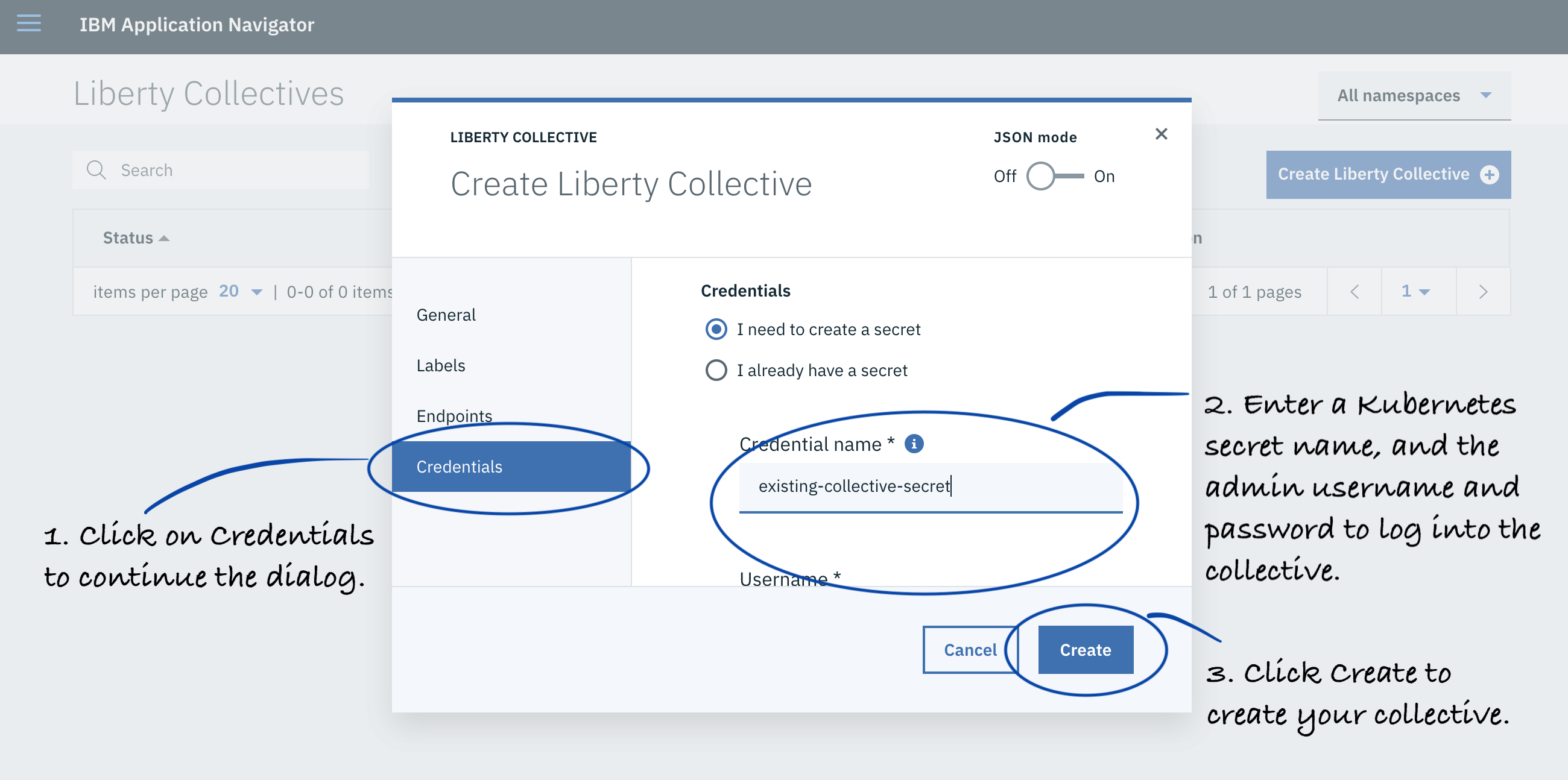
-
Click the Create button to create your credentials secret.
Attention: You can create a new Kubernetes secret or choose an existing one. For a new one, the user name and password you specify is stored as base 64 encoded values in the secret.
-
-
Optional: Inspect the collective.
-
Click collective name to see the detail view.
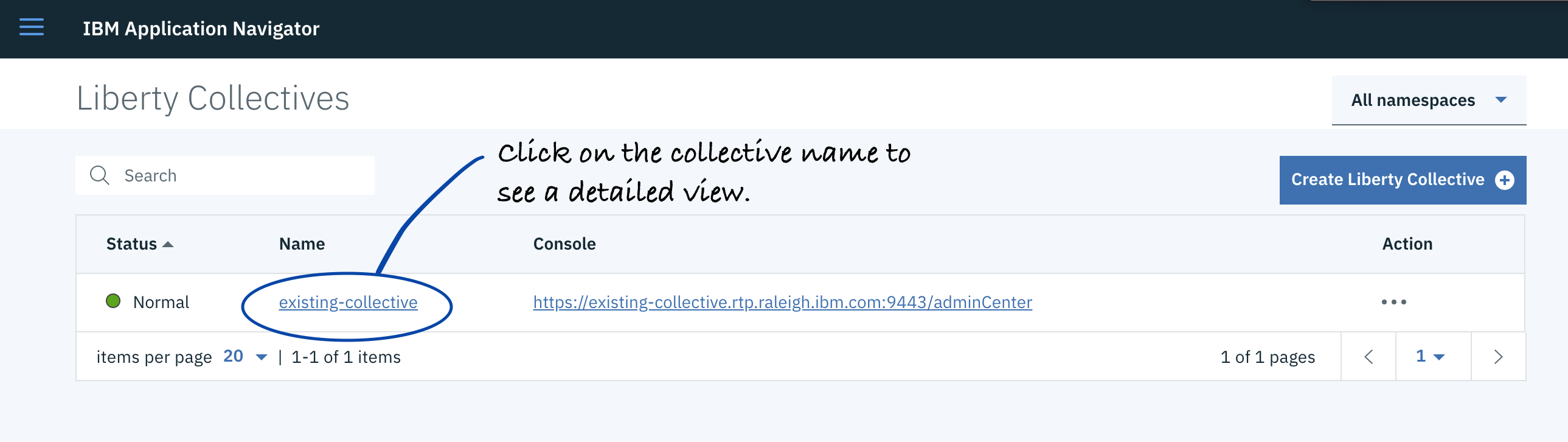
-
Use the detail view to see collective details.
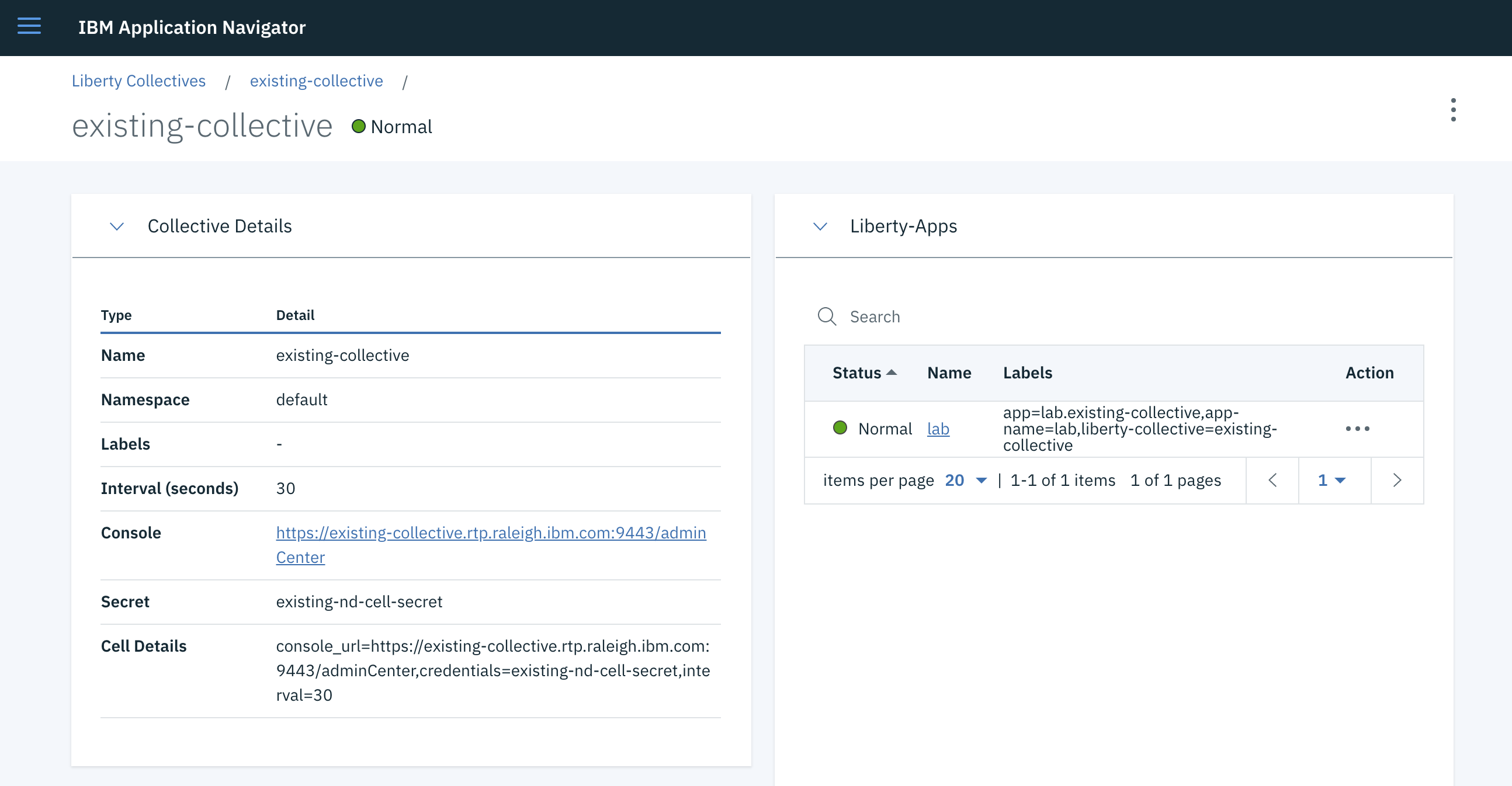
-
Import the WebSphere Liberty collective by using the Kubernetes command-line tool
- Create the WebSphere Liberty collective resource.
- All fields that are shown are required.
- Credentials are a Kubernetes secret in the same namespace.
- Interval is the controller polling interval for syncing collectives with Kubernetes resources.
-
Create the
collective.yamlfile:apiVersion: kappnav.io/v1beta1 kind: Liberty-Collective metadata: name: existing-collective namespace: default spec: console_url: https://existing-collective.example.com:9043/adminCenter credentials: existing-collective-secret interval: 30 -
Create the resource with the command:
kubectl create -f collective.yaml
- Create the secret for the collective credentials.
- The user name and password fields must be base 64 encoded.
- The secret must be in the same namespace as the corresponding collective.
-
Create the
secret.yamlfile.apiVersion: v1 data: password: dGVzdHVzZXJwd2Q= username: dGVzdHVzZXI= kind: Secret metadata: name: existing-collective-secret namespace: default -
Create the resource with the following command:
kubectl create -f secret.yaml
-
Inspect twas-apps resources.
Use the following commands to see your collective and its secret in the
yamlformat:kubectl get liberty-collective existing-collective -o yaml kubectl get liberty-apps -o yaml kubectl get secret existing-collective-secret -o yaml
Results
You get a Liberty-Collective Kubernetes resource that represents your WebSphere Liberty collective and one Liberty-App Kubernetes resource for each enterprise application deployed to that collective.