IBM DevSecOps Reference Implementation¶
IBM uses internally a common practice and process how to implement DevSecOps. This process has been published so that IBM clients, partners and developers can use it too. See DevSecOps Reference Implementation for Audit-Ready Compliance for details.
This project leverages the DevSecOps reference architecture to deploy the backend and frontend containers to Kubernetes and OpenShift on the IBM Cloud.
There is IBM Cloud documentation that describes how to set up the CI and CD toolchains. The documentation below adopts this information for the multi-tenancy sample application.
Overview¶
There are six steps to deploy the SaaS sample application.
- CI backend pull request: Get approval to merge backend code changes into main
- CI backend pipeline: Pipeline to build backend image and deploy it to a staging environment for testing
- CI frontend pull request: Get approval to merge frontend code changes into main
- CI frontend pipeline: Pipeline to build frontend image and deploy it to a staging environment for testing
- CD pull request: Pull request to deploy main for a specific tenant to production
- CD pipeline: After approval deploy backend and frontend for a specific tenant to production
Check out the following documents for details:
- CI pull request related to (1) and (3)
- CI pipeline related to (2) and (4)
- CD pull request related to (5)
- CD pipeline related to (6)
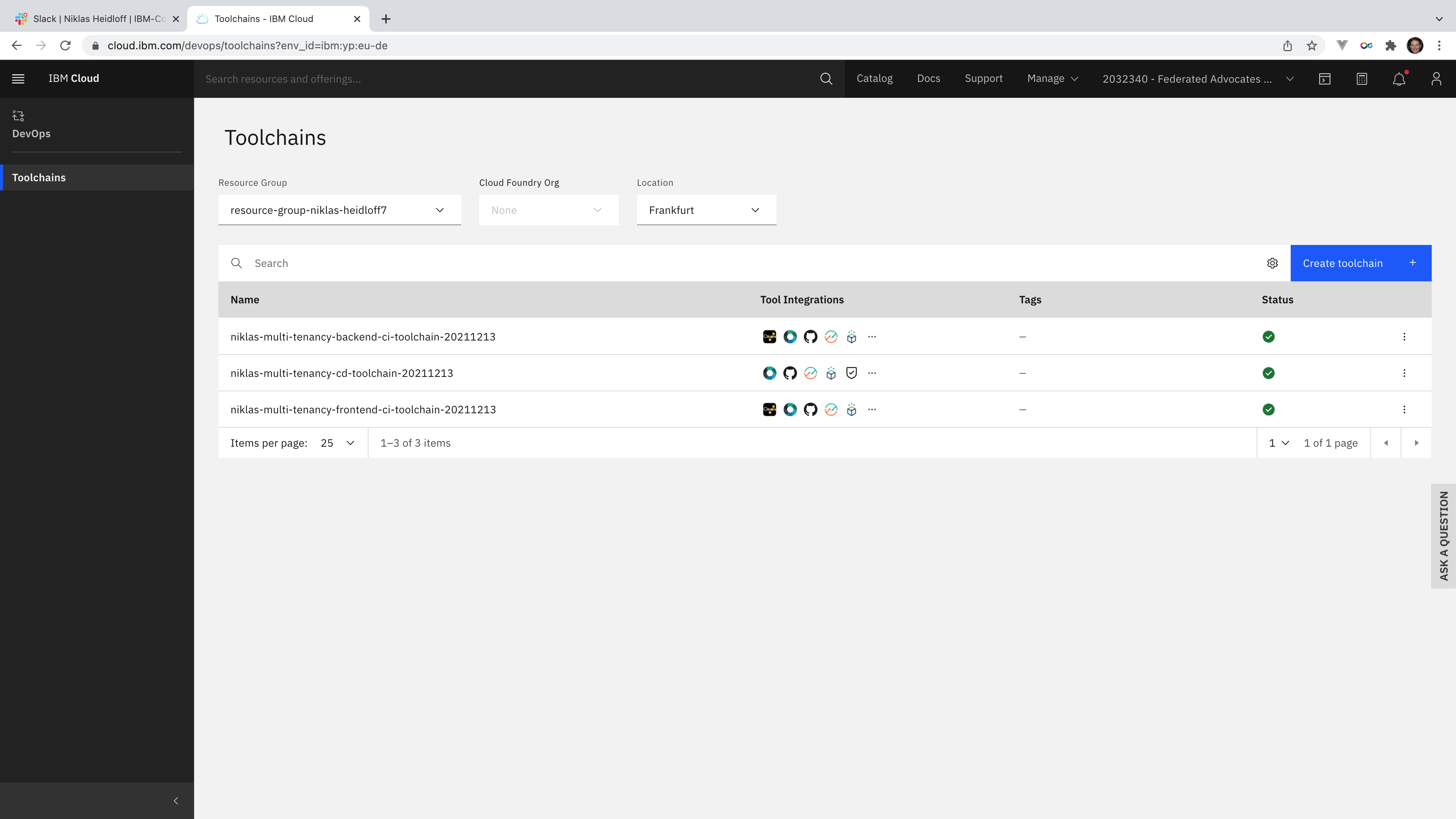
Toolchains¶
There are three toolchains:
- CI for backend
- CI for frontend
- CD
Repos¶
These three repos contain the code of the microservices and the toolchains (on github.com):
- multi-tenancy
- multi-tenancy-backend
- multi-tenancy-frontend
The following repos contain state information and are shared by the three toolchains (on IBM Cloud GitLab):
- inventory
- complicance change management
- compliance issues
- evidence
The following repo contains the code for the 'out-of-the-box' security checks (on IBM Cloud GitLab):
- compliance pipelines