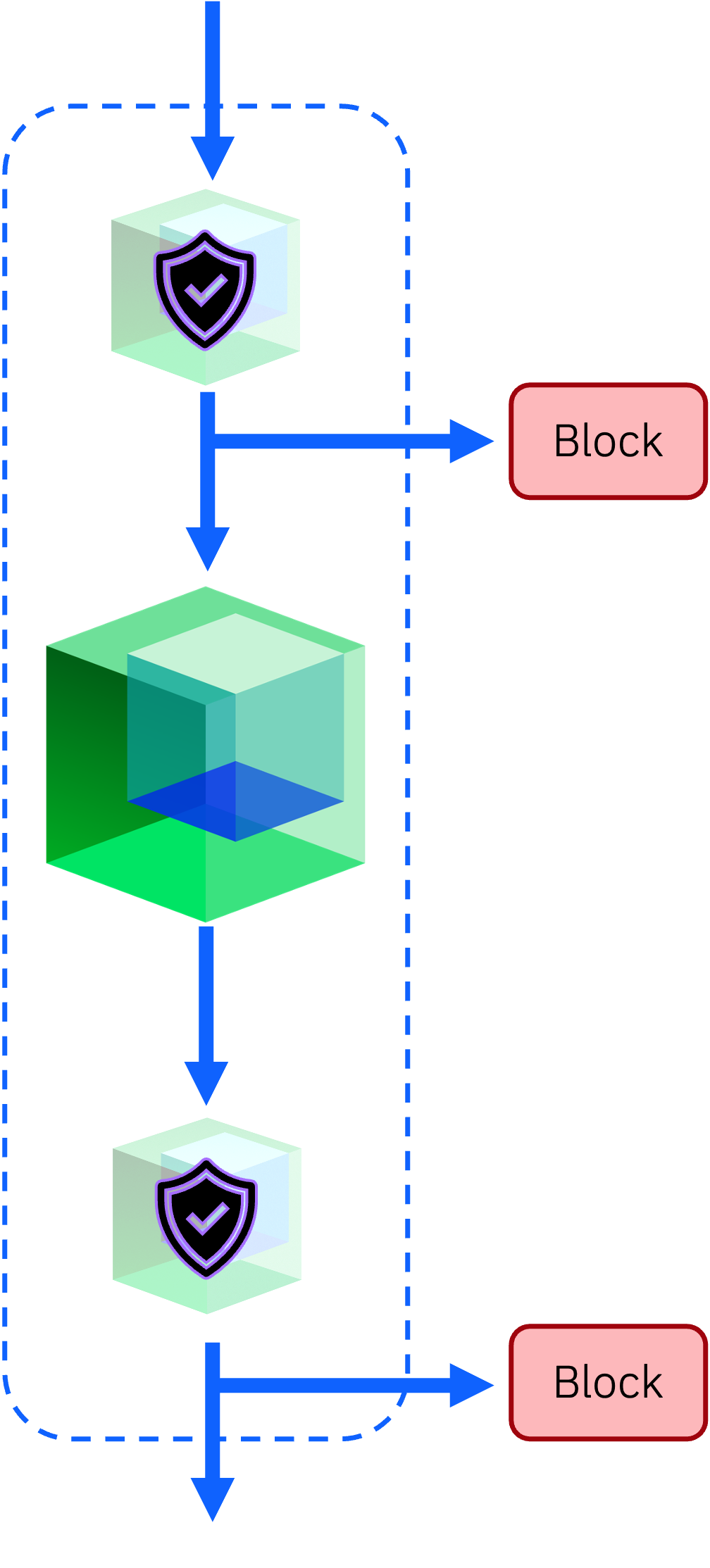
ARES with Guardrails
Optionally, the target node may include input and output guardrails. These act as filters for prompts sent to the model (input guardrail) and outputs returned by the model (output guardrail).
The input guardrail filters user requests made to the target connector. It attempts to identify and reject jailbreaks before the model is exposed to them.
The output guardrail filters responses from the target connector. It aims to detect and block harmful or complicit outputs resulting from jailbreak attempts.
Both guardrails can be configured using Granite Guardian.
Guardrails must be defined using a Connector. ARES includes support for IBM’s Granite Guardian and Google’s ShieldGemma.
Below is an example configuration using ibm-granite/granite-3.3-8b-instruct as the target model with Granite Guardian as both input and output guardrails:
target:
huggingface: # the target connector
model_config:
pretrained_model_name_or_path: ibm-granite/granite-3.3-8b-instruct
torch_dtype: bfloat16
tokenizer_config:
padding_side: left
pretrained_model_name_or_path: ibm-granite/granite-3.3-8b-instruct
input_guardrail: # the input guardrail
response: I'm sorry I cannot comply
granite-guardian-3.0:
output_guardrail: # the output guardrail
response: I'm sorry I cannot comply
granite-guardian-3.0: