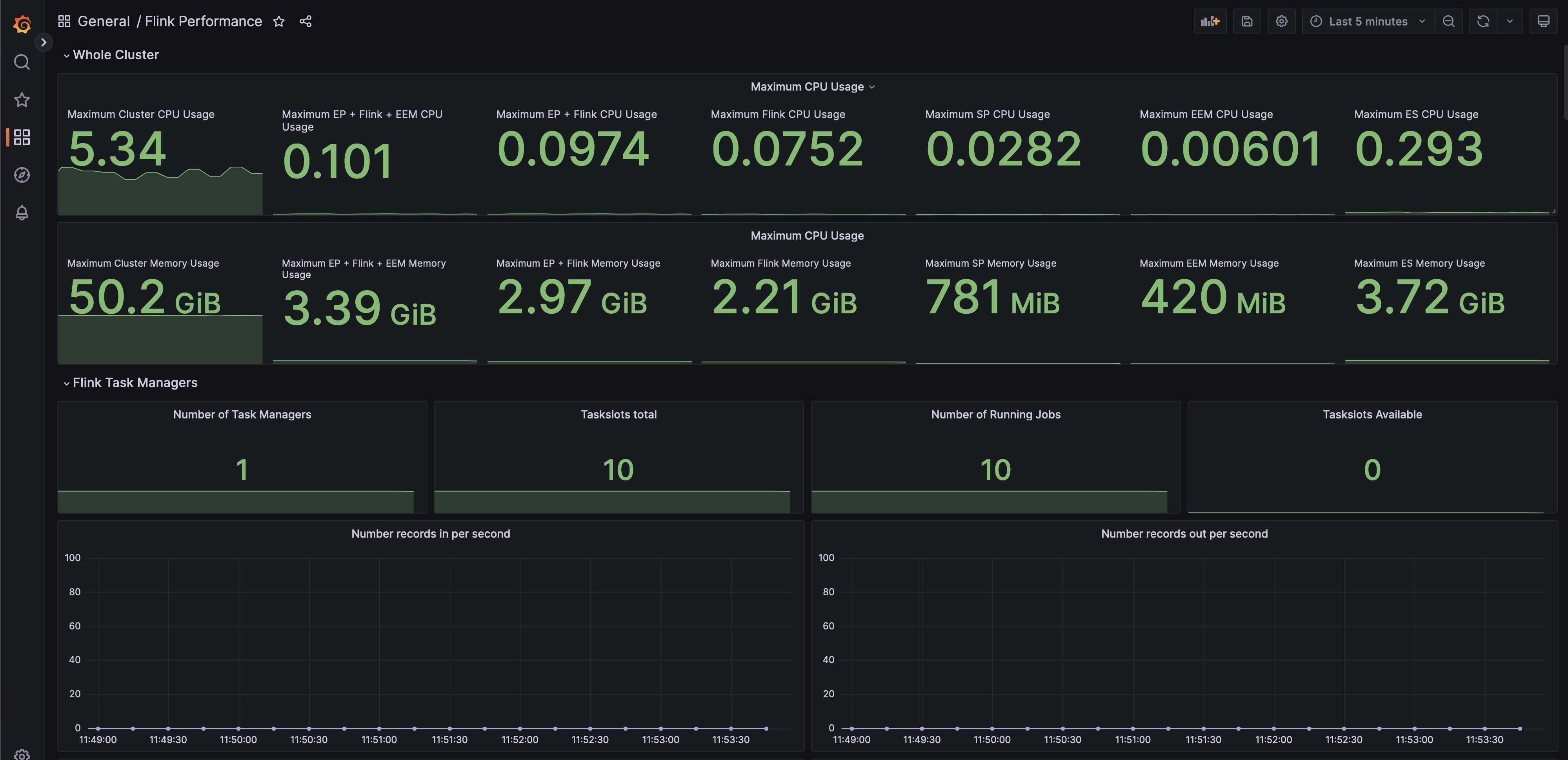
Prometheus and Grafana can be used to monitor a Flink instance by showing key metrics on dashboards and setting up alerts that trigger when the cluster is not functioning normally. Monitoring Flink is essential for ensuring the stability, performance, and reliability of Flink jobs.
To set up Prometheus for your Flink instance and visualize the collected metrics in Grafana dashboards, complete the following tasks as described in the following sections:
- Integrate Flink with Prometheus.
- Install and configure Grafana with Prometheus.
Integrating Flink with Prometheus
Before you can configure Grafana dashboards to view the metrics, integrate your Flink instance with Prometheus as follows.
-
Ensure you have installed the IBM Operator for Apache Flink on the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. Also ensure you have installed the Prometheus stack on your cluster by using the
kube-prometheusproject. For more information, see the kube-prometheus GitHub repository. -
Create the following ConfigMap in the
openshift-monitoringnamespace if it does not yet exist. If a ConfigMap already exist, ensure that the configuration is similar to the following:apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: cluster-monitoring-config namespace: openshift-monitoring data: config.yaml: | enableUserWorkload: true -
Change the existing
FlinkDeploymentto include the following metrics parameters:spec: flinkConfiguration: metrics.reporter.prom.class: org.apache.flink.metrics.prometheus.PrometheusReporter metrics.reporter.prom.factory.class: org.apache.flink.metrics.prometheus.PrometheusReporterFactory metrics.reporter.prom.port: 9250-9260 metrics.reporters: prom taskmanager.network.detailed-metrics: trueImportant: The
FlinkDeploymentmust be deployed in the namespace where the Flink operator is installed. -
Deploy the
PodMonitorresource in the same namespace whereFlinkDeploymentinstance is deployed:apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1 kind: PodMonitor metadata: labels: release: prometheus name: flink-pod-monitor spec: namespaceSelector: matchNames: - <your-namepace> podMetricsEndpoints: - path: / relabelings: - action: replace replacement: '$1:9250' sourceLabels: - __meta_kubernetes_pod_ip targetLabel: __address__ selector: matchLabels: type: flink-native-kubernetesImportant: Replace
<your-namespace>with the name of the namespace where yourFlinkDeploymentinstance is deployed.
The metrics sent by Flink to Prometheus are now visible in OpenShift Container Platform. To verify that the data is being made available, ensure that the data is visible by clicking Observe > Metrics.
Install and configure Grafana with Prometheus metrics
Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following set up:
- The IBM Operator for Apache Flink installed.
- The integration of Flink with Prometheus completed.
Installing Grafana
Install the Grafana operator and instance in the openshift-user-workload-monitoring namespace, and configuring the Grafana service account as described in the following sections.
Installing the Grafana operator
To install the operator by using the OpenShift Container Platform web console, do the following:
- Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console using your login credentials.
- Expand the Operators dropdown and select OperatorHub to open the OperatorHub dashboard.
- Select the project you want to deploy the instance in.
- In the All Items search box enter
Grafanato locate the operator title. - Click the Grafana Operator provided by Red Hat tile to open the install side panel.
- Click the Install button to open the Create Operator Subscription dashboard.
- Select the installation mode as A specific namespace on the cluster, select the target namespace as
openshift-user-workload-monitoring. -
Click Subscribe to begin the installation.
The installation can take a few minutes to complete.
Installing a Grafana instance
To install a Grafana instance through the OpenShift Container Platform web console, do the following:
- Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console using your login credentials.
- Expand the Operators dropdown and select Installed Operators to open the Installed Operators page.
-
Expand the Project dropdown and select the project where you installed Grafana operator.
Note: If the operator is not shown, it is either not installed or not available for the selected namespace.
- In the Operator Details dashboard, click the Grafana tab.
- Click the Create Grafana button to open the Create Grafana panel. You can use this panel to define an
Grafanacustom resource. -
In the YAML view, add the following YAML:
apiVersion: integreatly.org/v1alpha1 kind: Grafana metadata: name: example-grafana namespace: test01 spec: config: auth: disable_signout_menu: true auth.anonymous: enabled: true log: level: warn mode: console security: admin_password: secret admin_user: root - Click Create.
Configuring the Grafana service account
To configure the Grafana service account, do the following:
- Log in to your Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform as a cluster administrator by using the
ocCLI (oc login). -
Configure role-based access control (RBAC) for the Grafana service account:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-monitoring-view -z grafana-serviceaccount -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring -
The bearer API token for this service account is used to authenticate access to Prometheus in the
openshift-user-workload-monitoringnamespace. The following command will display this token.oc serviceaccounts get-token grafana-serviceaccount -n openshift-user-workload-monitoringFor new clusters in OpenShift 4.11 and above, a service account token secret can be created as follows:
oc create token grafana-serviceaccount --duration=8760h -n openshift-user-workload-monitoringAlternatively, In the OpenShift web console, expand the
grafana-serviceaccountservice account in theopenshift-user-workload-monitoringnamespace and copy the bearer API token from the secret. This bearer API token will be used in the following sections.
Configuring a Grafana data source
Create and configure a Grafana data source for Prometheus to integrate the Grafana with Prometheus. To create a Grafana data source, complete the following steps.
-
Get the Prometheus API URL by running the following command:
oc get route -n openshift-monitoring -
Create a
GrafanaDataSourcecustom resource in the namespaceopenshift-user-workload-monitoring:apiVersion: integreatly.org/v1alpha1 kind: GrafanaDataSource metadata: name: prometheus-grafanadatasource namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring spec: datasources: - access: proxy editable: true isDefault: true jsonData: httpHeaderName1: 'Authorization' timeInterval: 5s tlsSkipVerify: true name: Prometheus secureJsonData: httpHeaderValue1: 'Bearer <token>' type: prometheus url: '<prometheus-thanos-querier-url>' name: prometheus-grafanadatasource.yamlWhere
<token>is the bearer API token that you obtained earlier, and<prometheus-thanos-querier-url>is the Prometheus API URL. -
Create a route by running the following command:
oc expose svc/grafana-service -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring -
Retrieve the Grafana credentials from the
grafana-admin-credentialssecret in theopenshift-user-workload-monitoringnamespace. -
In the OpenShift web console, go to Workload > Networking > Routes and get the Grafana URL.
You can use this Grafana URL to create dashboards.
Access the Prometheus instance from an external Grafana instance
If you have configured an external Grafana instance and want to access your Prometheus instance from the external Grafana instance, complete the following steps.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following set up:
- Ensure you have installed the IBM Operator for Apache Flink on the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform. Also ensure you have installed the Prometheus stack on your cluster by using the
kube-prometheusproject. For more information, see the kube-prometheus GitHub repository. - Integration of Flink with Prometheus is completed.
Configuring integration between external Grafana and Prometheus
To enable a cluster to be monitored by an external Grafana, configure the cluster as follows.
- Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console using your login credentials.
-
Create a service account for Grafana in the openshift-user-workload-monitoring namespace.
oc create serviceaccount grafana-serviceaccount -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring -
In the same namespace, add the cluster-monitoring-view role to the Grafana service account.
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-monitoring-view -z grafana-serviceaccount -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring -
Go to the openshift-monitoring namespace, search
thanos-querier, and obtain the endpoint URL. -
Obtain the Grafana service account token that is used in the configuration of the external Grafana data source:
oc sa get-token grafana-serviceaccount -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring -
Log in to Grafana and in the Settings > Data Sources, create a new Grafana data source (or change the existing prometheus data source).
-
In the HTTP section, paste the endpoint URL that is obtained from step 3.
-
If you are using self-signed certificates, enable the Skip TLS Verify flag in the Auth section.
-
In the Custom HTTP Headers section, add a header called
Authorizationand in the Value field, enter Bearer<token>, where<token>is the bearer API token you obtained earlier. - Click Save & test.
Grafana data source is configured and you can create dashboards based on your requirement.
Creating a dashboard
Follow the instructions in the Grafana documentation to create a dashboard.