Event Streams can be configured such that Datadog can capture Kafka broker JMX metrics via its Autodiscovery service. For more information about Autodiscovery, see the Datadog documentation.
Prerequisites
- Ensure you have an Event Streams installation available. This tutorial is based on Event Streams version 11.0.4.
- Ensure you have the Datadog Kubernetes agent. This tutorial will focus on the helm-based installation rather than the Datadog operator.
When installing the agent, ensure the following settings:
- The Kubernetes agent requires a less restrictive PodSecurityPolicy than required for Event Streams. It is recommended that you install the agent into a different namespace than where Event Streams is deployed.
- For the namespace where you deploy the agent, apply a PodSecurityPolicy to allow the following:
- volumes:
hostPath
- volumes:
Configuring for Autodiscovery
For the Datadog Agent to collect metrics from Kafka, enable the JMX port (9999) by setting the spec.strimziOverrides.kafka.jmxOptions value to {}. For more information, see configuring external monitoring through JMX.
For example:
apiVersion: eventstreams.ibm.com/v1beta2
kind: EventStreams
# ...
spec:
# ...
strimziOverrides:
# ...
kafka:
jmxOptions: {}
Then, provide the YAML item that contains the necessary Check Templates for configuring Kafka JMX monitoring. The example configuration supplied explains the necessary fields.
The YAML object is then applied as annotations to the Kafka pods to enable the pods to be identified by the AutoDiscovery service of the Datadog Agent. Provide the external monitoring configuration using the annotation key ad.datadoghq.com/kafka.init_configs in the Kafka pod annotations. This arrangement is illustrated in the following section.
The Datadog annotation format is ad.datadoghq.com/<container-identifier>.<template-name>. However, Event Streams automatically adds the Datadog prefix and container identifier to the annotation, so the YAML object keys must only be <template-name> (for example check_names).
Providing Check Templates
Each Check Template value is a YAML object:
check_names:
- kafka
instances:
- host: %%host%%
port: 9999
max_returned_metrics: 1000
tags:
kafka: broker
logs:
- source: kafka
service: kafka
init_config:
- is_jmx: true
collect_default_jvm_metrics: true
collect_default_metrics: true
conf:
- include:
bean: <bean_name>
attribute:
<attribute_name>:
alias: <custom.metric.name>
metric_type: gauge
In this tutorial we will be configuring Kafka pods to collect metrics from Kafka. In the EventStreams custom resource, configure the annotations in the spec.strimizOverrides.kafka.template section by using the annotation from the YAML values listed earlier.
The following example demonstrates how to configure the annotation for the Kafka pods in the spec.strimizOverrides.kafka.template section of the custom resource.
template:
pod:
metadata:
annotations:
ad.datadoghq.com/kafka.instances: >-
[{"host": "%%host%%","port":"9999","max_returned_metrics":
1000}]
ad.datadoghq.com/kafka.logs: '[{"source":"kafka","service":"kafka"}]'
ad.datadoghq.com/kafka.check_names: '["kafka"]'
ad.datadoghq.com/kafka.init_configs: |
[
{
"is_jmx": true,
"collect_default_metrics": true,
"collect_default_jvm_metrics": true,
"conf": [
{
"include": {
"domain": "kafka.log",
"bean_regex": "kafka\\.log:type=Log,name=Size,topic=(.*?),partition=(.*?)(?:,|$)",
"tags": { "topic": "$1", "partition": "$2" },
"attribute": {
"Value": {
"alias": "kafka.log.partition.size",
"metric_type": "gauge"
}
}
}
},
{
"include": {
"domain": "kafka.server",
"bean_regex": "kafka.server:type=BrokerTopicMetrics,name=BytesInPerSec",
"tags": { "topic": "$1", "partition": "$2" },
"attribute": {
"Value": {
"alias": "kafka.net.bytes_in.rate",
"metric_type": "rate"
}
}
}
},
{
"include": {
"domain": "kafka.cluster",
"bean_regex": "kafka\\.cluster:type=Partition,name=UnderReplicated,topic=(.*?),partition=(.*?)(?:,|$)",
"tags": { "topic": "$1", "partition": "$2" },
"attribute": {
"Value": {
"alias": "kafka.cluster.partition.underreplicated",
"metric_type": "gauge"
}
}
}
},
{
"include": {
"domain": "kafka.controller",
"bean_regex": "kafka\\.controller:type=KafkaController,name=PreferredReplicaImbalanceCount",
"attribute": {
"Value": {
"alias": "kafka.controller.kafkacontroller.preferredreplicaimbalancecount",
"metric_type": "count"
}
}
}
},
{
"include": {
"domain": "kafka.controller",
"bean_regex": "kafka\\.controller:type=KafkaController,name=ActiveBrokerCount",
"attribute": {
"Value": {
"alias": "kafka.controller.kafkacontroller.activebrokercount",
"metric_type": "count"
}
}
}
},
{
"include": {
"domain": "kafka.server",
"bean": "kafka.server:type=app-info",
"attribute": {
"version": {
"alias": "kafka.server.cluster.version",
"metric_type": "gauge",
"values": {
"default": 1
}
}
}
}
},
{
"include": {
"domain": "kafka.controller",
"bean_regex": "kafka\\.controller:type=KafkaController,name=FencedBrokerCount",
"attribute": {
"Value": {
"alias": "kafka.controller.kafkacontroller.fencedbrokercount",
"metric_type": "count"
}
}
}
},
{
"include": {
"domain": "kafka.server",
"bean_regex": "kafka.(\w+)<type=(.+), name=(.+)Percent\w*><>MeanRate",
"attribute": {
"Value": {
"alias": "kafka_$1_$2_$3_percent",
"metric_type": "gauge"
}
}
}
}
]
}
]
Installing the Datadog Agent
The following YAML is an example content of the values.yaml file required to set up the Datadog Agent in the cluster by using Helm.
targetSystem: "linux"
datadog:
apiKey: <api_key>
appKey: <app_key>
# If not using secrets, then use apiKey and appKey instead
clusterName: datadog-agent-jmx-helm
tags: []
criSocketPath: /var/run/crio/crio.sock
# Depending on your DNS/SSL setup, it might not be possible to verify the Kubelet cert properly
# If you have proper CA, you can switch it to true
kubelet:
tlsVerify: false
confd:
cri.yaml: |-
init_config:
instances:
- collect_disk: true
logs:
enabled: true
containerCollectAll: true
apm:
portEnabled: false
processAgent:
enabled: true
processCollection: false
agents:
# The agent need java for accessing the logs from jmx
# hence the agent image should be gcr.io/datadoghq/agent:latest-jmx
image:
tagSuffix: "jmx"
useHostNetwork: true
podSecurity:
securityContextConstraints:
create: true
tolerations:
# Deploy Agents on master nodes
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
operator: Exists
# Deploy Agents on infra nodes
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/infra
operator: Exists
clusterAgent:
podSecurity:
securityContextConstraints:
create: true
clusterChecksRunner:
enabled: true
replicas: 2
kube-state-metrics:
securityContext:
enabled: false
Check Templates can be supplied to Helm CLI installations by using the following commands:
- Install the latest Helm as described in the Helm documentation.
- If this is a new installation, add the Helm Datadog repository as follows:
helm repo add datadog https://helm.datadoghq.com helm repo update -
Provide
-f values.yamlto thehelm installcommand ifvalues.yamlincludes the overridden values. You can find the credentials on the page for organization settings (in the bottom left corner of the Datadog dashboard).- The API key (api_key)
- The Application key (app_key)
-
Run the following command for the Helm installation:
helm install <release-name> --namespace <namespace> -f values.yaml --set datadog.site='datadoghq.com' --set datadog.apiKey='<api_key>' datadog/datadogWhere
<release-name>is the name for the Datadog Agent, for example,datadog-agent.
Tip: For more information about installing the Datadog Agent, see the Datadog documentation.
Viewing metrics
To view the Kafka metrics collected from the cluster, complete the following steps:
- Log in to Datadog, and go to the Datadog dashboard.
- Click Metrics in the navigation panel on the left.
- In the Input field, enter the metrics you configured earlier. For example, this is the
aliasconfigured earlier askafka.log.partition.size.
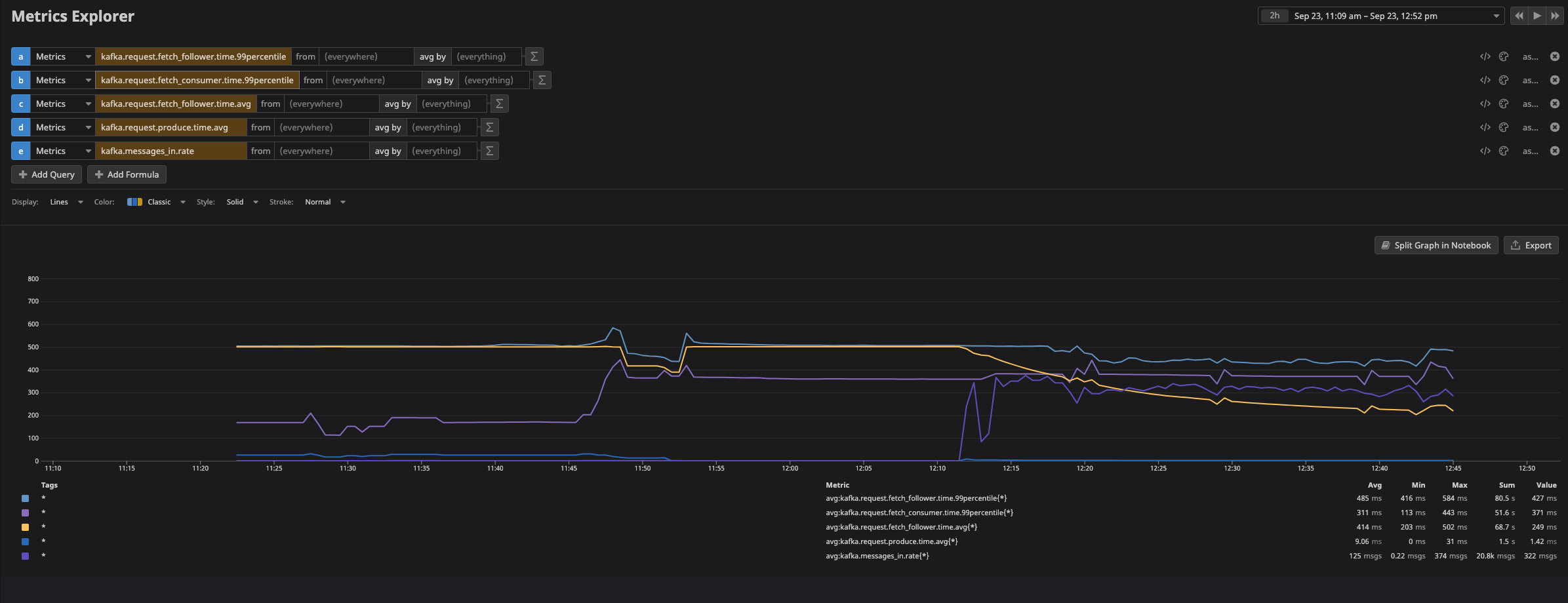
The following image shows the metrics collected from the Kafka cluster:
Upgrading and uninstalling by using the Helm CLI
To update the Helm deployment with a configuration change in the values.yaml, run the following command:
helm upgrade <release-name> --namespace <namespace> -f values.yaml datadog/datadog
If you want to delete a deployment, run the following command:
helm uninstall <release-name> --namespace es6
Troubleshooting
-
To see if the Kafka annotation setup was correctly picked up, run the following commands from the Datadog Agent CLI with the
agent statusoragent configcheck -voptions:kubectl exec <agent-pod-name> -- agent statuskubectl exec <agent-pod-name> -- agent configcheck -v -
Run Datadog Agent checks manually against
kafka. You can manually run checks by using the Datadog Agent CLI tool. As we provided the check name askafka, we can run the following command:kubectl exec <agent-pod-name> -- agent check kafka -
If you see the following error log in the agent pods, add
tagSuffix: "jmx"under theagentssection ofvalues.yaml. This error is caused by the agent not finding the location of the Java executable in the pod.check:kafka | Error running check: exec: "java": executable file not found in $PATH -
For more information about the Kafka dashboard configuration in Datadog, see the Datadog documentation about Kafka integration.
-
If you see a warning message about forbidden API keys similar to the following, update the Datadog site while running the Helm install command with the option
--set datadog.site='datadoghq.com'.2022-09-23 05:47:26 UTC | CORE | WARN | (pkg/logs/client/http/destination.go:301 in unconditionalSend) | failed to post http payload. code=403 host=agent-http-intake.logs.datadoghq.eu response={"errors":[{"status":"403","title":"Forbidden","detail":"Api key is either forbidden or blacklisted"}]} 2022-09-23 05:47:26 UTC | CORE | WARN | (pkg/logs/client/http/destination.go:301 in unconditionalSend) | failed to post http payload. code=403 host=agent-http-intake.logs.datadoghq.eu response={"errors":[{"status":"403","title":"Forbidden","detail":"Api key is either forbidden or blacklisted"}]} 2022-09-23 05:47:26 UTC | CORE | WARN | (pkg/logs/client/http/destination.go:301 in unconditionalSend) | failed to post http payload. code=403 host=agent-http-intake.logs.datadoghq.eu response={"errors":[{"status":"403","title":"Forbidden","detail":"Api key is either forbidden or blacklisted"}]} 2022-09-23 05:47:31 UTC | CORE | WARN | (pkg/logs/client/http/destination.go:301 in unconditionalSend) | failed to post http payload. code=403