Key Components
The figure below provides an overview of the principal components that are involved in the interaction between the chaincode process and the peer.
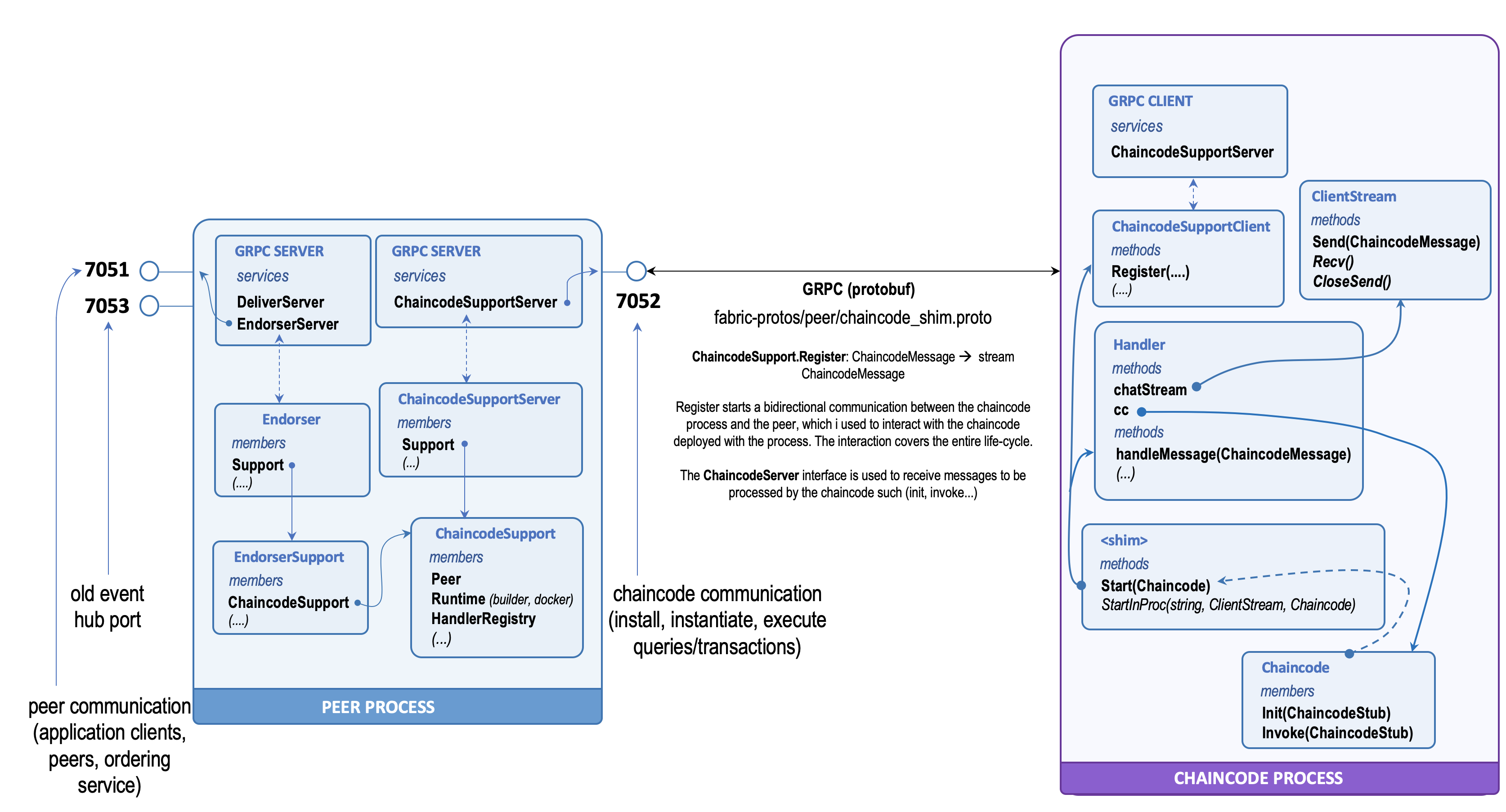
The protocol is implemented as an exchange of GRPC messages between the GRPC server on the peer and the GRPC client in the chaincode process. The GRPC server exposes the ChaincodeSupport service. The protobuf definition of this service is found in the chaincode_shim.proto file in the hyperledger fabric distribution repository. The service exposes only one method Register which opens a bidirectional stream between the chaincode and the peer. This is the channel where the exchange of messages happens.
Note
This interaction modality is also called chaincode as client, which is the only interaction mode available until Hyperledger Fabric 2.0. The implementation of the fabric shim for go chaincode also allows the initialisation of the chaincode process as a server in the message exchange between the two. This modality is known as chaincode as server but it is not in use until version 2.0 of Hyperledger Fabric.
Peer Components
In the peer, the ChaincodeSupport service is mapped to the ChaincodeSupportServer interface. This is implemented by the ChaincodeSupport struct, which is the point of connection between the other components of the peers and the communication channel with the chaincode process.
The ChaincodeSupport struct manages the connection and the interaction with all the chaincode processes. The listing below shows the attribute the struct.
type ChaincodeSupport struct {
Keepalive time.Duration
ExecuteTimeout time.Duration
UserRunsCC bool
Runtime Runtime
ACLProvider ACLProvider
HandlerRegistry *HandlerRegistry
Launcher Launcher
SystemCCProvider sysccprovider.SystemChaincodeProvider
Lifecycle Lifecycle
appConfig ApplicationConfigRetriever
HandlerMetrics *HandlerMetrics
LaunchMetrics *LaunchMetrics
}
This struct is the main entry point for the management of the chaincode processes within the peer. There are three main functions that this component performs:
- Chaincode Runtime Environment Management: this means building, starting up, and managing the runtime environment where the smart contract are executed (i.e. Runime and Launcher).
- Chaincode Interaction Protocol Management: this entails management of the connection with the chaincode processes and implementing the interaction protocol. Most of the functionalities are managed by the collection of Handler instances, one per chaincode process, that provide services to the smart contract such as ledger access and cross-chaincode invocations.
- Transaction Simulation: this entails forwarding transaction proposals to the appropriate chaincode process along with the required channel context to allow the smart contract to simulate the execution and provide results. Again, this capability is delegated to the associated
Handlerthat manages the interaction with a specific chaincode process.
Transactions simulations are initiated by application clients that submit transaction proposal through the EndorserServer GRPC service. The code listing below shows the details of the protobuf definition. The service has only one method ProcessProposal(....).
service Endorser {
rpc ProcessProposal(SignedProposal) returns (ProposalResponse) {}
}
The bindings for this service are represented by the Endorser component. This component coordinates the execution of the transaction simulation by interacting with the ChaincodeSupport instance previously discussed.
Note
As shown in the figure the Endorser has a Support component which is the liason to the ChaincodeSupport instance previously discussed.
For more details about these components see the Peer Architecture section.
Chaincode Components
The chaincode process contain a shim (i.e. shim.go), which is the main driver of the process and it is responsible for the coordination with the peer. The shim is initialised with an implementation of the Chaincode interface, which represents the smart contract hosted and executed in the process.
The connectivity with the peer is managed by the GRPC client which is used to retrieve a bidirectional stream used by the Handler. This component implements the interaction protocol with the peer and exchange ChaincodeMessage instances as a result of:
- the invocation of transactions by the peer; and
- ledger queries or cross chaincode invocations by the smart contract.
For more details about these components see the Shim Architecture section.