Consider the following when planning for geo-replication:
- If you want to use the CLI to set up geo-replication, ensure you have the Kubernetes CLI installed.
- Geo-replication requires both the origin and destination Event Streams instances to have client authentication enabled on the external listener and the internal TLS listener.
- If you are using geo-replication for disaster-recovery scenarios, see the guidance about configuring your clusters and applications to ensure you can switch clusters if one becomes unavailable.
- Prepare your destination cluster by creating an EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance and defining the number of geo-replication workers.
- Identify the topics you want to create copies of. This depends on the data stored in the topics, its use, and how critical it is to your operations.
- Message history is included in geo-replication. The amount of history is determined by the message retention option set when the topics were created on the origin cluster.
- The replicated topics on the destination cluster will have a prefix added to the topic name. The prefix is the name of the Event Streams instance on the origin cluster, as defined in the EventStreams custom resource, for example
my_origin.<topic-name>. - Configuration of geo-replication is done by the UI, the CLI or by directly editing the associated KafkaMirrorMaker2 custom resource.
Preparing a destination cluster
Before you can set up geo-replication and start replicating topics, you must create an EventStreamsGeoReplicator custom resource at the destination. The Event Streams operator uses the EventStreamsGeoReplicator custom resource to create a configured KafkaMirrorMaker2 custom resource. The KafkaMirrorMaker2 custom resource is used by the Event Streams operator to create geo-replication workers, which are instances of Kafka Connect running Kafka MirrorMaker 2.0 connectors. The number of geo-replication workers running at the destination cluster is configured in the EventStreamsGeoReplicator custom resource.
The number of workers depend on the number of topics you want to replicate, and the throughput of the produced messages.
For example, you can create a small number of workers at the time of installation. You can then increase the number later if you find that your geo-replication performance is not able to keep up with making copies of all the selected topics as required. Alternatively, you can start with a high number of workers, and then decrease the number if you find that the workers underperform.
Important: For high availability reasons, ensure you have at least 2 workers on your destination cluster in case one of the workers encounters problems.
You can configure the number of workers at the time of creating the EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance, or you can modify an existing EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance, even if you already have geo-replication set up and running on that cluster.
Configuring a new installation
If you are installing a new EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance for geo-replication to a destination cluster, you must specify the existing destination Event Streams instance you are connecting to. You can also specify the number of workers as part of configuring the EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance.
To configure the number of workers at the time of installation, see the following sections.
Using the UI on OpenShift Container Platform
If you are using OpenShift Container Platform, to create a new EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance for geo-replication by using the UI:
- Go to where your destination cluster is installed. Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console using your login credentials.
- From the navigation menu, click Operators > Installed Operators.
- In the Projects drop-down list, select the project that contains the existing destination Event Streams instance.
- Select the Event Streams operator in the list of installed operators.
- In the Operator Details > Overview page, find the Geo-Replicator tile in the list of Provided APIs and click Create Instance.
- In the Create EventStreamsGeoReplicator page, edit the provided YAML to set values for the following properties.
- In the metadata.labels section, set the eventstreams.ibm.com/cluster property value to the name of your destination Event Streams instance.
- Set the metadata.name property value to the name of your destination Event Streams instance.
- Set the spec.replicas property value to the number of geo-replication workers you want to run.
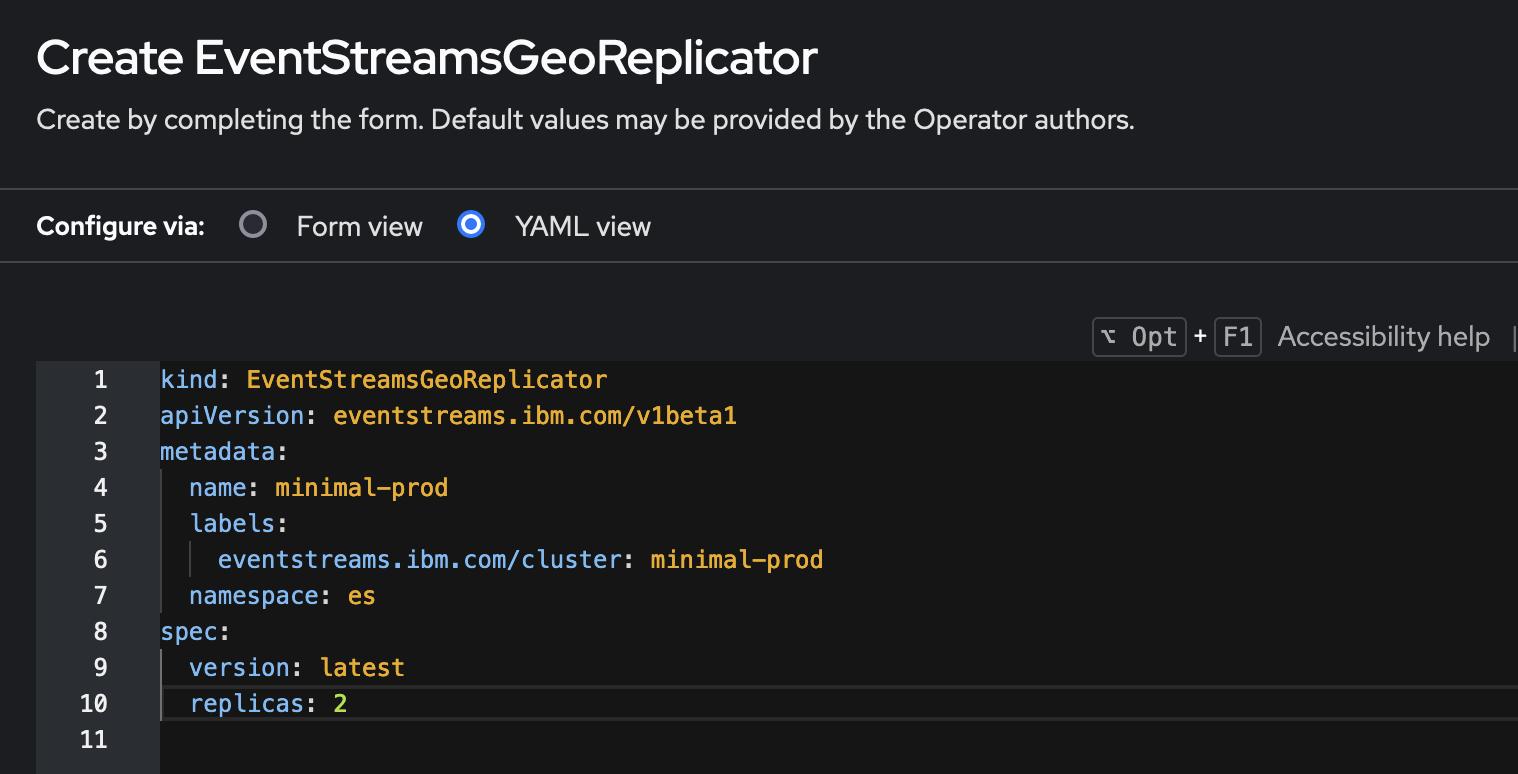
- Click Create.
- The new EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance is listed in the Operator Details > EventStreamsGeoReplicator page.
If the EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance is configured correctly, a KafkaMirrorMaker2 custom resource is created. You can see the details for the KafkaMirrorMaker2 custom resource in the Kafka Mirror Maker 2 tab of the Operator Details page.
Using the CLI
To create a new EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance for geo-replication by using the CLI:
- Go to where your destination cluster is installed. Log in to your Kubernetes cluster as a cluster administrator by setting your
kubectlcontext. -
Run the following command to set the namespace that contains the existing destination cluster:
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=<namespace-name> -
Define an EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance in a file. For example, the following YAML defines an EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance in the
my-projectproject that is connected to the Event Streams instance namedmy-dest-clusterand has 3 geo-replication workers.apiVersion: eventstreams.ibm.com/v1beta1 kind: EventStreamsGeoReplicator metadata: labels: eventstreams.ibm.com/cluster: my-dest-cluster name: my-dest-cluster namespace: my-project spec: version: 11.2.5 replicas: 3Note: The EventStreamsGeoReplicator
metadata.nameproperty andeventstreams.ibm.com/clusterlabel property must be set to the name of the destination Event Streams instance that you are geo-replicating to. -
Run the following command to create the EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance:
kubectl create -f <path-to-your-eventstreamsgeoreplicator-file> - The new EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance is created.
-
Run the following command to list your EventStreamsGeoReplicator instances:
kubectl get eventstreamsgeoreplicators -
Run the following command to view the YAML for your EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance:
kubectl get eventstreamsgeoreplicator <eventstreamsgeoreplicator-instance-name> -o yaml
When the EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance is ready, a KafkaMirrorMaker2 instance will be created. Run the following command to list your KafkaMirrorMaker2 instances:
kubectl get kafkamirrormaker2s
Run the following command to view the YAML for your KafkaMirrorMaker2 instance:
kubectl get kafkamirrormaker2 <kafka-mirror-make-2-instance-name> -o yaml
Note: If you have Strimzi installed, you might need to fully-qualify the resources you are requesting. The fully-qualified name for the KafkaMirrorMaker2 instances is kafkamirrormaker2.eventstreams.ibm.com.
Configuring an existing installation
If you want to change the number of geo-replication workers at a destination cluster for scaling purposes, you can modify the number of workers by using the UI or CLI as follows.
Using the UI on OpenShift Container Platform
If you are using OpenShift Container Platform, to modify the number of workers by using the UI:
- Go to where your destination cluster is installed. Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform web console using your login credentials.
- From the navigation menu, click Operators > Installed Operators.
- In the Projects drop-down list, select the project that contains the destination Event Streams instance.
- Select the Event Streams operator in the list of installed operators.
- Click the Geo-Replicator tab to see the list of EventStreamsGeoReplicator instances.
- Click the EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance that you want to modify.
- Click the YAML tab.
- Update the spec.replicas property value to the number of geo-replication workers you want to run.
- Click Save.
Using the CLI
To modify the number of workers by using the CLI:
- Go to where your destination cluster is installed. Log in to your Kubernetes cluster as a cluster administrator by setting your
kubectlcontext. -
Run the following command to set the namespace that contains the existing destination cluster:
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=<namespace-name> -
Run the following command to list your EventStreamsGeoReplicator instances:
kubectl get eventstreamsgeoreplicators -
Run the following command to edit the YAML for your EventStreamsGeoReplicator instance:
kubectl edit eventstreamsgeoreplicator <eventstreamsgeoreplicator-instance-name> - Update the spec.replicas property value to the number of geo-replication workers you want to run.
- Save your changes and close the editor.
