Event Streams 10.3.0 and later versions are built on Strimzi. Strimzi 0.14.0 and later support distributed tracing based on the open-source OpenTracing and Jaeger projects.
Distributed tracing provides a way to understand how applications work across processes, services, or networks. Tracing uses the trail they leave behind based on requests made, carrying tracing information in the requests as they pass from system to system. Through tracing, you can monitor applications that work with Event Streams, helping you to understand the shape of the generated traffic, and pinpoint the causes of any potential problems.
To use distributed tracing for your Kafka client applications, you add code to your applications that gets called on the client’s send and receive operations. This code adds headers to the client’s messages to carry tracing information.
Note: In IBM Cloud Pak for Integration 2022.4.1 and later, the integration tracing capability with the Operations Dashboard is deprecated. For more information, see the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration documentation.
Distributed tracing with Operations Dashboard (deprecated)
Event Streams provides support for tracing through IBM Cloud Pak for Integration. Your applications can send tracing data into the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration Operations Dashboard runtime as “external applications”.
Deployment architecture
To send tracing data to the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration Operations Dashboard, the Kafka client application must be deployed into the same OpenShift Container Platform cluster as IBM Cloud Pak for Integration. The application runs in a pod into which two sidecar containers are added, one for the tracing agent and one for the tracing collector.
The Kafka client OpenTracing code runs as part of your application. It forwards tracing spans over UDP to the agent. The agent decides which spans are to be sampled and forwards those over TCP to the collector. The collector forwards the data securely to the Operations Dashboard Store in the Operations Dashboard namespace.
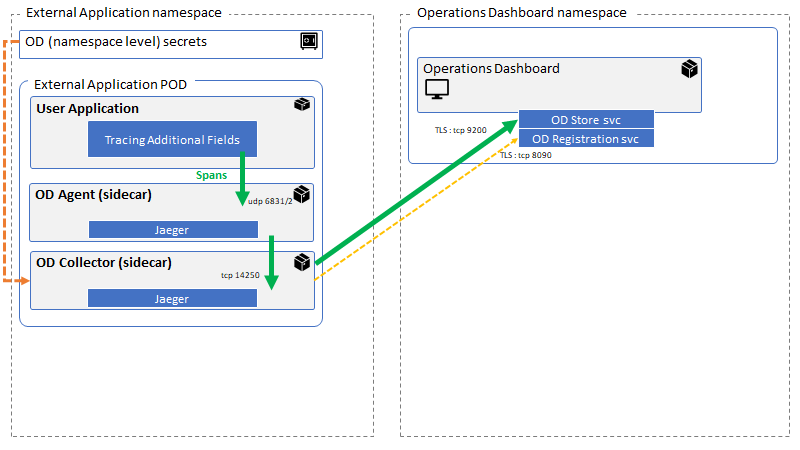
The namespace in which the application runs must be registered with the Operations Dashboard. The registration process creates a secret which is used by the collector to communicate securely with the Operations Dashboard Store.
Preparing your application to use tracing
For detailed instructions about how to use Operations Dashboard with external applications, see the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration documentation.
At a high level, the steps required are as follows.
Step 1 - Configure the Operations Dashboard to display external applications tracing data
To enable the Operations Dashboard to display tracing data from external applications:
- Log into IBM Cloud Pak for Integration.
- Open the Operations Dashboard Web Console by clicking Tracing in the Platform Navigator.
- Navigate to System Parameters > Display in the Manage section of the console.
- In the Display settings, set Show external app data in the dashboards to true, and click Update.
Now the Operations Dashboard is ready to receive data from external applications.
Step 2 - Modify your application code to enable tracing
The most convenient way to enable tracing in a Kafka application is to use the Kafka client integration which has been contributed to the OpenTracing project. Then you have a choice of configuring OpenTracing interceptors and using the regular KafkaProducer and KafkaConsumer classes, or using Tracing variants of the KafkaProducer and KafkaConsumer which wrap the real classes. The latter is more flexible but requires additional code changes to the application.
There are sample applications which show you how to do this. You can clone the repository and build them yourself, or copy the techniques for your own applications.
Step 3 - Deploy your application with the agent and collector sidecar containers
After it is built, you can deploy your application, complete with the Operations Dashboard agent and collector containers. Without these additional containers, your application will not be able to communicate with the Operations Dashboard Store and your tracing data will not appear. The sample applications include an example of the Kubernetes deployment that includes these containers.
Slightly unusually, when you deploy your application, you’ll notice that it’s running normally but the two sidecar container are not starting successfully. That’s because they depend upon a Kubernetes secret that contains credentials to connect to the OD Store. The next step creates that secret and enables the containers to start.
Step 4 - Complete the registration process for the application
The final stage is to use the Operations Dashboard Web Console for registering the external application to Operations Dashboard.
To enable the Operations Dashboard to display tracing data from external applications:
- Log into IBM Cloud Pak for Integration.
- Open the Operations Dashboard Web Console by clicking Tracing in the Platform Navigator.
- Navigate to System Parameters > Registration requests in the Manage section of the console.
- In the list of registration requests, approve the request for your application’s namespace.
- Copy the command displayed by the console, and run it to create the Kubernetes secret which enables your application to send data to the Operations Dashboard Store.
Using the Operations Dashboard to view tracing information
You can use the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration Operations Dashboard to view tracing information and analyze spans.
For more information about setting up, using, and managing the dashboard, see the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration documentation.
OpenTelemetry tracing with Instana
OpenTelemetry (OTel) aims to simplify and automate the collection and analysis of telemetry data by providing a unified and extensible instrumentation framework that can be integrated into any application or infrastructure component.
Integrating OpenTelemetry with Event Streams can provide a powerful way to gain real-time insights into the performance and behavior of your event-driven applications. By streaming telemetry data to Event Streams, you can monitor the health of your applications, troubleshoot issues quickly, and optimize your applications for better performance.
IBM Instana supports OpenTelemetry for collecting distributed traces, metrics, and logs from various sources. Instana can seamlessly integrate with OpenTelemetry and can also enhance the data from OpenTelemetry. As an observability backend for OpenTelemetry, use Instana to monitor and analyze the performance and health of your applications in real-time.
There are two ways to ingest the generated OpenTelemetry traces and metrics with Instana: by using the Otel collector or by using an Instana host agent.
Note: The OpenTelemetry operator available for the OpenShift Container Platform does not support Instana as an exporter while using the Otel collector. To collect OTel trace details on an OpenShift deployment of Event Streams, use an Instana host agent as described in the following sections.
Configuring the host agent and OpenTelemetry
Instana host agent for OpenTelemetry is a powerful tool for collecting and analyzing telemetry data from hosts, infrastructure, and various applications.
Use the host agent to seamlessly integrate OpenTelemetry data into the Instana observability platform, providing a unified view of telemetry data, which you can use to analyze and troubleshoot issues quickly and efficiently.
To configure the host agent and OpenTelemetry:
-
Install and configure an Instana host agent for Event Streams.
-
Configure OpenTelemetry to send tracing and metric data to the Instana host agent.
Enabling OpenTelemetry tracing
You can enable OpenTelemetry tracing for the following components in Event Streams:
- Kafka Connect
- Kafka Bridge
To enable OpenTelemetry tracing:
-
Enable OpenTelemetry by setting the
spec.tracing.typeproperty toopentelemetryin the custom resource for the selected component as follows (KafkaConnectandKafkaBridge):spec: # ... tracing: type: opentelemetry -
Configure the tracing environment variables in
spec.templatefor the required custom resource as follows:Configuration for Kafka Bridge:
spec: #... template: bridgeContainer: env: - name: OTEL_SERVICE_NAME value: <instana-agent-service-name> - name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT value: <instana-agent-address> tracing: type: opentelemetryConfiguration for Kafka Connect:
spec: #... template: connectContainer: env: - name: OTEL_SERVICE_NAME value: <instana-agent-service-name> - name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT value: <instana-agent-address> tracing: type: opentelemetry
For more information about tracing in Apache Kafka and OpenTelemetry, see the Strimzi documentation.
