The following processor nodes are available in Event Processing:
Filter
A filter node takes in a stream of events and applies an expression to determine which events to allow to pass and which to block. The output of the filter node is a single stream of events that can be used for analysis or other processing. This node helps to reduce the amount of data by allowing events that match the expression.
Adding a filter node
To add a filter node, complete the following steps:
- Ensure that a stream of events is available, from an event source node or from the output of any previously configured node.
- In the Palette, under Processors, drag the Filter node into the canvas.
- Connect the node to an event source by dragging the Output port from a source node into the Input port of this node. A purple checkbox
is displayed on the filter node indicating that the node is yet to be configured.
- Hover over the node and click
Edit to configure the node.
The Configure a Filter window opens.
Configuring a filter node
To configure a filter node, complete the following steps:
- In the Details section, enter a name for your node. The output stream of events from this node will be referred with the name you entered.
-
Click Next to open the Define Filter pane.
Note: A tree view of the event structure is available. To view all the input properties of the current node, click View input properties in the upper-right corner of the pane.
-
Enter an expression in the Filter Expression field to filter the events and click Insert expression.
The expression consists of a property, a mathematical condition, and a value. Depending on your requirements, you can create a simple expression with one condition or a complex expression with multiple conditions. For complex expressions, you can add multiple conditions within an expression by using
ANDorOR.Alternatively, you can use the assistant to create an expression. Select Assistant at the right end of the Filter Expression field to open the assistant. The assistant provides a drop-down list of properties and conditions that you can use to create the expression.
In Event Processing 1.4.5 and later:
- You can use the Assistant to create complex expressions with multiple filter conditions.
- To add an
ANDorORoperation to the root of the expression, click the Add operation button located at the bottom of the last condition.
Note: Expressions are prioritized based on operator precedence.
Examples:
-
Simple expression:
example_property > 100 -
Complex expression:
example_property1 > 50 AND example_property2 > 30 OR example_property3 < 25 AND example_property4 < 250 -
Expression with complex object property:
example_property.nested_property IS NOT NULL AND example_property.nested_property.leaf_property > 100 -
Expression with an array property:
example_array_property[1] IS NOT NULL AND ARRAY_CONTAINS(example_array_property, 10) -
Expression with complex array property:
example_array_of_array_property[1][1] IS NOT NULL AND ARRAY_CONTAINS(example_array_of_array_property[1][1], 10)Note: The index of arrays starts at 1, not at 0.
Note: The Assistant drop-down menu does not support array properties. However, you can manually write the expressions by selecting the property from the list that appears when you press Ctrl+Space in the Expression field.
In Event Processing 1.4.6 and later, you can update your existing expression in the filter assistant. Open the Filter assistant, make your changes, and click Update expression to apply them.
Note: Expressions manually edited in the Filter expression field must be cleared before you use the assistant again.
-
Click Next to open the Output properties pane. The properties that you added in the previous step are displayed in the Output properties pane. You can manage the properties that come from this node to suit your requirements.
Only leaf properties are listed in the Properties to keep table.
-
Optional: Click Remove property
to remove a property from being displayed in the output. You can remove specific properties from an object, or if you want to remove the entire object, remove all the properties related to it one by one.
Note:
- Nested properties are displayed by using a period (
.) as a separator for each level of nesting. For example,product . idorcustomer . address . city. - If a nested property name contains a period (
.), the nested property is displayed within backticks (``) to distinguish the property name. For example,name .`billing.address`. customerwherebilling.addressis the name of the property.
- Nested properties are displayed by using a period (
- Optional: To rename a property, hover over the property name and click the Edit icon
.
- In the text field, enter a new name for your property.
- Click outside the text field or press Enter on your keyboard to rename the property.
Within nested properties, you can only rename the last nested property. You cannot rename the top-level or any other properties in between. For example, in the case of
customer . address . city, you can only renamecity, but notaddressorcustomer.Note: To rename the top-level property
customerin the examplecustomer . address . city, create a new property by using the transform node. - Optional: To add a property that was previously removed, go to the Properties to remove table that lists the removed properties. For the property you want to add back, click the Add icon
.
-
- Scroll down and click Configure Filter to complete the configuration.
A green checkbox 

User actions are saved automatically. For save status updates, see the canvas header.
Transform
A transform node takes in a stream of events to modify your existing properties or create new properties. Existing properties can be removed or renamed, and new properties can be added. The value of a new property is determined by the expression you create.
Transform node supports various functions to create an expression. For more information about functions, see the Flink documentation.
Adding a transform node
To add a transform node, complete the following steps:
- Ensure that a stream of events is available, from an event source node or from the output of any previously configured node.
- In the Palette, under Processor, drag-and-drop the Transform node into the canvas.
- Connect the node to an event source by dragging the Output port from a source node into the Input port of this node. A purple checkbox
is displayed on the transform node indicating that the node is yet to be configured.
-
Hover over the node and click
Edit to configure the node.
The Configure Transform window appears.
Configuring a transform node
To configure a transform node, complete the following steps:
- In the Details section, enter a name for your node. The output stream of events from this node will be referred with the name you entered.
-
Click Next to open the Create properties pane.
Note: A tree view of the event structure is available. To view all the input properties of the current node, click View input properties in the upper-right corner of the pane.
- Click Create new property to add a new property to the table.
- Hover over the property name and click the Edit icon
and enter a name for your property.
-
Enter your expression in the Expression text box to define your property.
Examples:
-
Simple expressions:
- example_number_property1 * example_number_property2 - POWER(`example_number_property1`, 2) -
Complex expressions:
- REGEXP_EXTRACT(`example_property`, '([A-Z]+)\-([0-9]+)\-([0-9]+)', 1) - IF(`example_number_property` >= 20, 'high', 'low') - TO_TIMESTAMP(example_string_property, 'EEE MMM dd HH:mm:ss zzz yyyy') - DAYOFWEEK( CAST(example_timestamp_property AS DATE) ) -
Expressions with complex object property:
- example_property.nested_object_property - example_property.nested_object_property.leaf_property - CONCAT( CAST(example_property.nested_object_property.leaf_property AS STRING), ‘$’) -
Expressions with array properties:
- ARRAY_JOIN(`example_string_array_property`, ', ') - ARRAY_REMOVE(example_property.nested_object_property.leaf_array_property, NULL) - example_property BETWEEN example_array_property[1] AND example_array_property[2] - example_property.nested_object_property.leaf_array_property -
Expressions with complex array properties:
- CARDINALITY(example_array_of_object_property) = 1 - CARDINALITY(example_array_of_array_of_object_property[1][1].stringArray) = 1 AND example_array_of_array_of_object_property[1][1].stringArray[1] LIKE 'red' - CARDINALITY(example_array_of_array_of_object_property[1][1].booleanArray) = 1 AND ELEMENT(example_array_of_array_of_object_property[1][1].booleanArray) IS TRUE - ARRAY_CONTAINS(example_array_of_array_property[2], 'red')
Note: The expression can also simply refer to existing properties. This is particularly useful when renaming complex object properties or when moving nested properties to the top-level.
-
- Optional: To use the assistant to enter an expression, complete the following steps:
- Click the Assistant drop-down menu to open the assistant.
- From the Function list, select a function with which you want to create an expression.
- In the function you selected previously, enter the required values.
-
Select Insert into expression to add the expression in the text-box.
Note: Ensure you choose the values with correct data type for your expression. Properties that are used as values in the comparison operations must be of the same data type. Arithmetic operations are only allowed on integer and double data types. String operations are only possible with properties of string data type. Some temporal functions require a timestamp data type.
Note: The Assistant drop-down menu does not support array properties. However, you can manually write the expressions by selecting the property from the list that appears when you press Ctrl+Space in the Expression field.
- Optional: Repeat steps 3 to 6 to create more properties.
- Click Next to open the Output properties pane. You can manage the properties that come from this node to suit your requirements.
-
Only leaf properties are listed in the Output properties table. You can remove specific properties from an object, or if you want to remove the entire object, remove all the properties related to it one by one.
Click Remove property
to remove a property so that it is not displayed in the output.
Note:
- Nested properties are displayed by using a period (
.) as a separator for each level of nesting. For example,product . idorcustomer . address . city. - If a nested property name contains a period (
.), the nested property is displayed within backticks (``) to distinguish the property name. For example,name .`billing.address`. customerwherebilling.addressis the name of the property.
- Nested properties are displayed by using a period (
-
Only leaf properties are listed in the Output properties table. You can only rename the last nested property within nested properties, you cannot rename the top-level or any other properties in between. For example, in the case of
customer . address . city, you can only renamecity, but notaddressorcustomer.Note: To rename the top-level property
customer . address . city(in this case,customer), create a new property and add details in the following fields:- Property name: Add a new name for the property.
- Expression: Add the name of the property to rename, for example, customer.
- Optional: To rename a property, hover over the property name and click the Edit icon
.
- In the text-box, enter a new name for your property.
- Click outside the text-box or press Enter on your keyboard to rename the property.
- Optional: To add a property that was previously removed, go to the Properties to remove table that lists the removed properties. For the property you want to add back, click the Add icon
.
- To complete the transform node configuration, click Configure.
A green checkbox 

User actions are saved automatically. For save status updates, see the canvas header.
Unpack arrays
An unpack arrays node takes an existing array of elements in a stream of events to unpack it. You can unpack each array element into a new property in separate events, or unpack the array elements into new properties that are all included in the same event.
Adding an unpack arrays node
To add an unpack arrays node, complete the following steps:
- Ensure that a stream of events is available, from an event source node or from the output of any previously configured node.
- In the Palette, under Processors, drag-and-drop the Unpack arrays node into the canvas.
-
Connect the node to an input stream by dragging the Output port from an input node into the Input port of this node. A purple checkbox
is displayed on the unpack arrays node indicating that the node is yet to be configured.
-
Hover over the node, and click
Edit to configure the node.
The Configure unpack node window opens.
Configuring an unpack arrays node
To configure the unpack arrays node, complete the following steps:
- In the Details section, enter a name for your node. The output stream of events from this node will be referred with the name you entered.
-
Click Next to open the Array selection pane.
Note: A tree view of the event structure is available. To view all the input properties of the current node, click View input properties in the upper-right corner of the pane.
-
Select the radio button
of the array you want to unpack.
Note: You can use the search bar to search for a particular array. As you start typing the array name in the search bar, you get a filtered list of matching arrays.
- Click Next to open the Unpacking the array pane.
-
The following options are available to unpack the array:
- Unpack into events: To unpack each array element into a new property in separate events, in the Property name field, provide a name for the property that represents the array element. You will have as many events as array elements and each event contains the property with one of the array elements.
-
Unpack into properties: To unpack each array element into properties within an event, provide a name in the Property name field for each property that represents the array element. By default, properties are listed sequentially (1, 2, 3,…).
- To add a property, click Add next element, and provide a name for the property in the Property name field.
- To remove a property, click the Delete property icon
corresponding to the property you want to remove.
- To edit the name of a property, hover over the name, and click the Edit icon
.
Note:
- The order of the properties in the table corresponds to the order in the array: For example, if you define the properties p1, p2, and p3 in this order, and you have the array [1, 2, 3], then the first property p1 is mapped to the first array element 1, p2 is mapped to 2, and p3 is mapped to 3.
- If the array contains more elements than the number of properties, elements with no mapping are dropped: For example, if you define the properties p1, p2, and p3 in this order, and you have the array [1, 2, 3, 4], then the first property p1 is mapped to the first array element 1, p2 is mapped to 2, p3 is mapped to 3, and 4 is dropped.
- If the array contains fewer elements than the number of properties, then the properties with no mapping carries a null value: For example, if you define the properties p1, p2, and p3 in this order, and you have the array [1, 2], then the first property p1 is mapped to the first array element 1, p2 mapped to 2, and p3 is null.
- If you define a property p, and you have the array [1, 2], you will have one event where p equals 1 and another event where p equals 2.
-
Click Next to open the Output properties pane.
The properties that you added in the previous step are displayed in the Output properties pane. You can manage the properties that come from this node to suit your requirements.
Note: The array that you selected to unpack is not part of the output properties.
- To complete an unpack node configuration, click Configure.
A green checkbox 

Detect patterns
The detect patterns node identifies sequences of events across the input streams that match a defined pattern within a time interval.
Important concepts
- Each input stream must contain a single event type. For example, one stream contains credit card shipped events, another stream contains credit card delivery events, and a third stream contains credit card activation events.
- The events on the input streams are combined into an ordered sequence of events for each unique context. For example, if the input streams contain events for 100 different credit cards, then there is an ordered sequence for each credit card number.
- A pattern is matched for each unique context across the input streams. For example, the output pattern match event will identify which credit card it is associated with.
There are two types of patterns:
- A pattern that can be matched as soon as the final event arrives on the stream within the time interval. For example, a credit card is shipped, delivered, and then activated within a week.
- A pattern that specifies the absence of events. The pattern is evaluated at the end of the time interval and is matched if the events have not arrived on the stream within the interval. For example, a customer places three items into their cart, but does not check out within an hour.
Adding a detect patterns node
To add a detect patterns node, complete the following steps:
- Ensure that a stream of events is available, from an event source node or from the output of any previously configured node.
- In the Palette, under Processors, drag-and-drop the Detect patterns node into the canvas.
- Connect the node to one or more input streams by dragging the Output Port from an input node into the Input Port of this node. A purple checkbox
is displayed on the detect patterns node indicating that the node is yet to be configured.
- Hover over the node, and click
Edit to configure the node. The Configure detect patterns window opens.
Note: If an input stream contains two or more different event types (typically differentiated by the enumerated value of an event property), you can split the stream by using filter nodes to create streams containing each specific event type. For example, a stream containing both activated and transaction events can be split with a filter on eventType LIKE 'activated' and another of eventType LIKE 'transaction':
{
"cardNumber": <number>,
"eventType": "activated" | "transaction"
}
The flow that uses this split of the unique input stream can look as follows:

Important: The filters must be mutually exclusive to ensure that an event is directed to only one or none of the subsequent streams.
Configuring a detect patterns node
To configure the detect patterns node, complete the following steps:
- In the Details section, enter a name for your node. The output stream of events from this node will be referred with the name you entered.
-
Click Next to open the Define context pane.
Note: A tree view of the event structure is available. To view all the input properties of the current node, click View input properties in the upper-right corner of the pane.
-
Select the property for each incoming event that can be used to correlate events into the same context. For example:
-
There are two input streams -
credit card activationandcredit card transaction.-
The
credit card activationevent schema:{"creditcardNumber": ..., "activationDate": ...} -
The
credit card transactionevent schema:{"credit_card_number": ..., "amount": ...} -
The context is defined using the
creditcardNumberandcredit_card_numberproperties
-
Note: The properties must all have the same SQL data type. If the required data type is unavailable, consider using a transform node upstream to create a property with the matching data type.
-
- Click Next to open the Define pattern pane.
-
Define the pattern to detect.
A pattern is defined using event occurrences and conditions.
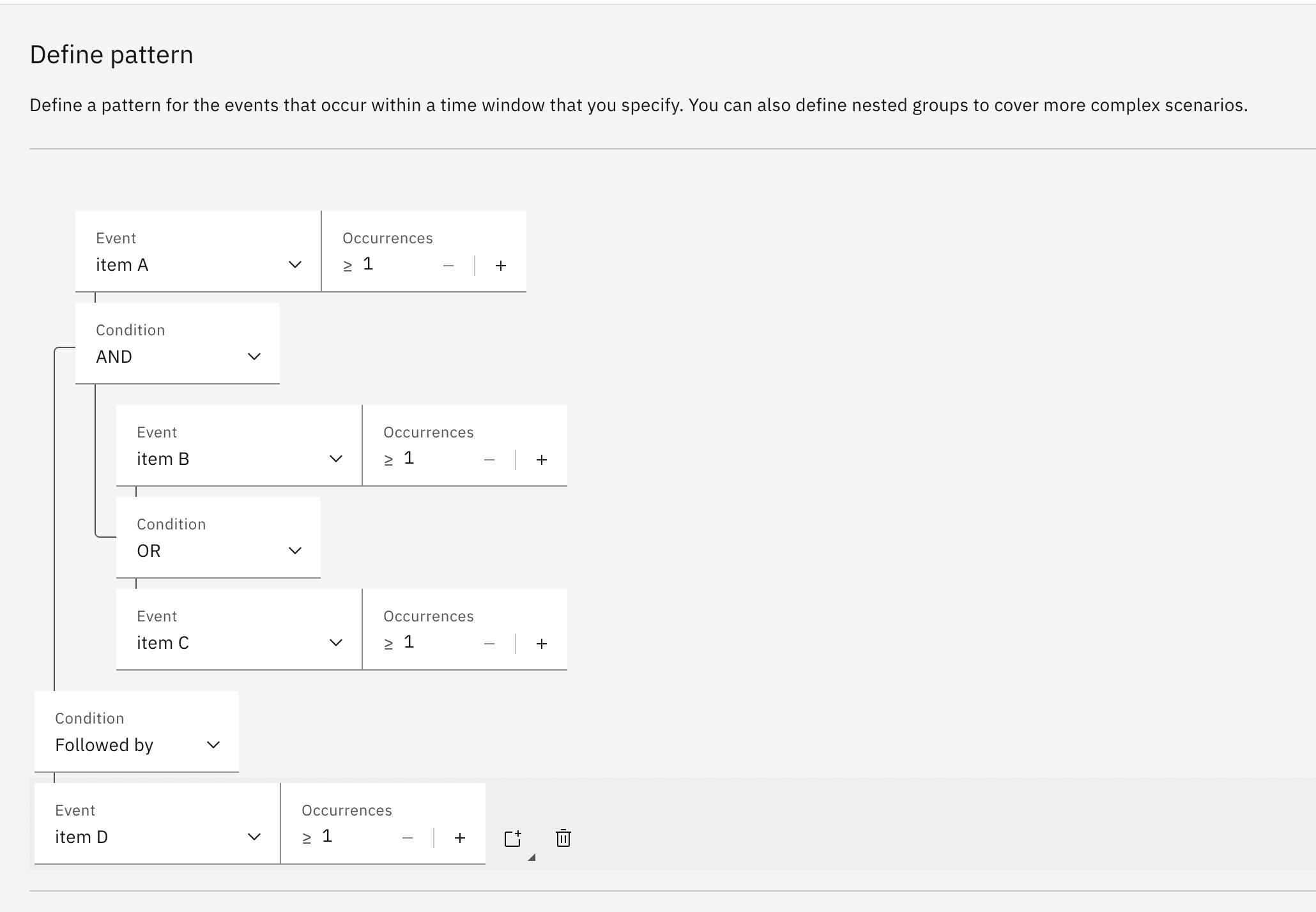
Occurrences
Occurrences specify the minimum number of occurences of an event to result in a match. The events must occur in a sequence together. For example,
>=3 ordersmeans the detect pattern node receives at least three order events in a row, within the same context (that is three or more orders by the same customer).Conditions
Each condition takes two inputs, where the input can be either an occurrence or another condition. For example, in
>=2 orders and >=1 cancellationtheandis a condition that takes two occurrences as input. A more complex pattern could be>=2 orders and >=1 cancellation or 1 refund, where the first conditionandtakes an occurrence (2 orders) and a condition (1 cancellation or 1 refund) as input.The pattern is matched when all the conditions evaluate to true. The following table lists all the available conditions:
Condition Description Example (where orders = O, cancellations =C)And There is a sequence of events containing the first input and the second input in either order, but with no events in between. >=3 orders AND >=2 cancellations: the condition matches the sequence of eventsO O O C CorC C O O Ofor a particular context. ButO O O C O C Cwould not match because there are two eventsO Cbetween the two inputs of theandcondition.Or There is a sequence of events containing the first input OR the second input >=3 orders OR >=2 cancellation: the condition matches the sequence of eventsO O OorC C.Followed by There is a sequence of events containing the first input. There can be 0 or more unrelated events, then there is a sequence of events containing the second input. >=3 orders followed by >=2 cancelations: the condition matchesO O O C C. Unlikeand, the sequenceO O O C O C Cdoes match becauseO O Ois followed byC C. Conversely,C C O O Odoes not match because the orders (O) must happen first.Not followed by There is a sequence of events containing the first input and there is not a following sequence that contains the second input within the pattern duration. >=3 orders not followed by >=1 cancellations: will match if at the end of the duration there is a sequence of eventsO O Othat are not followed byC.Nesting groups
When building complex patterns, conditions have different levels of precedence. The UI represents this by using visual groups. For example, when building the pattern
>=3 orders AND >=2 cancellations OR >=2 refunds, the UI will create a group such that the pattern evaluates as>=3 orders AND (>=2 cancellations OR >=2 refunds). To change the precedence, highlight a condition, and click the Create group iconto create a group around it.
Condition interaction
When multiple conditions are combined and nested, their semantics might change. In the following examples, brackets are added to represent the groups in the node configuration UI.
>=2 orders AND ( >=2 refunds OR >=2 cancellations )- the sequenceO O R R C O Ocontains a match because:- There are two orders and two refunds with no events between the. So, the
ANDand theORconditions are satisfied. - The remaining part of the sequence potentially contributes to a later pattern match.
- There are two orders and two refunds with no events between the. So, the
>=2 orders AND ( >=2 refunds OR >=2 cancellations ) AND >=2 orders- the sequenceO O R R C O Odoes not match because:- There are two orders and two refunds. So, the
ANDand theORconditions are satisfied. - But, then there is a cancellation.
- The
... AND >=2 ordersmeans that after the second refund there is then at least two orders with no other events between them.
- There are two orders and two refunds. So, the
(>=2 orders AND ( >=2 refunds OR >=2 cancellations ) ) followed by >=2 orders- The sequenceO O R R C C O Omatches because:- There are two orders and two refunds. So, the
ANDand theORconditions are satisfied. - But, then there is a cancellation.
- This time, the cancellation is ignored because
... followed by >=2 ordersallows other events to occur before the two orders. - The pattern is then matched by the final two orders.
- There are two orders and two refunds. So, the
-
In the Event time property to detect patterns drop-down list, select the property of the event that corresponds to an event time. If there is only one input stream and a single event time property, the event time property is automatically selected by default.
-
In the Time window duration field, set the value and the unit for the pattern time interval. The interval is measured relative to event time, an interval of one hour means that a pattern will match if the event time property of the last event in the pattern is within an hour of the event time for the first event.
-
Choose a detection mode:
As discussed in step 10 of event nodes, events can arrive out of order. To perform pattern matching, the events must be sorted into chronological order according to their event time. The watermarks from each input stream are used for the sorting process to handle out of order events. The watermarks are also used for identifying when a pattern match duration has elapsed.
If an input stream temporarily stops receiving events, the watermark is stalled. When one or more of the watermarks for the inputs to the detect pattern node stall, it might cause pattern matching to pause.
For example, a pattern ending with
not followed by X in an hourcannot resolve because the stalled watermark means the elapsed pattern time does not increase past the hour duration.Another example is that a pattern of
>=3 orderscannot resolve when there are three order events on the input streams, but the sorting of events prior to the matching step cannot progress without a newer watermark.As such, there are two detection modes available with respect to how the detect pattern node handles a stalled watermark:
- Real time (default): The watermark for an active input stream is progressed by using new events. If an input stream is idle, the detect pattern node will simulate new events to cause the watermark to progress in real time.
- Event time: The watermark for an active input stream is progressed by using new events. If an input stream is idle, patterns are stalled until the stream is active again.
Real time ensures patterns that are stuck behind a stalled watermark can be detected promptly. In most situations this has no adverse effect, as the next event produced to an idle stream will have an event time newer than the progressed watermark.
However, if the next event has an event time that is late compared to the progressed watermark, the event will not contribute to pattern matching and patterns that would have otherwise matched will be unable to match. For example, an event producer sends one batch of events per hour where a batch contains the last hour’s events. The stream becomes idle after the first batch and the watermark is progressed by an hour. When the next batch is produced, it will contain events with event time spanning that hour. Most of these events will be late because the watermark has been progressed by an hour due to idleness.
Event time is the appropriate mode for that situation because the watermark will not progress without new events, so all the events in the batch can contribute to pattern matching.
Important: Ensure that the events for the same value of the context property have distinct timestamps.
- Click Next to open the Output properties pane. You can manage the properties that come from this node to suit your requirements. By default, the following properties are included:
contextKey: contains the value of the property you selected for defining the context.patternMatchTime: the event time for the output event. For use in downstream operations that require an event time property. Contains the timestamp, in event time, of the final event in the detected pattern.startPatternMatchTime: the timestamp, in event time, of the first event in the detected pattern.-
endPatternMatchTime: the timestamp, in event time, of the final event in the detected pattern.Note: When a pattern includes a Not followed by condition, the final event timestamp is the end of the time interval.
- Optional: To remove a property so that it is not included in the output, click Remove property
.
- Optional: To rename a property, hover over the property name and click the Edit icon
.
- In the text-box, enter a new name for your property.
- Click outside the text-box or press Enter on your keyboard to rename the property.
- Optional: To add a property that was previously removed, go to the Properties to remove table that lists the removed properties. For the property you want to add back, click the Add property icon
.
-
To complete the configuration, click Configure.
A green checkbox
is displayed on the detect patterns node if the node is configured correctly. If there is any error in your configuration, a red checkbox
is displayed.
Deduplicate

Deduplication is useful in multiple scenarios such as:
- In IoT systems, to eliminate repeated sensor readings caused by network glitches.
- E-commerce platforms often face duplicate order submissions due to retries or page refreshes.
- In email campaign tracking, to count only one open or click event per user per email.
- In financial systems, to ensure each transaction is processed only once.
- Eliminates repeated log entries from distributed services.
Adding a deduplicate node
To add a deduplicate node, complete the following steps:
- Ensure that a stream of events is available, from an event source node or from the output of any previously configured node.
- In the Palette, under Processors, drag the Deduplicate node into the canvas.
-
Connect the node to an event source by dragging the Output port from a source node into the Input port of this node.
A purple checkbox
is displayed on the deduplicate node indicating that the node is yet to be configured.
- Hover over the node, and click
Edit to configure the node.
The Configure deduplication window opens.
Configuring a deduplicate node
To configure a deduplicate node, complete the following steps:
- In the Details section, enter a name for your node. The output stream of events from this node will be referred with the name you entered.
-
Click Next to open the Define deduplication pane.
Note: A tree view of the event structure is available. To view all the input properties of the current node, click View input properties in the upper-right corner of the pane.
- In the Event time property to start the deduplication drop-down list, select the property of the event that corresponds to an event time. If there is only one event time property, it is selected by default.
-
Select the deduplication mode:
As discussed in step 10 of event nodes, events can arrive out of order. To perform deduplication, the events are sorted in chronological order based on their event time. Watermarks from each input stream are used in the sorting process to handle out-of-order events.
There are two deduplication modes available to determine how the deduplicate node removes duplicate events:
- Fixed interval (default): In this mode, duplicates are removed within a fixed time window that starts when the first event is received. The window remains active for the specified duration (for example, 5 minutes). After the time window expires, the next event starts a new window of the same fixed interval.
- Inactivity: This mode removes duplicate events based on the time elapsed since the most recent occurrence of the same event. Each duplicate event becomes the key event for the next comparison, ensuring only events separated by the defined interval are emitted.
-
In the Time interval field, specify a time interval to limit deduplication to a specific duration. If duplicate events occur within this interval, only the first event is retained and all subsequent duplicates are removed. Events outside this interval are not considered duplicates.
-
Select one or more properties to define the uniqueness of an event. These properties act as keys for deduplication. If two events have the same values for the selected properties, only the first event is retained.
Note: In the case of arrays, you can only select the entire array.
Click Next to open the Output properties pane.
-
The properties that you added in the previous step are displayed in the Output properties pane. You can manage the properties that come from this node to suit your requirements.
Only leaf properties are listed in the Properties to keep table.
-
Optional: Click Remove property
to remove a property from being displayed in the output. You can remove specific properties from an object, or if you want to remove the entire object, remove all the properties related to it one by one.
-
Optional: To rename a property, hover over the property name and click the Edit icon
.
Note: To rename the top-level property, use the transform node.
-
Optional: To add a property that was previously removed, go to the Properties to remove table and click the Add icon
.
-
- To complete the configuration, click Configure.
A green checkbox 

User actions are saved automatically.
