Db2 objects
IBM Db2 Developer Extension provides a clean, intuitive tree-based interface for exploring and managing database objects. With this organized view, you can quickly navigate through schemas and access objects such as tables, views, indexes, and stored procedures.
The extension offers a seamless way to drill down into object details and manage your Db2 environment efficiently.
Exploring Db2 objects
After you create a database connection, the following object types associated with that connection are listed under it.
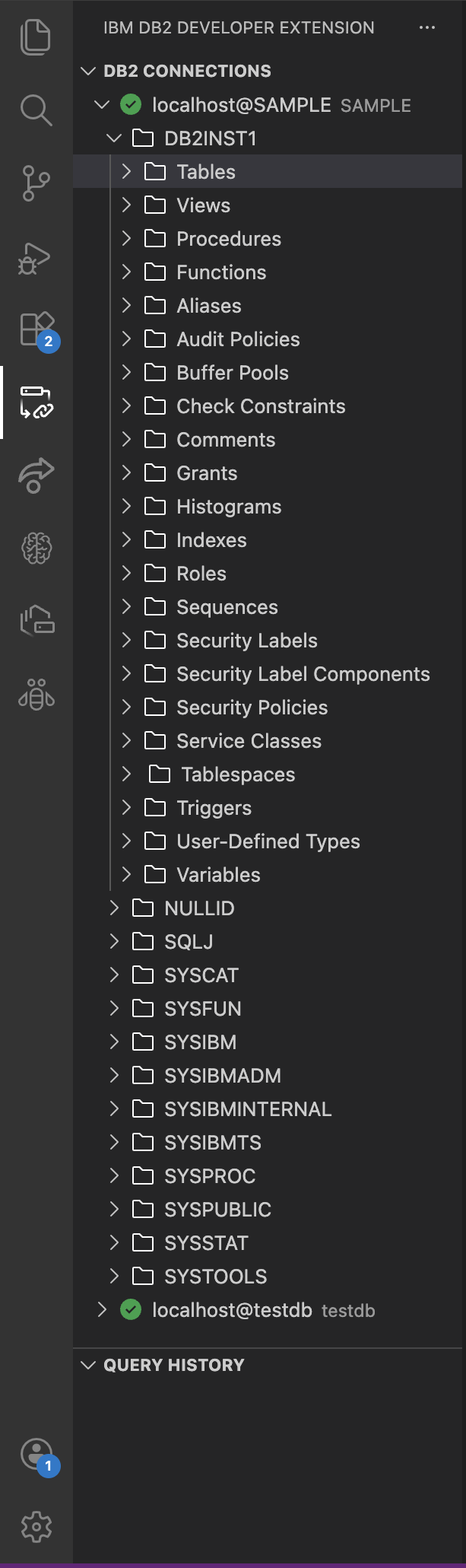
- Tables: A table is a structured collection of rows and columns that are used to store data in a relational format. Each column has a defined data type, and each row represents a record.
- Views: A view is a virtual table that is created by a query that retrieves data from one or more tables.
- Procedure: Procedures are precompiled sets of SQL statements that perform specific tasks. They can accept input parameters, return output, and help encapsulate business logic within the database.
- Indexes: Indexes are structures that improve query performance by allowing faster data retrieval based on column values.
- Functions: User-defined or built-in functions perform operations on data and return a single value. They can be scalar (return one value) or table functions (return a set of rows).
- Aliases: An alias is an alternative name for a table, view, or sequence. It simplifies referencing objects, especially across schemas or when renaming is needed without changing the original object.
- Audit Policies: Define rules for tracking and recording database activities to ensure security and compliance by specifying which actions to log.
- Buffer Pools: A buffer pool is an area in memory that is used to cache table and index pages for faster data access.
- Check Constraints: Check constraints enforce conditions on column data, ensuring only values that satisfy the condition are accepted.
- Comments: Comments are descriptive text that is attached to database objects (for example, tables) to provide documentation or clarification.
- Grants: Grants are permissions that are given to users or roles to perform actions on database objects (for example, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE).
- Histograms: Histograms store statistical information about column data distribution.
- Roles: Roles are collections of privileges that can be assigned to users, simplifying security management.
- Sequences: A sequence generates numeric values in a defined order, often used for auto-incrementing primary keys.
- Security Labels: Security labels classify data for access control based on security policies.
- Security Label Components: Components define the structure of security labels, such as levels, categories, or compartments.
- Security Policies: Security policies govern how security labels are applied and enforced for data access.
- Service Classes: Service classes define workload management rules, controlling resource allocation for different workloads.
- Table spaces: A table space is a storage structure that groups tables and indexes, managing how data is physically stored on disk.
- Triggers: Triggers are actions that automatically run in response to specific events on a table (for example, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE).
- User-defined Types: Custom data types created by users to represent complex structures beyond built-in types.
- Variables: Variables store temporary values during the execution of SQL statements or procedures.
When you click an object type in a schema, it expands to show all objects of that type. For example, if you click Tables, it expands to show all the tables in a schema.
Viewing table details in a schema
-
Under the database connection, click the specific schema that you want to explore. When you click a schema, the extension opens a detailed view showing all tables in that schema, including key information such as table name, table space, row count, owner, creation time, and organization.
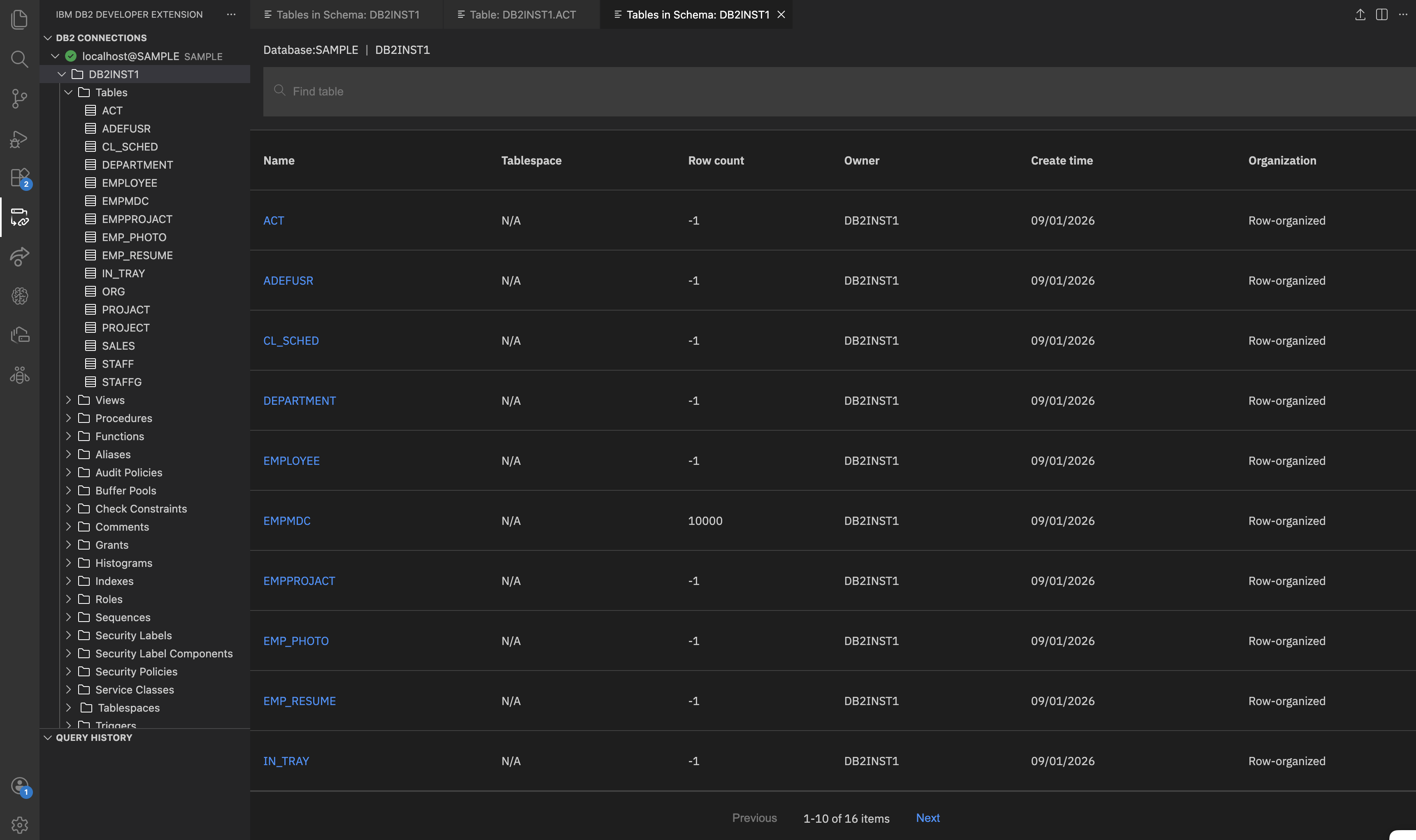
Each column provides specific details:
- Name: Unique name that is assigned to the table within the schema.
- Table space: Logical storage location where the data within the table resides.
- Row count: Number of rows (records) currently stored in the table.
- Owner: The user who owns the table.
- Creation date: Date and time when the table was created in the database.
- Organization Type: Specifies how the data within the table is physically organized. Common types include row-organized or column-organized.
-
Click the table name that you want to view (for example, EMPMDC table). It displays the following details.
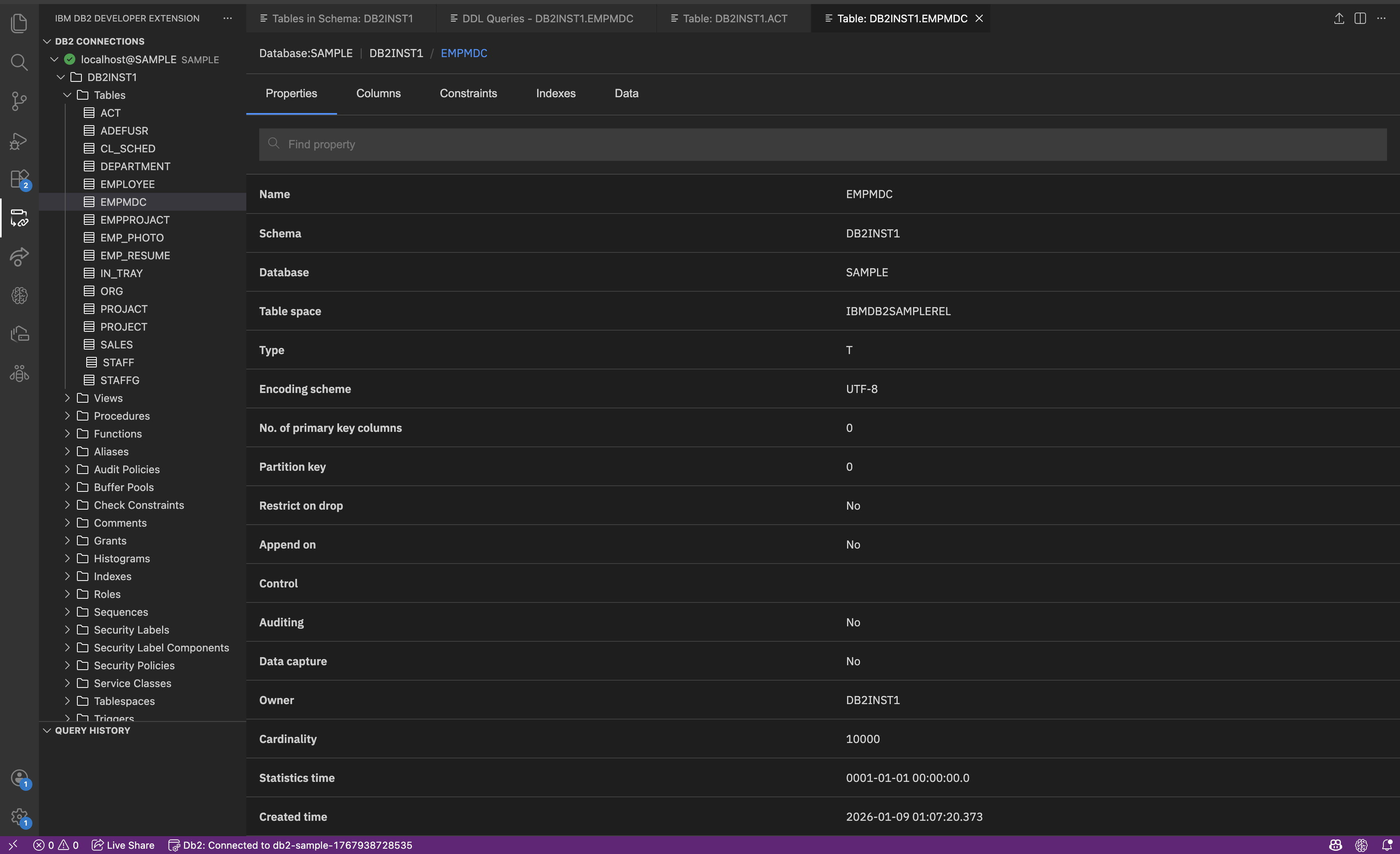
- Properties: General details such as table name, schema name, type, encoding scheme, owner.
- Columns: Lists all column names along with their data types and constraints.
- Constraints: Rules that apply to table columns.
- Indexes: Shows relationships with other objects (like views or indexes).
- Data: Shows the actual rows that are stored in the table.
You can also view the details of a particular table by expanding the Tables section under the schema in the DB2 CONNECTIONS pane and clicking the table name. For example, EMPMDC. For more information about the table properties, see Exploring table object details.
You can follow the same process to explore other Db2 objects.