Exploring tables
In Db2, every table is associated with a set of metadata and structural components that define its behavior, organization, and relationships. These components are collectively referred to as table details. They include:
- Properties
- Columns
- Constraints
- Indexes
- Data
Viewing table details
- Click the database connection and then the schema that you want.
-
Expand the Tables section and click the table name. It shows the following table details:
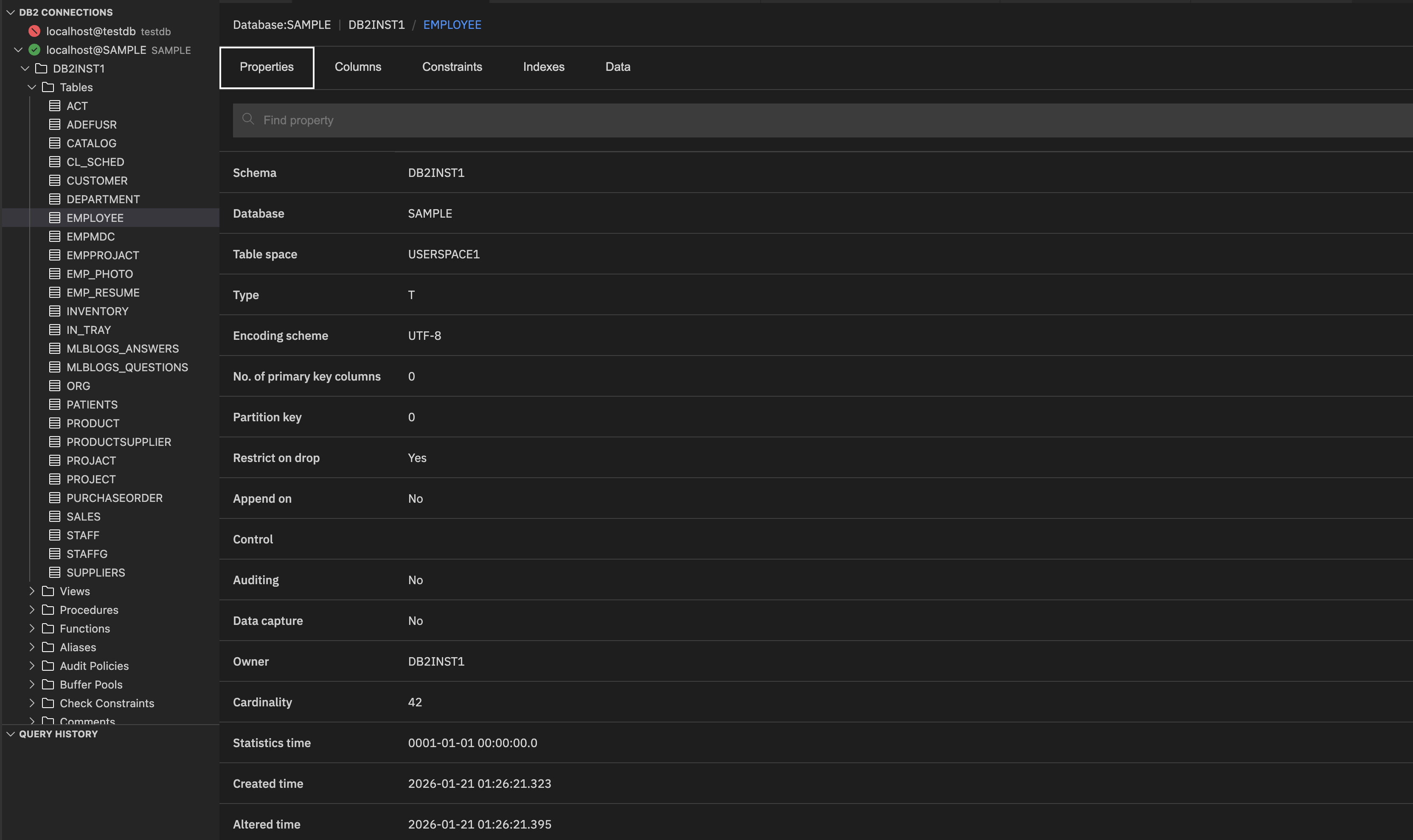
Properties: General details such as table name, schema name, type, encoding scheme, owner, etc.
The Properties tab shows the following details:
- Schema: Schema under which the table resides.
- Database: Database name.
- Table space: Logical storage location.
- Type: Object type (Table).
- Encoding scheme: Character encoding used for the text data in the table (for example, UTF-8).
- No. of primary key columns: Number of columns that are defined as the primary key in metadata.
- Partition key: Indicates if the table is partitioned and how many columns are used as partition keys.
- Restrict on drop: Prevents accidental table deletion until you explicitly remove the restriction.
- Append on: If set to Yes, new rows are appended at the end of the table. Here, it is disabled.
- Control: Indicates whether special control features are enabled.
- Auditing: Specifies if auditing is enabled for this table. Auditing tracks changes for compliance.
- Data capture: Indicates whether data capture for replication or change tracking is enabled.
- Owner: The user who owns the table.
- Cardinality: Estimated number of rows in the table.
- Statistics time: Shows the timestamp of the last statistics update. A default value indicates that statistics have not yet been collected.
- Created time: Timestamp indicating when the table was created.
- Altered time: Timestamp indicating when the table was last modified.
Columns: Lists all column names along with their data types and constraints.
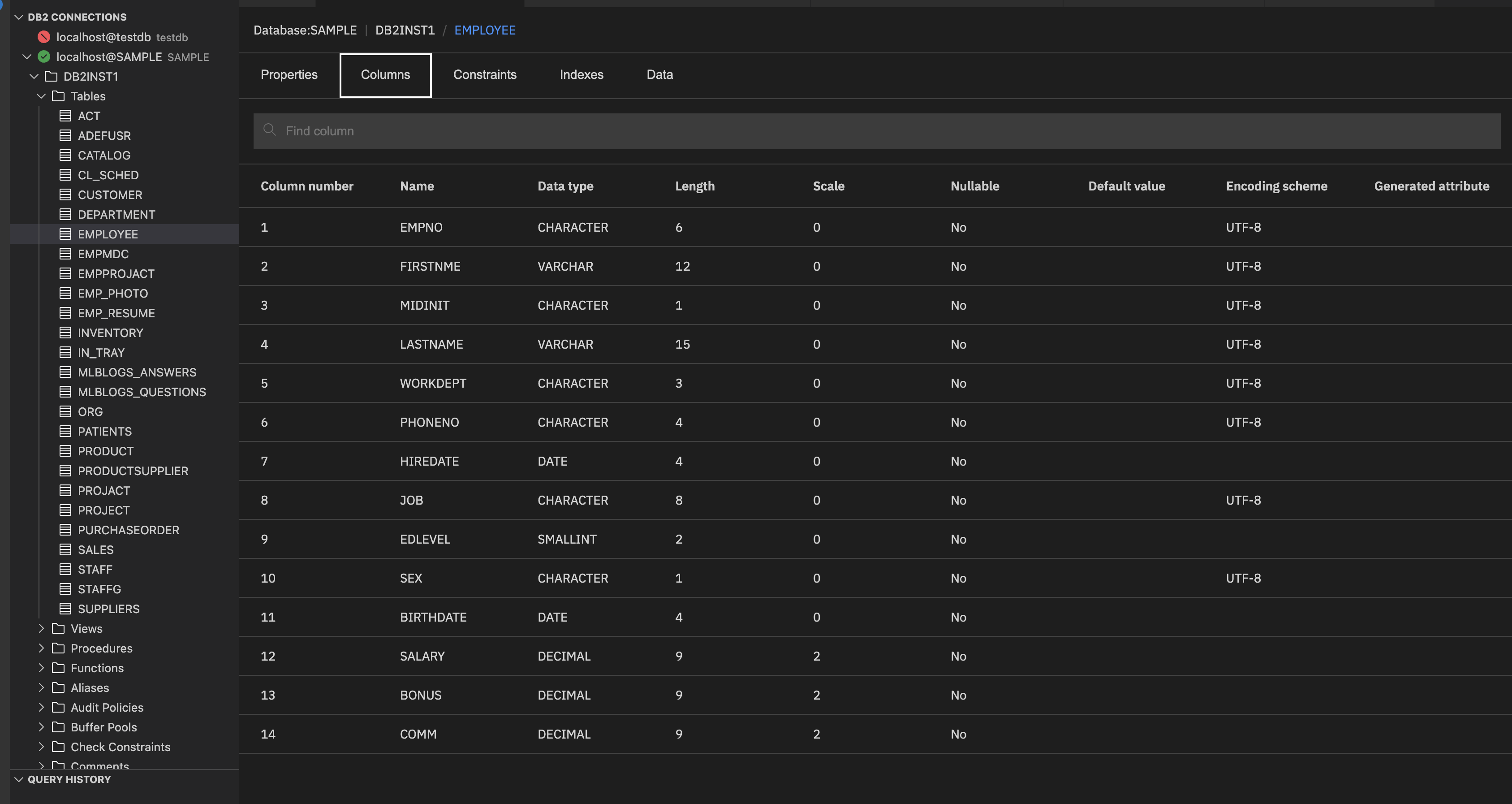
It shows the following details:
- Column number: Position of the column in the table.
- Name: Unique identifier for the column within the table.
- Data type: Specifies the type of data the column can store (for example, INTEGER, VARCHAR, DECIMAL, DATE).
- Length: Maximum size of the column data.
- Scale: Number of digits to the right of the decimal point (used for DECIMAL types).
- Nullable: Indicates whether the column can contain NULL values.
- Default value: Value automatically assigned if no value is provided during insert.
- Encoding scheme: Character encoding used for text columns (for example, UTF-8).
- Generated attribute: Indicates if the column is auto-generated.
Constraints: The rules applied to the columns of the table. Shows details such as constraint name and type.
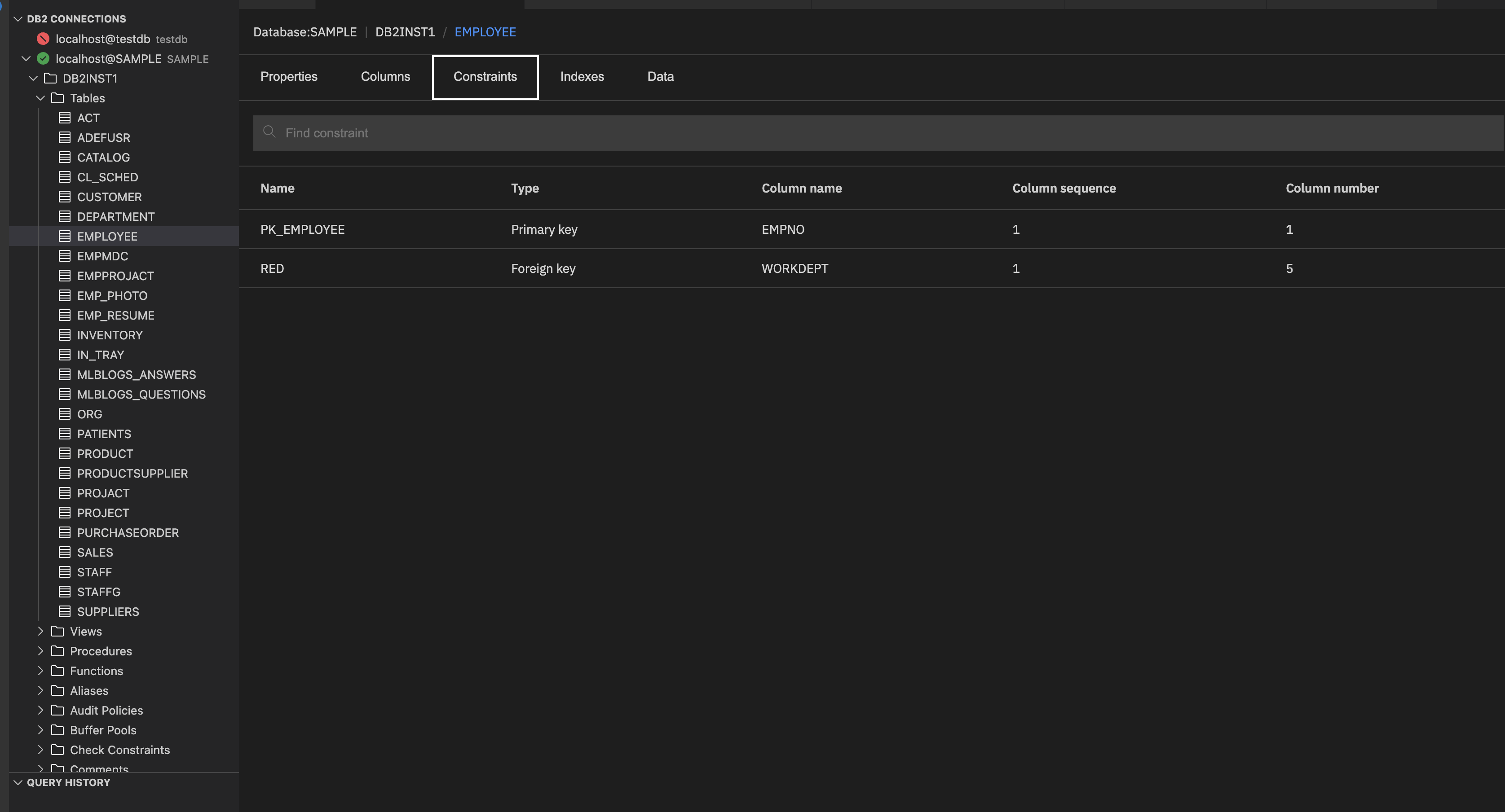
It shows the following details:
- Name: Name of the constraint.
- Type: Type of constraint applied to the table. It indicates the rule enforced on the columns.
Common Types include:
- Primary key: Ensures that each row has a unique identifier.
- Foreign key: Links to another table for referential integrity.
- Unique: Ensures that column values are unique.
- Check: Validates data against a condition.
- Column name: Shows which columns the constraint applies to.
- Column sequence: Order of columns in the constraint when multiple columns are involved.
- Column number: Position of the column in the table structure.
Indexes: Shows relationships with other objects, such as views.
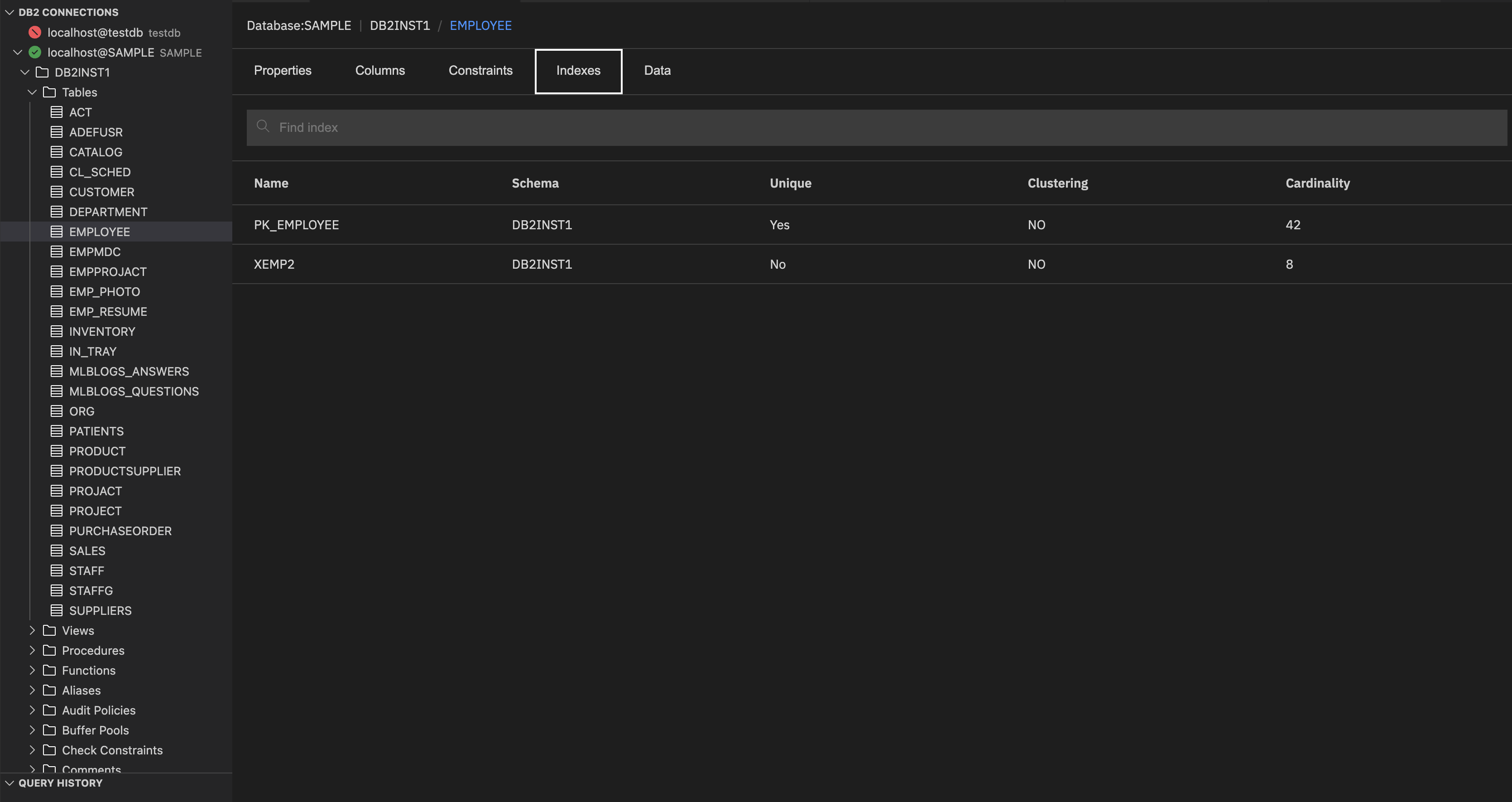
It shows the following details:
- Name: Name of the index.
- Schema: Schema under which the index is created.
- Unique: Specifies whether the index enforces uniqueness. If the value is Yes, the index ensures that no two rows have the same value for the indexed columns.
- Clustering: Refers to whether the index is a clustered index or not. If the value is Yes, it means that the table rows are physically sorted by the index column.
- Cardinality: Number of distinct values in the indexed columns.
Data: Shows the actual rows that are stored in the table.
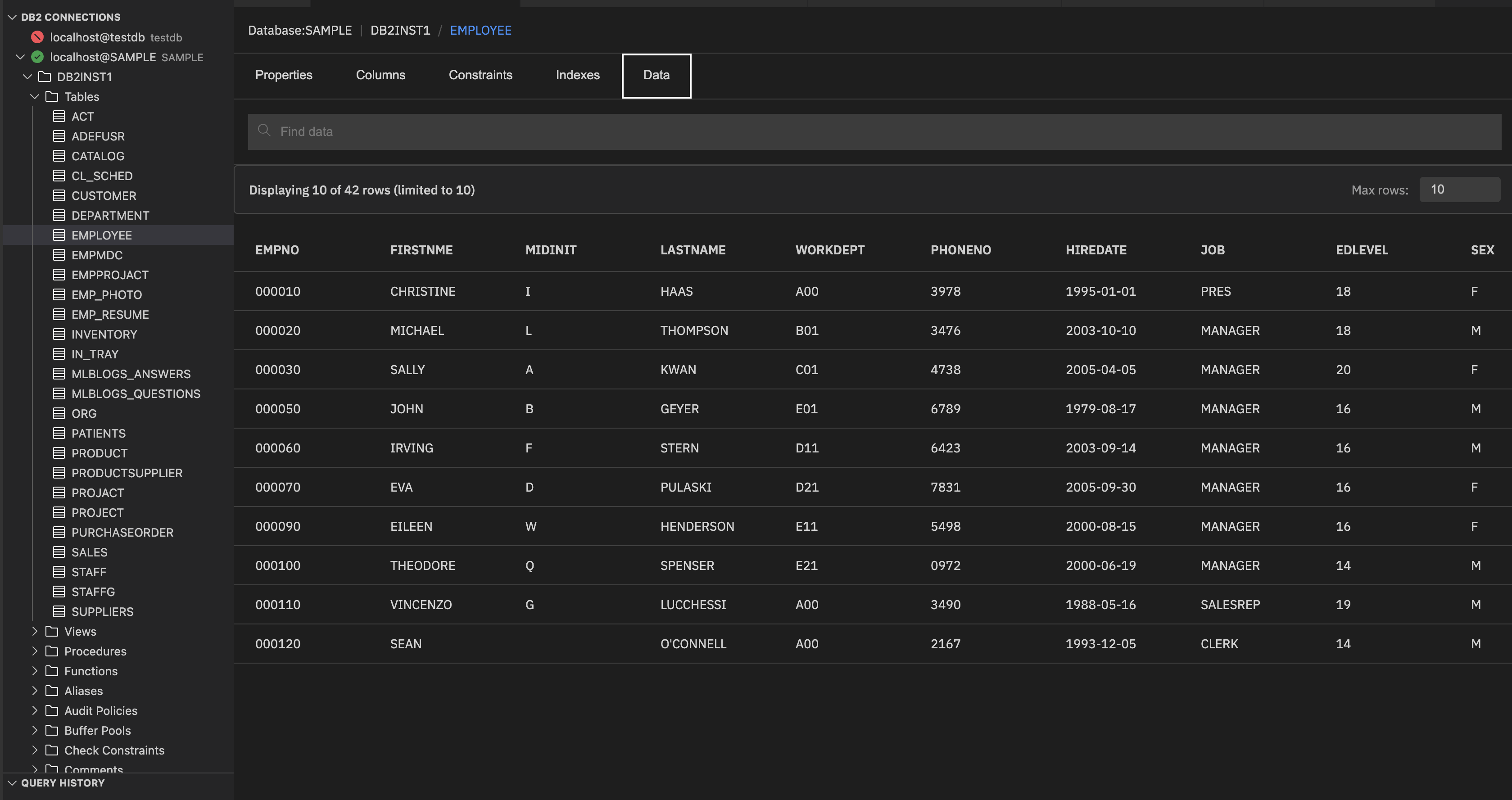
Note: The Max rows specifies the maximum number of rows to show in the data preview. Enter the required value in the Max rows and press Enter to refresh the preview. You can also set the row limit by using the Db2service: Max Rows extension setting. See Limiting the number of rows returned for more information. The Max rows field is synchronized with the Db2service: Max Rows extension setting, and changes made in either location automatically update both.