Creating native SQL procedures
The topic covers how to create native SQL procedures. You can create procedures by creating .spsql files or by using the SQL Editor.
Method 1: Creating procedures using .spsql files
You can create procedures by creating .spsql files:
Step 1: Create a new .spsql file
-
In VS Code, create a new file by clicking File > New File.
-
Save the file with a
.spsqlextension (for example,MyProcedure.spsql). -
In your
.spsqlfile, start typingCREATE PROCEDURE. You need to type only a few characters before the CREATE PROCEDURE code snippet appears in the list of available snippets.Select the CREATE PROCEDURE statement (SQL - native) snippet to populate your file with the basic CREATE PROCEDURE structure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE SCHEMA_NAME.PROCEDURE_NAME ( IN p_input_param1 datatype, IN p_input_param2 datatype, OUT p_output_param1 datatype, OUT p_output_param2 datatype ) LANGUAGE SQL SPECIFIC PROCEDURE_NAME BEGIN -- Declare local variables DECLARE v_variable1 datatype; DECLARE v_variable2 datatype; -- Your procedure logic here -- Example: Query data SELECT column1, column2 INTO v_variable1, v_variable2 FROM table_name WHERE condition; -- Set output parameters SET p_output_param1 = v_variable1; SET p_output_param2 = v_variable2; END; -
Customize the snippet:
- Replace
SCHEMA_NAMEwith your schema (for example,DB2INST1). - Replace
PROCEDURE_NAMEwith your procedure name (appears twice: in the procedure signature and in the SPECIFIC clause). - Define your input parameters (IN) with appropriate names and datatypes (for example,
p_employee_id INTEGER). - Define your output parameters (OUT) with appropriate names and datatypes (for example,
p_result_message VARCHAR(100)). - Declare local variables as needed using the DECLARE statement (for example,
DECLARE v_salary DECIMAL(9,2)). - Add your procedure logic, including:
- SQL queries with SELECT INTO to populate variables.
- Conditional logic (IF/ELSE statements).
- SET statements to assign values to output parameters.
- Replace placeholder datatypes with actual Db2 datatypes (INTEGER, VARCHAR, DECIMAL, DATE, and so on).
- Replace
Example: Complete .spsql file
The following procedure is used to calculate an employee’s bonus. This procedure takes an employee ID and bonus rate as input parameters, retrieves the employee’s salary from the database, calculates the bonus amount, and returns both the calculated bonus and a status message as output parameters:
-- File: CalculateBonus.spsql
-- Description: Calculate employee bonus based on salary and bonus rate
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DB2INST1.CalculateBonus (
IN p_employee_id INTEGER,
IN p_bonus_rate DECIMAL(5,2),
OUT p_bonus_amount DECIMAL(9,2),
OUT p_status_message VARCHAR(100)
)
LANGUAGE SQL
SPECIFIC CalculateBonus
BEGIN
DECLARE v_salary DECIMAL(9,2);
-- Get employee salary
SELECT salary INTO v_salary
FROM employee
WHERE empno = p_employee_id;
-- Calculate bonus
IF v_salary IS NOT NULL THEN
SET p_bonus_amount = v_salary * p_bonus_rate;
SET p_status_message = 'Bonus calculated successfully';
ELSE
SET p_bonus_amount = 0;
SET p_status_message = 'Employee not found';
END IF;
END;
Step 2: Run the procedure from the .spsql file
- Click Run (
 ).
). - Select a database connection from the connection dropdown (For example, localhost@SAMPLE).
-
Reload (
 ) the objects in your database. This action refreshes the Procedures section under your schema (for example, DB2INST1) in the selected database (for example, SAMPLE), and the newly created procedure appears under the Procedures section.
) the objects in your database. This action refreshes the Procedures section under your schema (for example, DB2INST1) in the selected database (for example, SAMPLE), and the newly created procedure appears under the Procedures section.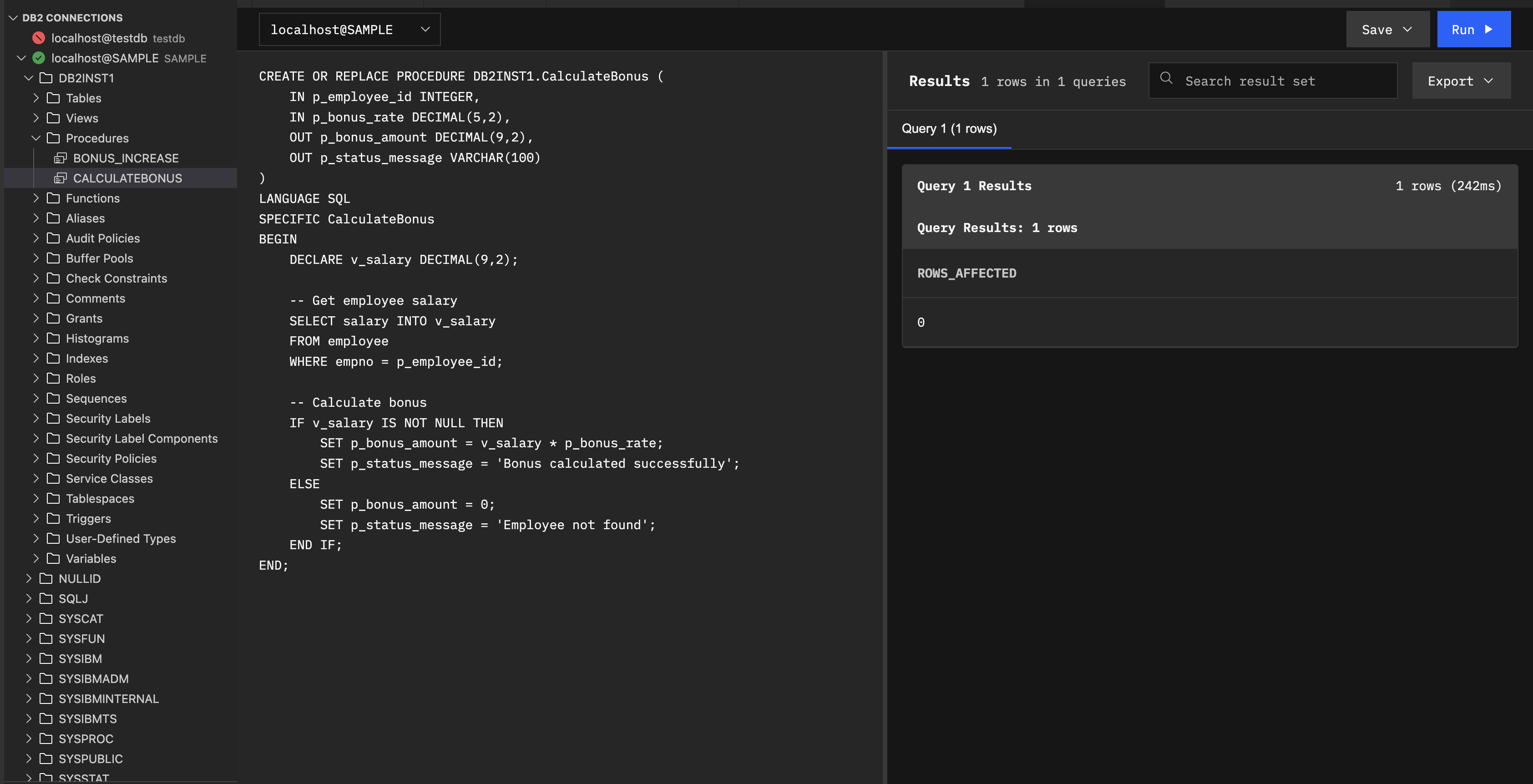
Method 2: Creating procedures in the SQL Editor
You can create procedures in the SQL Editor:
-
Open the editor by clicking the Open SQL Editor (
 ) in the DB2 CONNECTION pane.
) in the DB2 CONNECTION pane. -
Select your database connection from the dropdown menu (for example,
localhost@SAMPLE). -
Write your procedure.
-
Click Run.
-
Reload (
 ) the objects in your database. This action refreshes the Procedures section under your schema (for example, DB2INST1) in the selected database (for example, SAMPLE), and the newly created procedure appears under the Procedures section.
) the objects in your database. This action refreshes the Procedures section under your schema (for example, DB2INST1) in the selected database (for example, SAMPLE), and the newly created procedure appears under the Procedures section.
What’s next
After creating your procedure: