Exploring procedures
A procedure in Db2 is a precompiled and named set of SQL statements that is stored in the database and is invoked by using the CALL statement. When you open a procedure, you can see the following three tabs:
- Properties
- Parameters
- Text
Viewing the procedure details
- Click the database connection and then the schema that you want.
-
Expand the Procedures section and click the procedure name. It shows the following procedure details:
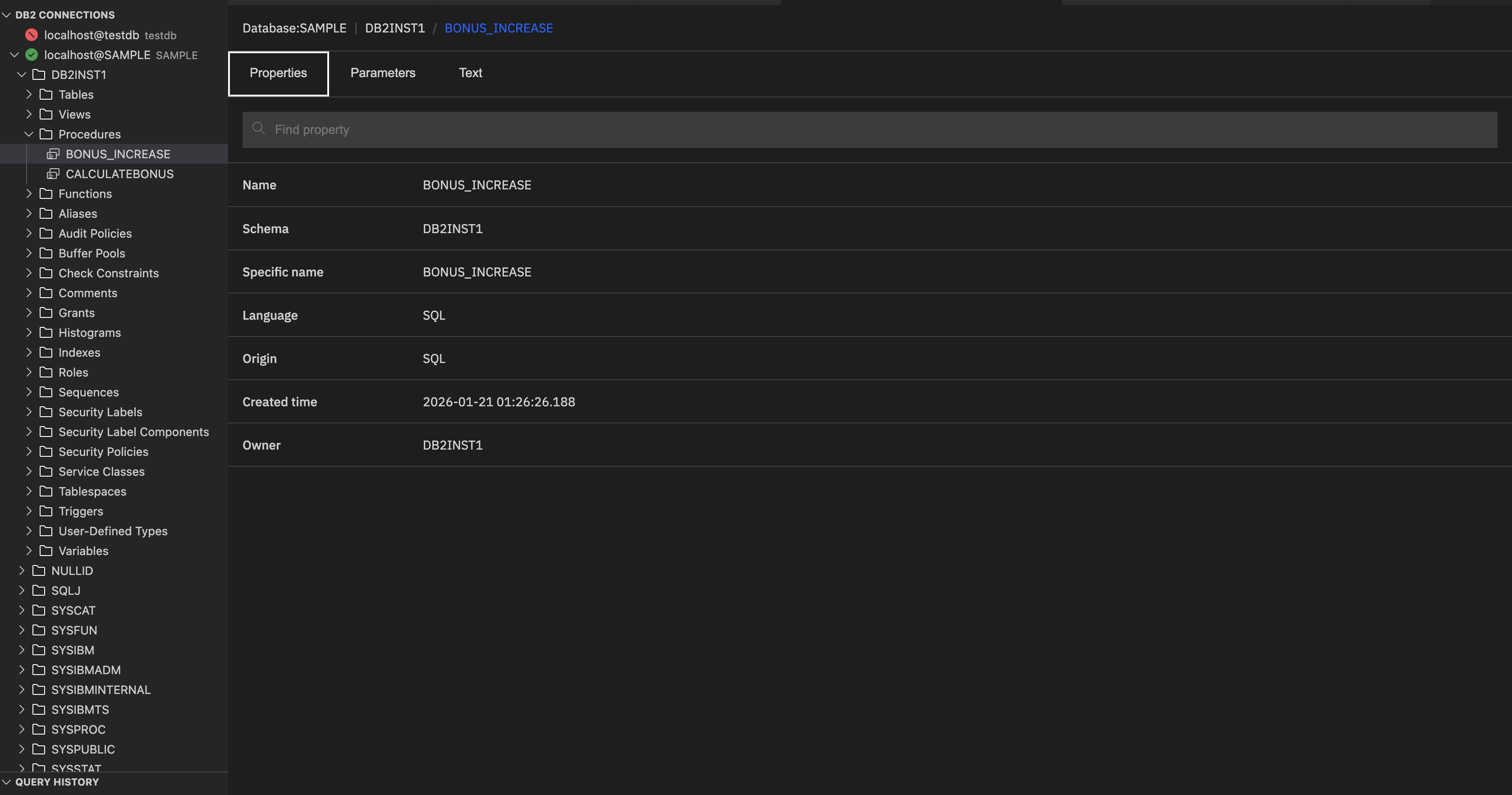
Properties: Provides the metadata about the procedure.
- Name: Logical name of the procedure.
- Schema: Schema under the procedure resides.
- Specific name: System-generated unique identifier for this procedure version.
- Language: Language in which the procedure is written.
- Origin: Indicates how the procedure was created. The screenshot shows SQL, which means that the procedure was created directly with SQL statements, not in an external language.
- Created time: Timestamp indicating when the procedure was created.
- Owner: The database user who created the procedure.
Parameters: The Parameters section lists all the input and output parameters defined for the procedure.
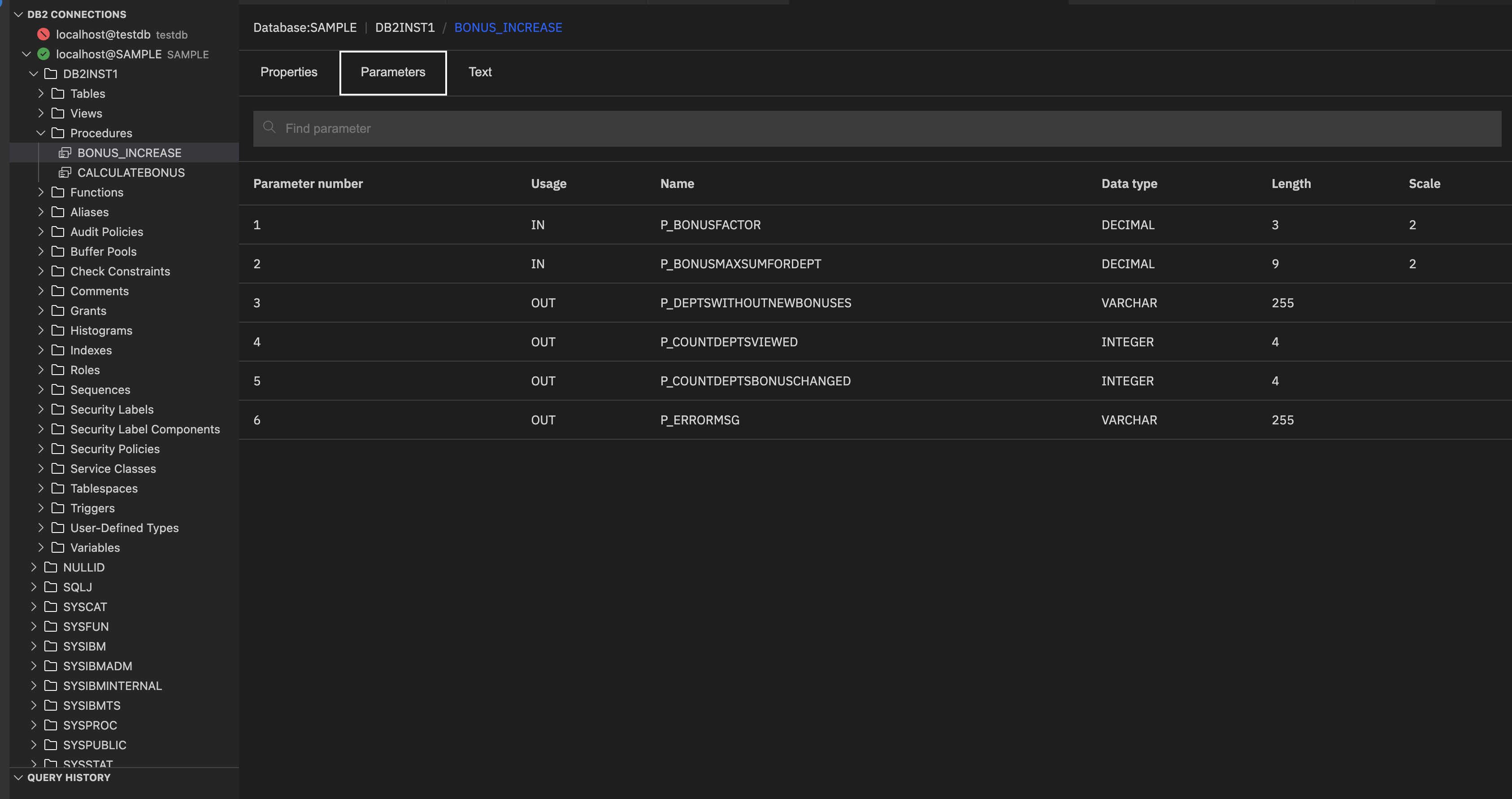
Each column provides specific details:
- Parameter number: Sequential position of the parameter in the procedure definition.
-
Usage: Indicates how the parameter is used:
- IN: Passed into the procedure as input.
- OUT: Returned as output.
- INOUT: Used for both input and output.
- Name: Identifier of the parameter as defined in the procedure.
- Data type: Specifies the type of data the parameter holds (for example, INTEGER, VARCHAR, BLOB, CLOB, XML).
-
Length: Maximum size of the parameter value:
- For numeric types, it’s typically the byte size (for example, 4 for INTEGER).
- For character or LOB types, it’s the maximum number of characters or bytes.
- Scale: Indicates the number of digits to the right of the decimal points.
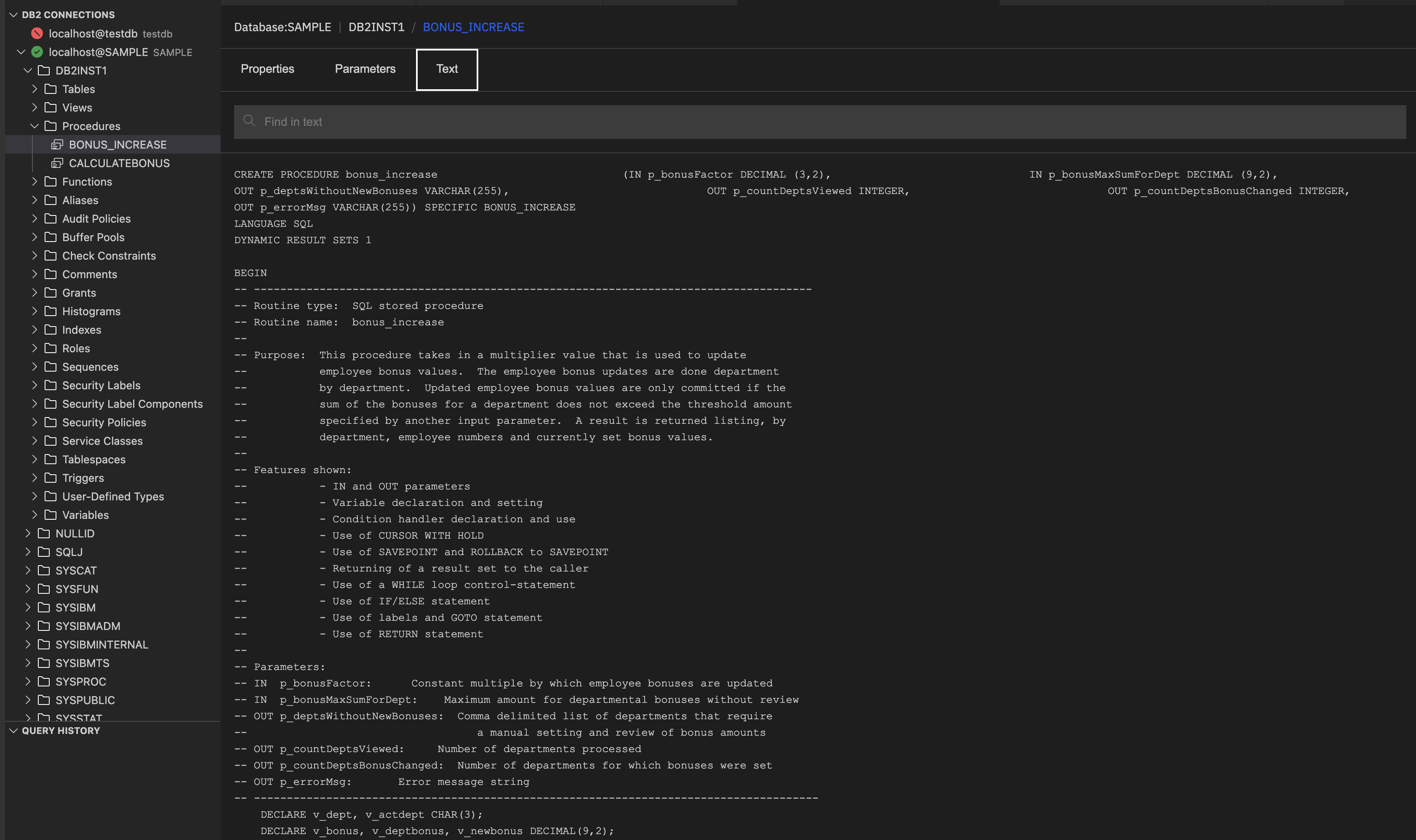
Text: It shows the full source code of the procedure, including its definition, parameters, language, and SQL logic.