Setting up an SQL Tuning Services environment
This article describes how to set up an SQL Tuning Services environment in Db2 for z/OS Developer Extension.
Important: The SQL tuning features of Db2 Developer Extension require additional software. See Software requirements for using the SQL tuning features for details. Make sure that one of the SQL tuning options is installed on your system before you start to set up your SQL tuning environment.
Adding an SQL Tuning Services server
The first step in setting up an SQL tuning environment is adding an SQL Tuning Services server.
-
In the SQL TUNING SERVICES SERVERS view, click the plus sign (+) to open the Add SQL Tuning Services Server dialog.
-
Specify the hostname or IP address and port of the system where the SQL Tuning Services server is installed and a valid user ID and password for connecting to that server.
-
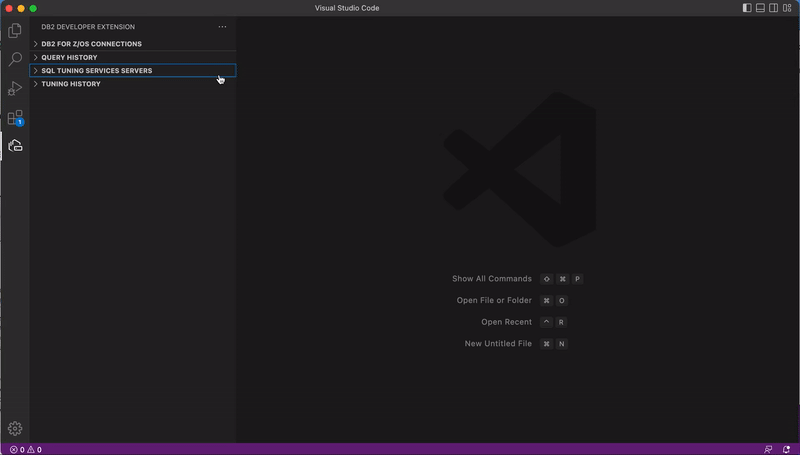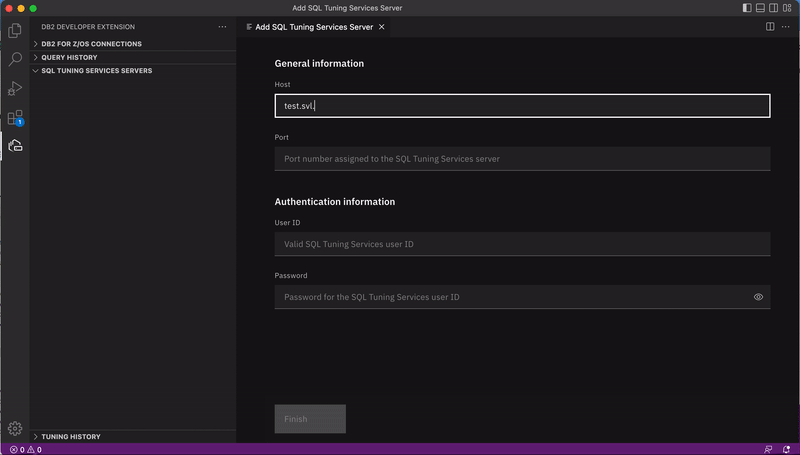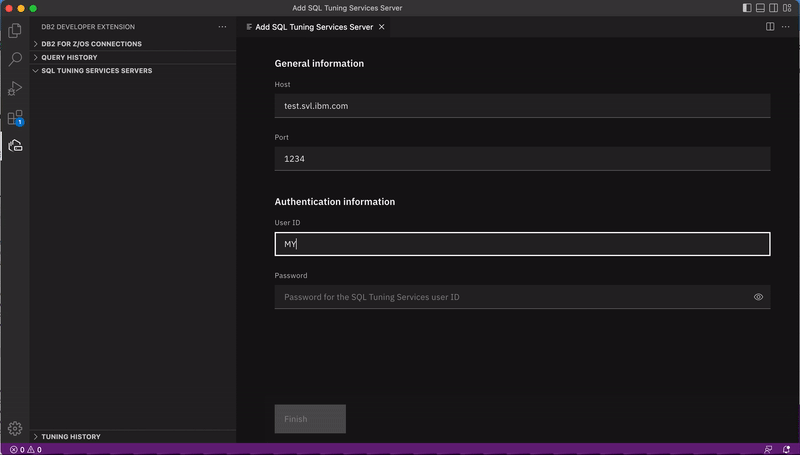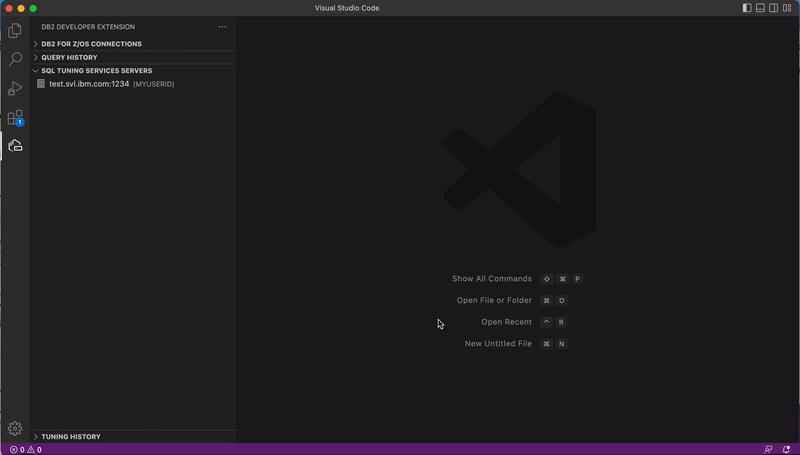
Click Finish.
The server you just created is displayed in the SQL TUNING SERVICES SERVERS view.
Supported security mechanisms
Db2 Developer Extension supports the following security mechanisms for SQL tuning. Your options for using or not using a tuning profile are dependent on the security mechanism that you use in your environment.
-
If you are using security mechanism 18 (SSL) to tune SQL, you must create and use tuning profiles to tune SQL. See Creating a tuning profile for instructions.
-
Security mechanisms 7 and 9 do not support the use of tuning profiles. If you are using one of these security mechanisms to tune SQL, see Tuning without a tuning profile for more information.
-
Security mechanism 3 supports both methods for tuning SQL.
Creating a tuning profile
Tuning profiles enable a SQL Tuning Services server to access the Db2 for z/OS database that contains the SQL that you want to tune. A tuning profile includes a valid Db2 for z/OS user ID and password, security information, and location information for the target database (host, location, and so on).
Note: The use of tuning profiles is optional in certain situations. See Tuning without a tuning profile for details. However, if you are using security mechanism 18, you must use a tuning profile.
The benefit of using tuning profiles is that they can be reused and shared. For example, a database administrator can create a single tuning profile with specific credentials and make it available to multiple Db2 Developer Extension users. However, if you specify a Db2 for z/OS password when you create a tuning profile, this password must be updated whenever the password is updated in RACF. To avoid this additional overhead, you can use multi-factor authentication instead of a password when you create a tuning profile.
To create a tuning profile:
-
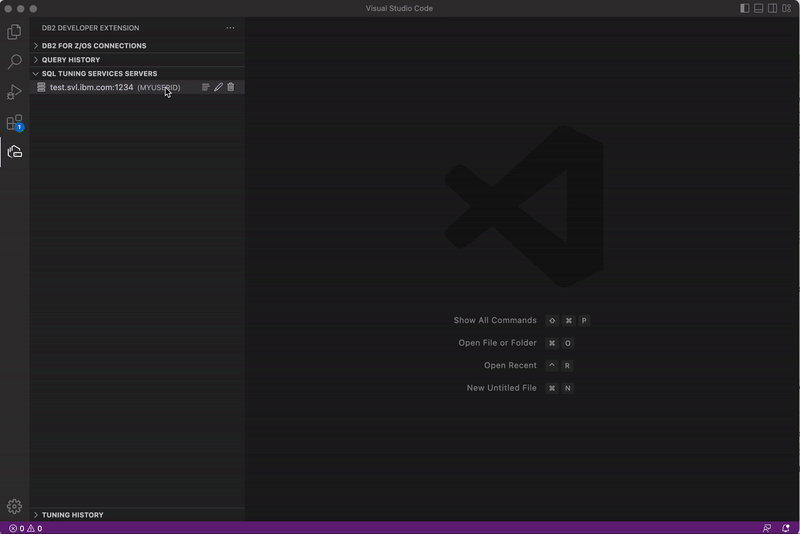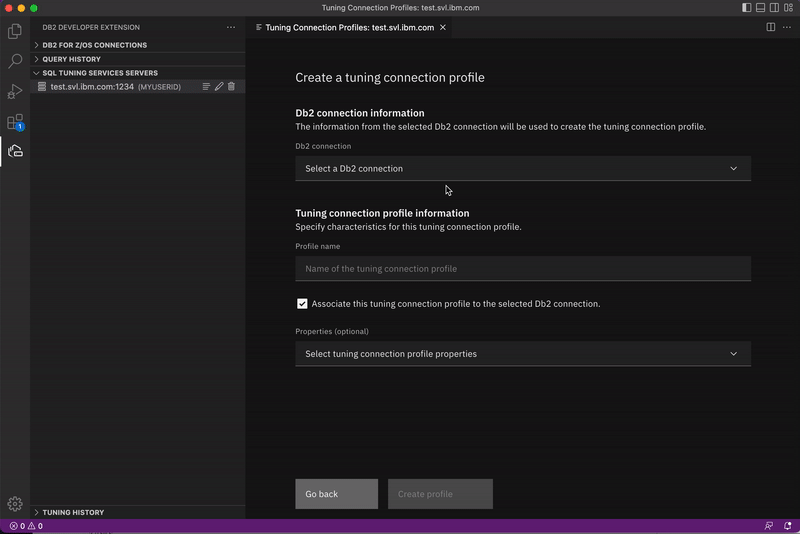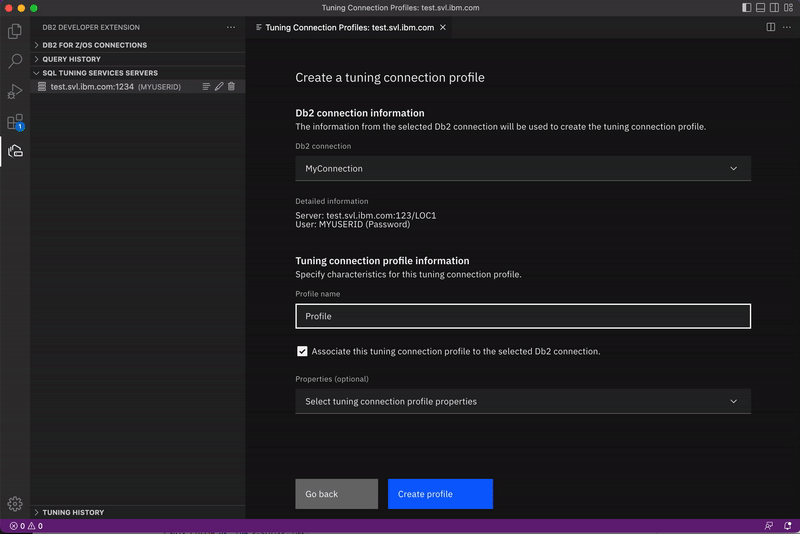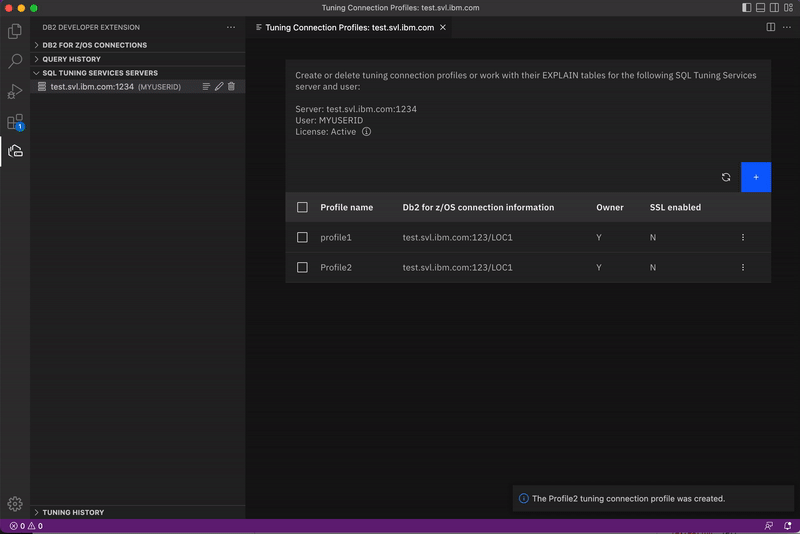
From the SQL TUNING SERVICES SERVERS view, right-click an SQL Tuning Services server and click Show Tuning Connection Profiles. The Tuning Connection Profiles window opens for the server you selected.
-
Click the blue plus sign on the right side of the dialog. The Create a tuning profile window opens.
-
Select a Db2 connection to associate with the tuning connection profile and assign a name. Optionally, you can specify additional properties such as the type of security mechanism to use and SSL properties.
-
Leave the Associate this tuning connection profile to the selected Db2 connection check box selected.
Important: Clear this checkbox only if you don’t intend to use this profile to start tuning your SQL right away. If you clear this checkbox now, you’ll need to associate this profile to a Db2 connection before you can use it to tune your SQL.
-
Click Create profile. A list of existing profiles is displayed, including the profile you just created. Keep this window open. You’ll need it for the next task.
Optionally, you can specify JDBC properties when creating a tuning profile. Db2 Developer Extension supports the following JDBC properties:
currentPackagePathencryptionAlgorithmsecurityMechanismsslCertLocationsslConnectionsslKeyStoreLocationsslKeyStorePasswordsslTrustStoreLocationsslTrustStorePasswordsslTrustStoreType
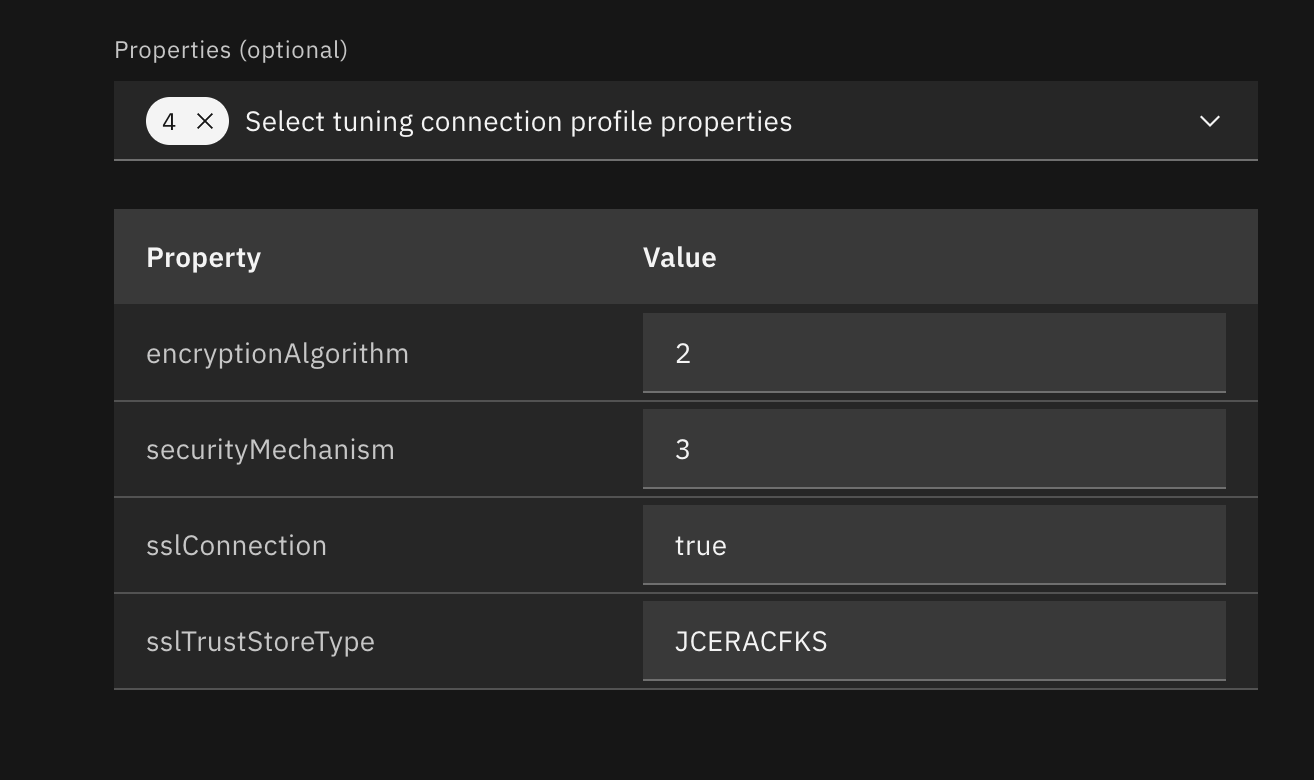
When you select the
currentPackagePathproperty to use a package in a collection ID that you specify, you can specify more than one collection ID. If a package is not found in the first collection ID that you specified, the next collection ID in the list is checked.Note: After you set a collection ID or multiple collection IDs for the
currentPackagePathproperty, you can reset the collection IDs by removing thecurrentPackagePathproperty from your tuning profile, saving the change, and then adding thecurrentPackagePathproperty back to your tuning profile. This process will automatically reset thecurrentPackagePathproperty with the valueNULLID, IBMTMS. You can also reset thecurrentPackagePathproperty by deleting the existing tuning profile and creating a new profile to set a new value for thecurrentPackagePathproperty.
Now that you’ve created a tuning profile, you must associate it with a Db2 database connection.
-
Either create a new Db2 connection or edit an existing Db2 connection.
-
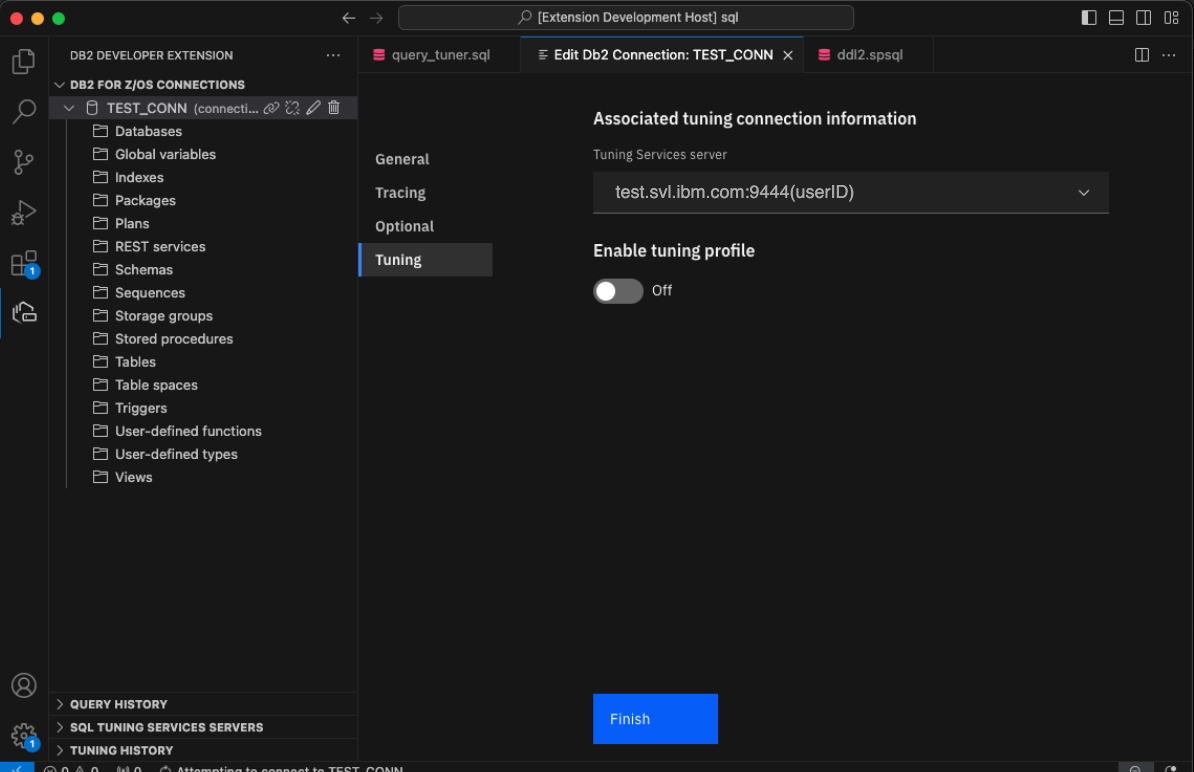
Go to the Tuning tab and select a Tuning Services server.
-
Turn the Enable tuning profile toggle on and select your tuning profile from the dropdown list.
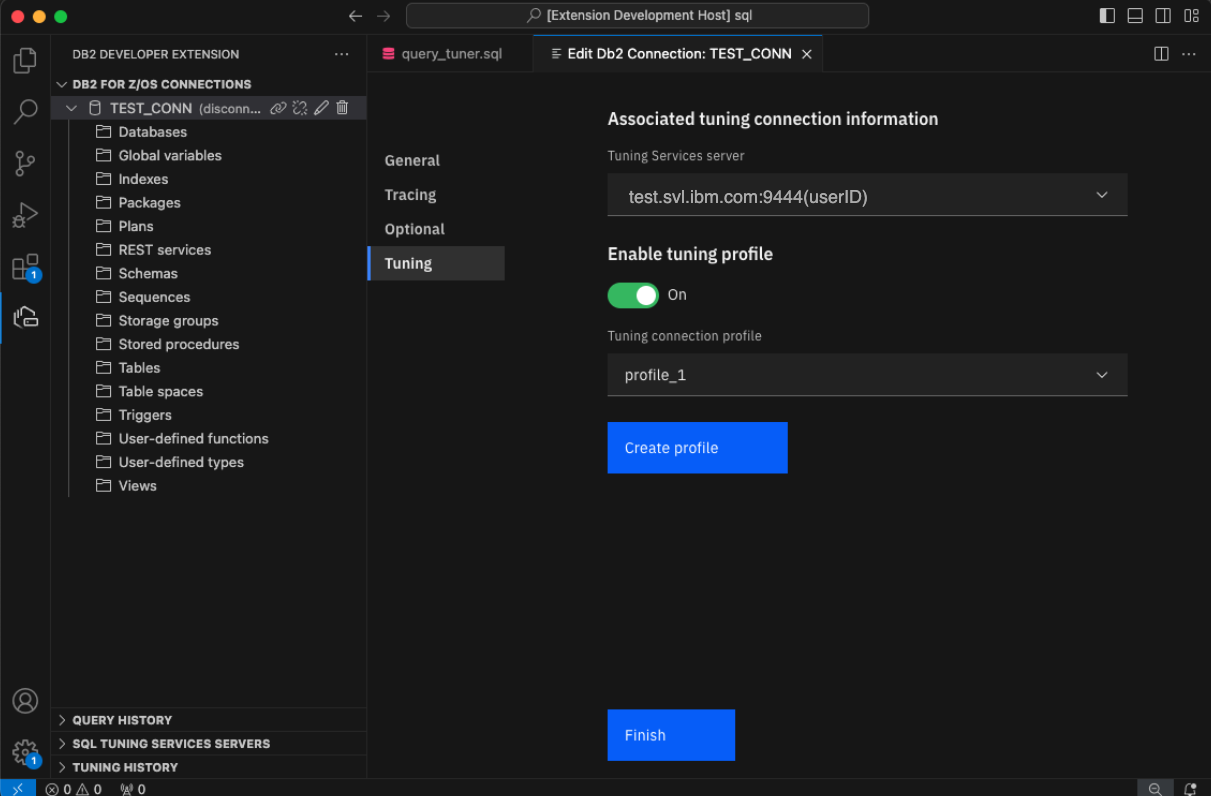
Note: When the Enable tuning profile toggle is on, you can click Create profile to create additional tuning profiles.
-
Click Finish to save the Db2 connection.
Tuning without a tuning profile
The use of tuning profiles is optional if you are using Db2 Developer Extension 2.1.6 and SQL Tuning Services APAR PH60806 has been applied. If you decide to not use a tuning profile, the authentication information in the database connection is used instead. Tuning without a profile supports security mechanism 3 and is required for security mechanism 7 and 9.
If you are tuning SQL without a tuning profile and you are using MFA, you will be prompted to enter an MFA token twice: when you first connect to Db2 and again when you initiate the tuning action. The tokens must be unique. Use the IBM Verify app to generate these MFA tokens.
Note: Tuning without a profile enables you to select and run multiple tuning actions simultaneously. When you do so, the results for each of the tuning actions that you run will share the same Job ID.
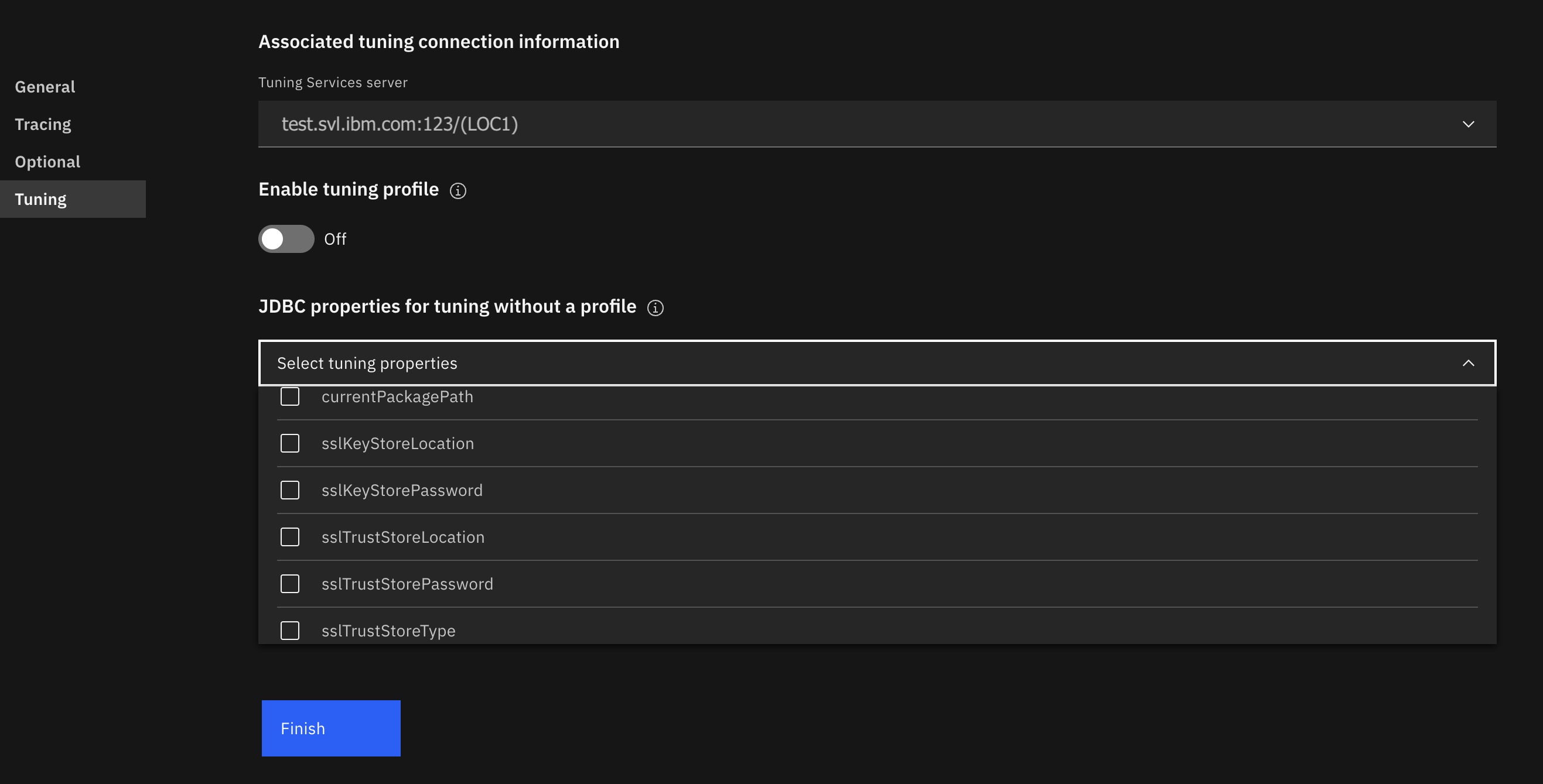
When you are tuning without a profile, you can specify JDBC properties. In most cases, specifying JDBC properties is optional; however, if you are using SSL to connect to Db2 and you are using a secure port without a public CA, you can specify the following SSL-related properties:
sslTrustStoreLocationsslTrustStorePasswordsslTrustStoreTypesslKeyStoreLocationsslKeyStorePassword
If you are not using SSL or you are using SSL with a public CA, you do not need to specify these properties.
Usage notes:
- When the
sslConnectionproperty is set totrue, if you specify these properties in the Optional tab, the property names will be automatically specified in the Tuning tab but no values will be assigned. - You can manually specify unique values for these properties in the Tuning tab; however, if you don’t specify unique values in the Tuning tab, the values in the Optional tab are used for tuning actions.
- Any values specified in the Tuning tab take precedence over values specified in the Optional tab.
- If you delete a property from the Tuning tab, but the property still exists in the Optional tab, the property name will automatically be specified in the Tuning tab.
- You can add these properties directly in the Tuning tab without specifying them in the Optional tab.
In addition to the SSL-related properties, you can use the currentPackagePath property, which enables you to use a package in a collection ID that you specify. You can specify more than one collection ID for the currentPackagePath property. If a package is not found in the first collection ID that you specified, the next collection ID in the list is checked.
When the currentPackagePath property is specified in the Optional tab, both the property name and the specified value are automatically populated in the Tuning tab.
Creating EXPLAIN tables
Db2 uses EXPLAIN tables to store information about SQL statements, access paths, and other elements that can affect SQL performance. The tuning connection profile needs its own set of EXPLAIN tables.
-
Click three vertical dots at the end of the tuning connection profile you just created, and select Create EXPLAIN tables. The Create EXPLAIN tables window opens.
-
Although all of the fields are optional, you’ll typically want to provide at least a schema name and SQL ID.
-
Click Create. A status message indicates that the EXPLAIN tables are being created.
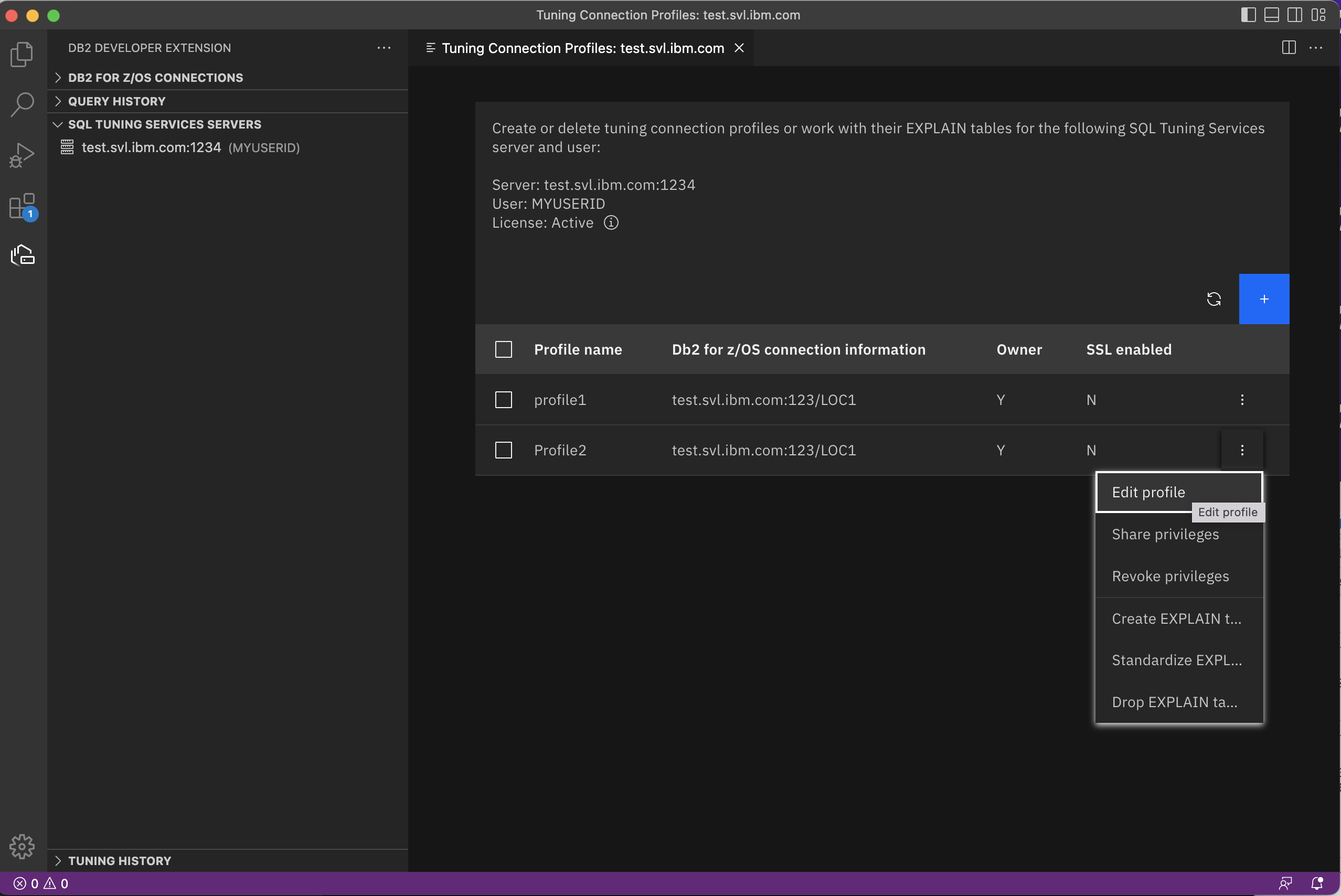
You can also standardize and drop EXPLAIN tables by clicking the three vertical dots.