Preparing to run an SQL statement
When you have some valid SQL and you have a valid database connection, you’re just about ready to run it. There’s a little bit of optional set up you might want to do first.
-
Create and save a simple SQL statement. For example, the following statement selects the entire contents (a single row) of the Db2 sample table SYSIBM.SYSDUMMY1:
SELECT * FROM SYSIBM.SYSDUMMY1 -
Right-click anywhere in your .sql file and select Run SQL Options from the context menu to open the following view:
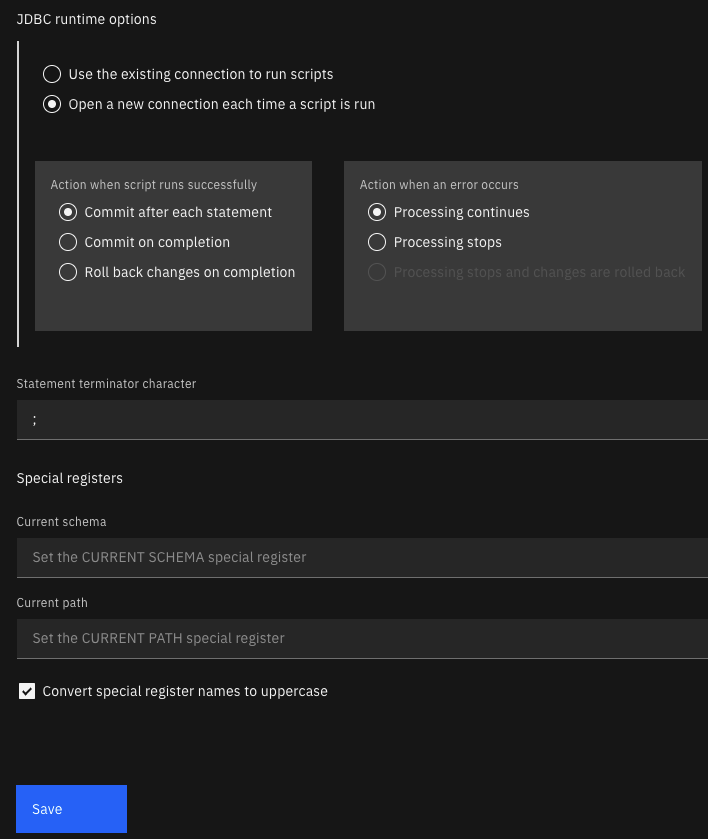
Use this view to set the following options for running your SQL:
- Whether to always use an existing database connection to run this script or open a new database connection every time you run this script.
- The circumstances under which changes are committed or rolled back.
- The statement termination character to use if you don’t want to use the default semicolon (;) character.
- Values for the CURRENT SCHEMA and CURRENT PATH special registers and whether these values are always converted to uppercase letters.
-
Now, you can run your SQL by using any of the following methods:
-
Right-click anywhere in your SQL file and click Run All.
-
Highlight your SELECT statement, right-click anywhere in your SQL file and click Run Selected SQL. This option is useful for testing and debugging individual SQL statements.
-
Use the Visual Studio Code Command Palette.
The results are displayed in the SQL Results page that opens when the statement completes and stored in the QUERY HISTORY menu in the sidebar. You can also save the results in a .csv file or in a spreadsheet.
-