Deploying user-defined functions¶
This article shows you how to use Db2 Developer Extension to deploy an SQL user-defined function (UDF) with various deployment options: altering previous deployments, setting target schema, and others.
One big advantage of using Db2 Developer Extension to deploy a UDF, as opposed to manually executing SQL, is that you can save the various deployment options separately from the SQL itself, which means that you can push your code into a source code manager, such as GitHub, without having to remove your personal deployment options first.
Another advantage is that you don’t need to specify --#SET TERMINATOR in the header of .udfsql files. Db2 Developer Extension uses the number sign character (#) as the default terminator character, but you can use any terminator character you want by setting an SQL routine option.
Note: Currently, Db2 Developer Extension deployment option supports only one UDF per .udfsql file. When UDF options are specified, only the first UDF in the file will be executed; additional UDFs and SQL statements will be ignored.
We’ll use the following SQL user-defined function throughout this article to demonstrate how to deploy a UDF. This UDF takes in a string as input and returns the text in reverse order. You can paste it into a file so that you try things out for yourself.
REVERSE.udfsql
CREATE FUNCTION ADMF001.REVERSE(INSTR VARCHAR(4000))
RETURNS VARCHAR(4000)
VERSION V1
DETERMINISTIC NO EXTERNAL ACTION CONTAINS SQL
BEGIN
DECLARE REVSTR, RESTSTR VARCHAR(4000) DEFAULT '';
DECLARE LEN INT;
IF INSTR IS NULL THEN
RETURN NULL;
END IF;
SET (RESTSTR, LEN) = (INSTR, LENGTH(INSTR));
WHILE LEN > 0 DO
SET (REVSTR, RESTSTR, LEN)
= (SUBSTR(RESTSTR, 1, 1) CONCAT REVSTR,
SUBSTR(RESTSTR, 2, LEN - 1),
LEN - 1);
END WHILE;
RETURN REVSTR;
END
Here’s how that same SQL user-defined function looks in Db2 Developer Extension:
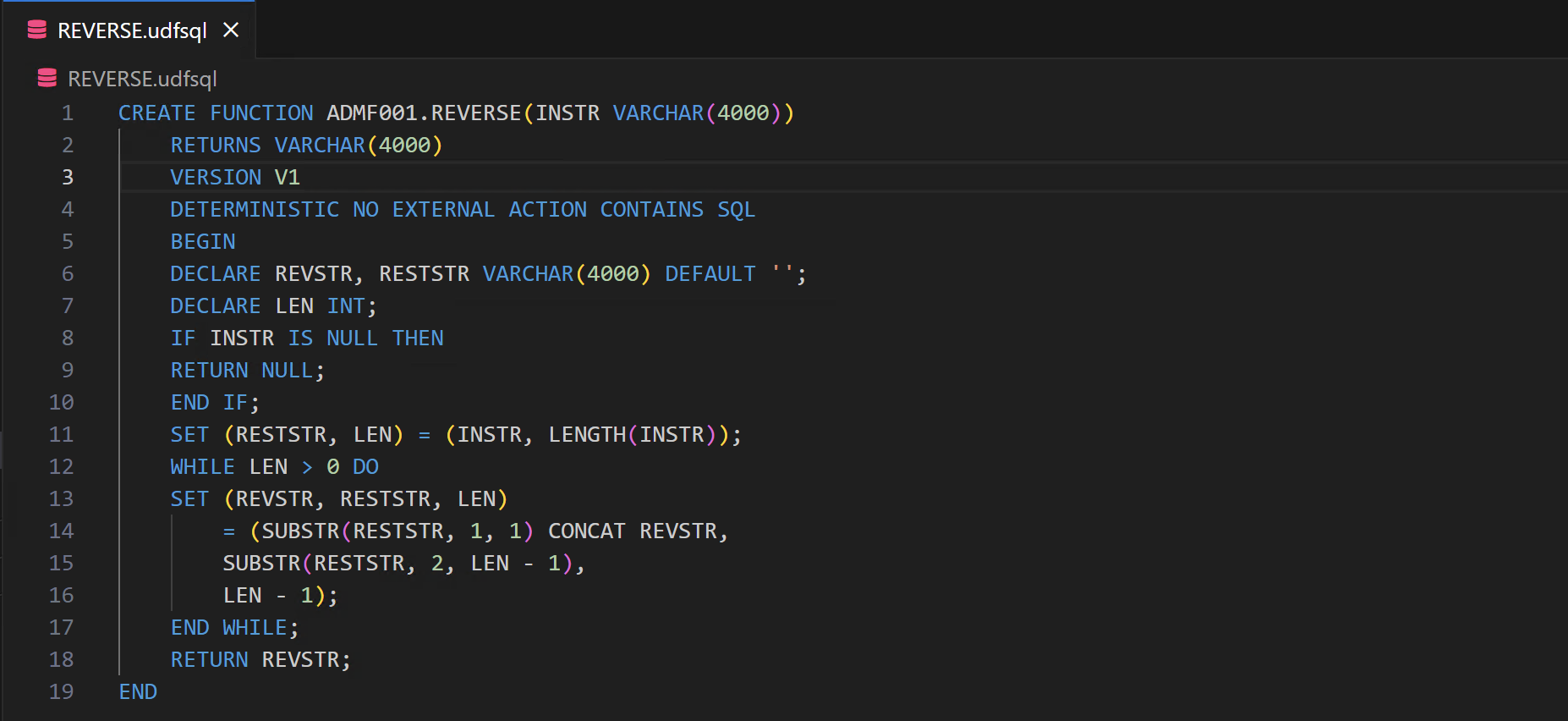
The file extension of .udfsql identifies it as an SQL user-defined function. When you open a .udfsql file in Db2 Developer Extension, the Deploy action is displayed in the toolbar in the upper right corner of the view:
![]()
Deploying a user-defined function¶
Click the Deploy action to open the Deployment view. This is where you can set and customize deployment options and save the options for the .udfsql file. These options are used only during deployment and do not impact the DDL source code.
The Deployment view consists of two sections: Deployment options and Routine options.
Deployment options¶
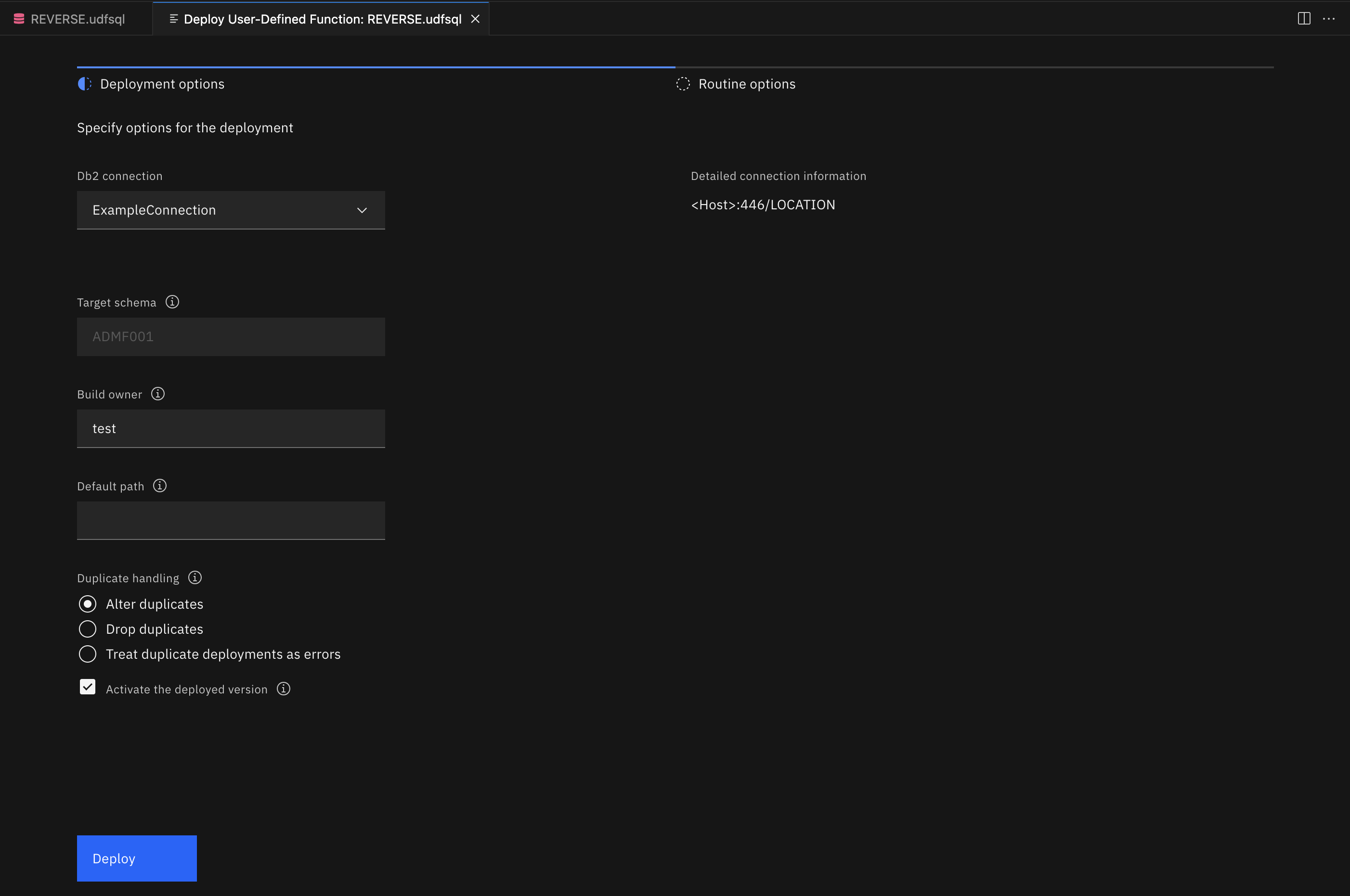
-
Use the Database connection option to select a connection from the list of defined connections. See Creating a database connection for more information.
-
Use the Target schema option for unqualified UDFs. This field is enabled only for unqualified UDFs. If the UDF is qualified (like the one in our example CREATE FUNCTION statement, which is qualified to ADMF001), the field is disabled. If you leave this field empty, the JDBC property
currentSchemawill be used. IfcurrentSchemais not set, the JDBC connection username will be used. -
Use the Build owner option to specify the owner of the UDF. If this field is left empty, the JDBC property
currentSQLIDwill be used. IfcurrentSQLIDis not set, the JDBC connection username will be used. -
Use the Default path option for resolving an unqualified data type, function, or procedure referenced by the UDF that’s being deployed. You can specify multiple schemas, each one separated by a comma. For example:
"ADMF002","ADMF003","ADMF004"
-
Use the Duplicate handling option to specify the behavior of the deployment if the UDF already exists:
-
Alter duplicates modifies the CREATE FUNCTION DDL to ALTER FUNCTION if the UDF already exists. Optionally, you can choose not to activate the UDF upon deployment; otherwise, it’s activated by default. If
VERSIONis not specified in the DDL, the Alter duplicates option is not displayed. -
Drop duplicates calls DROP FUNCTION before running the CREATE FUNCTION if the UDF already exists, creates the UDF, and activates it upon deployment. By default, Db2 activates the first version of a UDF.
-
Treat duplicate deployments as errors returns an error if the UDF already exists.
-
Routine options¶
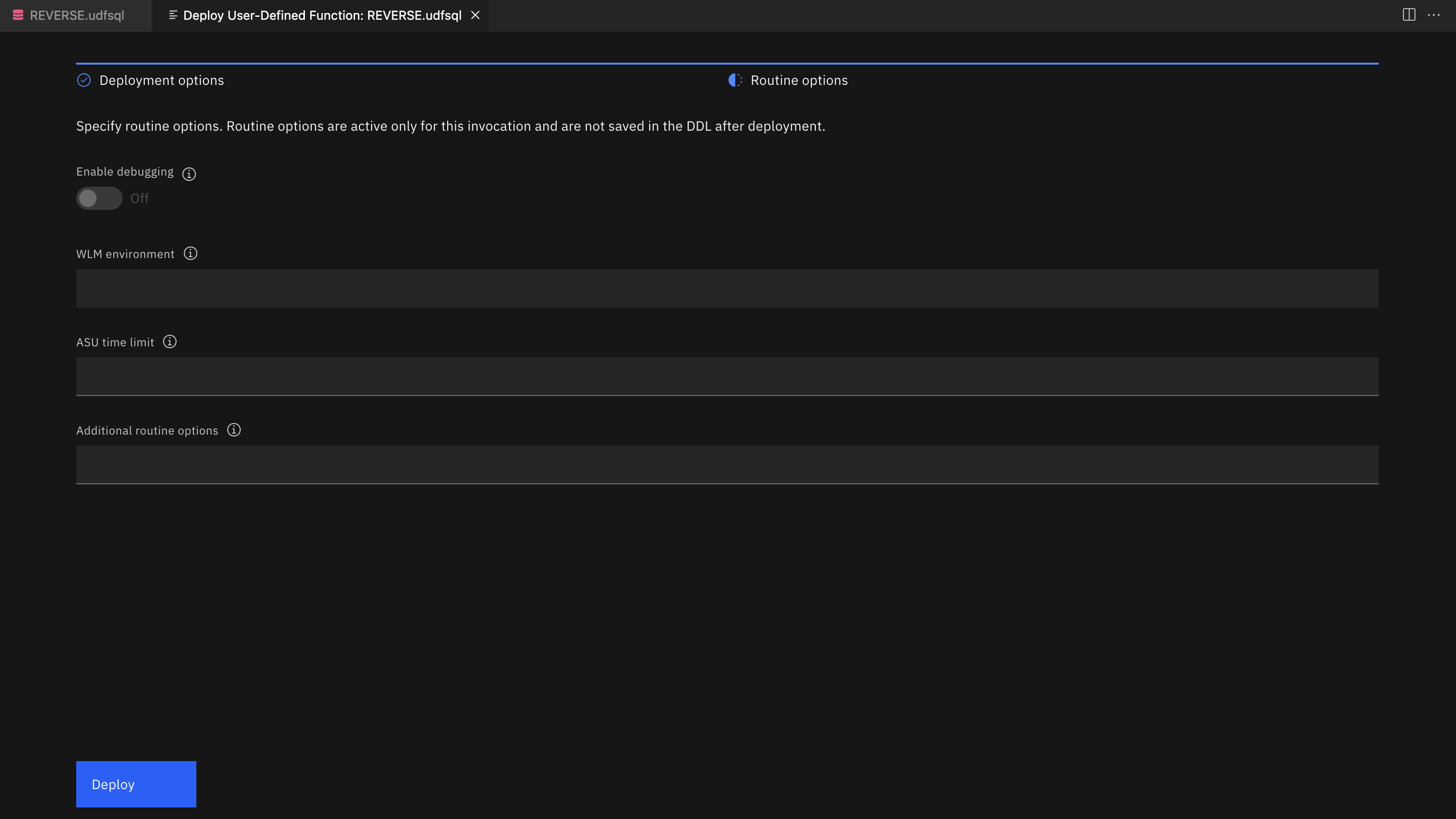
-
The Enable debugging option is currently not available for user-defined functions.
-
The WLM environment option is disabled because debugging is currently not available for user-defined functions.
-
Use the ASU time limit option to set the ASUTIME, which is the number of CPU seconds permitted for each SQL statement. The default value of 0 means NO LIMIT and is not recommended.
-
Use the Additional routine options field to specify any additional options that you want to include. Separate each option with a semicolon. For example:
QUALIFIER ADMF002; ISOLATION LEVEL RS
Note: The Routine options tab is only available for compiled SQL scalar functions.
Click Deploy to finish the configuration and begin the deployment process for the UDF.
After your SQL user-defined function is executed, the following output is displayed in the Status tab.
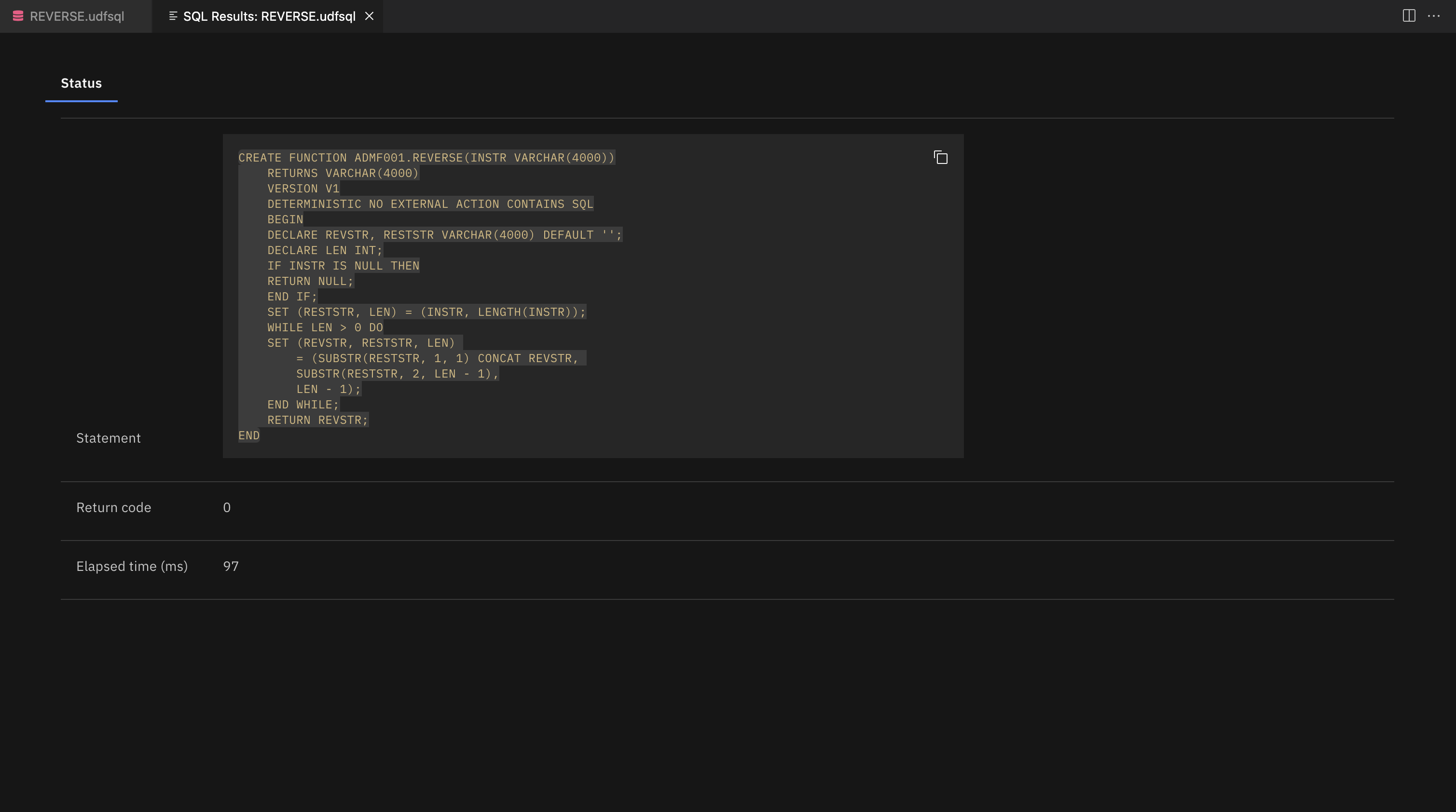
The Status tab contains overall execution status. If an error occurred, the status will contain SQL code, SQL state, and Message text.