Linting with IBM ZCodeScan
IBM® ZCodeScan enables developers to scan mainframe applications for security vulnerabilities and perform code reviews across z/OS® applications.
New: IBM ZCodeScan now supports PL/I in addition to COBOL, expanding its capabilities to cover more mainframe development languages.
ZCodeScan in Z Open Editor includes the following features:
Security vulnerabilities scanner to identify potential issues in COBOL and PL/I source code, including SQL injection risks, buffer overflow issues, unprotected credentials, and other security concerns.
Built-in rules to simplify code reviews. These rules cover typical best practices in COBOL and PL/I coding, such as proper variable initialization, safe call statements, and secure SQL usage.
Custom rules to define organization-specific coding standards and best practices. Custom rule models enable you to extend ZCodeScan with domain-specific rules tailored to your development requirements. Custom rules must be defined in separate rule model files, such as,
rules-domains.yaml, and referenced in your ZAPP profile configuration. See the IBM Developer for z/OS documentation to learn more about custom rules.Real-time code review with linting which provides instant feedback on code quality within Z Open Editor as you edit your COBOL and PL/I programs.
MCP tools for integration with AI agents which provides the results of a code scan of the currently open program or a scan of many programs specified by a Glob search pattern to AI Chat clients using the Model Context Protocol. See the Agent Mode feature for more details.
IBM ZCodeScan is provided as part of IBM Developer for z/OS Enterprise Edition, which also includes a Command Line Interface (CLI) that enables code reviews to be run from anywhere for increased flexibility. For example, the CLI can be invoked from a developer's workstation, a pipeline orchestrator, or any build framework. To learn more about the CLI, see the IBM Developer for z/OS documentation.
Currently, IBM ZCodeScan can scan COBOL programs copybook files and PL/I programs that are free of syntax errors. See Known Issues for a complete list.
Configuring ZCodeScan Rules
Important: Starting with Z Open Editor 6.2.0, ZCodeScan configuration must be done through ZAPP file(s). Configuration through zcodescan-rules.yaml at the workspace root only is no longer supported.
Overview
ZCodeScan configuration is now managed through ZAPP profiles. You can define global rules and application-specific rule overrides using YAML files referenced in your zapp.yaml configuration.
Note:
- If no ZCodeScan profile is declared in the ZAPP file(s), all the predefined rules are applied to your source code.
Creating a ZAPP Profile for ZCodeScan
Create or update the zapp.yaml file at your workspace root and define a ZCodeScan profile with the following structure:
profiles:
- name: zcodescan
type: zcodescan
settings:
rules:
- type: local
locations:
- "zcodescan/sam-rules.yaml"
- "zcodescan/rules.yaml"
customRuleModels:
- type: local
locations:
- "zcodescan/rules-domains.yaml"
customRuleJars:
- type: local
locations:
- "zcodescan/rules-domains.jar"
Note:
- The
locationsproperty supports glob patterns, enabling you to target multiple YAML files with a single pattern. For example, you can use patterns such as"zcodescan/*-rules.yaml"to match all rule files in the directory, or"zcodescan/**/*.yaml"to recursively match YAML files in subdirectories. - See our samples GitHub repository wazi-main branch for an example ZAPP file and example rules files for COBOL and PL/I that can be used with the sample programs available in this repository as well.
- To learn more about custom rules, see the IBM Developer for z/OS documentation.
Global Rules Configuration
Define global rules in a file such as zcodescan/rules.yaml. This file contains standard rules with their default severities that apply across your entire workspace.
Example structure:
rules:
rules:
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.BinarySubscriptRule
severity: LOW
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.RequireEndClauseRule
severity: HIGH
statements:
- name: "If"
value: true
- name: "Call"
value: true
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.UnprotectedAuthCredentialRule
severity: LOW
Application-Specific Rule Overrides
Create application-specific rules files (e.g., zcodescan/sam-rules.yaml) to override global definitions for particular applications. This allows you to adjust rule severities or enable/disable specific rules To override the global rules in the profile this file must be before the global rule file..
Example:
rules:
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.BinarySubscriptRule
severity: BLOCKER
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.UnprotectedAuthCredentialRule
severity: OFF
Note:
- The Multi-root VS Code workspace example contains a concrete sample of rules overriding..
Running a Code Scan
On-Demand Scan
Manually trigger a scan from the editor:
- Open a COBOL program file.
- Right-click in the editor and select Execute IBM ZCodeScan.
- Alternatively, open the VS Code Command Palette and select IBM Z Open Editor: Execute IBM ZCodeScan.
Live Scan
To enable ZCodeScan in Z Open Editor:
- Open User settings (Cmd/Ctrl + ,)
- Go to IBM Z® Open Editor or search for
zcodescan - Enable Zcodescan: Enable Live Z Code Scan
ZCodeScan will now run on your COBOL files and provide instant feedback on code quality.
Reviewing Scan Results
Issues identified by the scanner are presented through a linter-style interface, with squiggly underlines in the code and corresponding entries in the VS Code Problems View. These issues are highlighted based on the configurable severity of each rule:
- BLOCKER: Red
- HIGH: Red
- MEDIUM: Yellow
- LOW: Yellow
- INFO: Blue
Viewing Issue Details
If you hover over an issue in the editor, a Quick Fix menu appears, which offers the Learn more about the issue option. This opens a separate view beside the editor that displays the Rule Details document, as shown in the screenshot below.
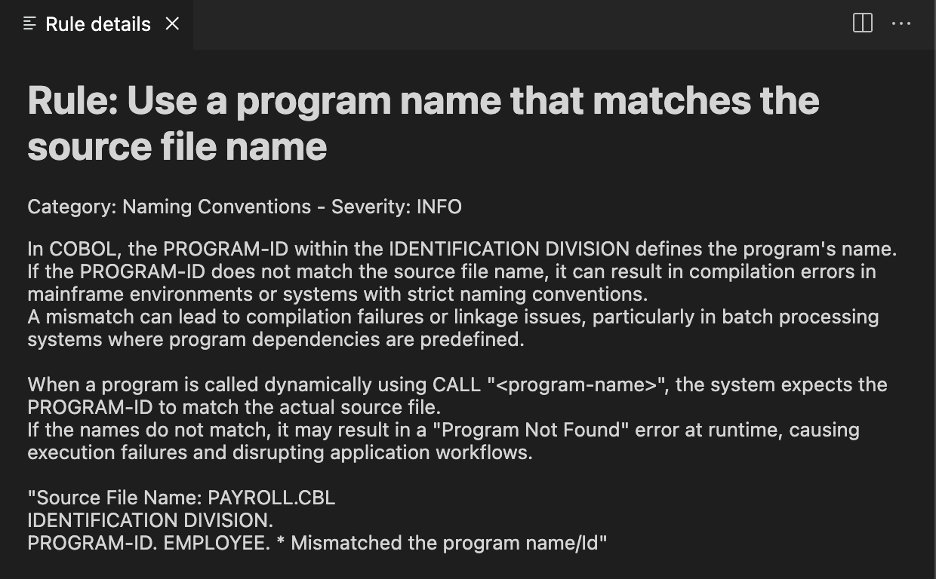
You can also see the list of issues and details in the Problem View. Click the 💡 icon to view the Learn more about this IBM ZCodeScan issue and open the details view.
Managing Rules
Available Rules
By default when no ZCodeScan profile is declared in ZAPP file(s), all defined IBM ZCodeScan rules apply to the current VS Code workspace. The IBM Developer for z/OS documentation contains reference pages for rule management:
- See Defining Rules for the list of available rules.
- See Client Rule for details on rule configuration.
Enabling or Disabling Rules
If you do not want all predefined rules to be included in your scan, you can create a file named zcodescan/rules.yaml edit the ZAPP zapp.yaml file and create a ZCodeScan profile. The following is an example of a rules file. For detailed syntax, refer to the linked documentation.
rules:
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.ProgramIdRule
severity: INFO
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.CallSyntaxRule
severity: INFO
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.SqlWhereRule
severity: HIGH statements:
- name: "Select"
value: True
- name: "Delete"
value: True
- name: "Update"
value: true
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.RequireEndClauseRule
severity: HIGH statements:
- name: "If" value: true
- name: "Evaluate"
value: true
- name: "Read"
value: true
- name: "Search"
value: true
- name: "Call"
value: True
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.AcceptRule
severity: INFO
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.GotoRule severity: INFO
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.GotoParagraphRule
severity: MEDIUM
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.UnprotectedAuthCredentialRule
severity: HIGH
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.BufferOverflowRule
severity: INFO
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.UninitialzedVariablesRule
severity: MEDIUM
- id: zcodescan.cobol.rules.AcceptDateTimeRule
severity: MEDIUM
- id: zcodescan. cobol.rules.SqlInjectionRule
severity: INFO
You can also find this example in the Z Open Editor samples Git repository at https://github.com/IBM/zopeneditor-sample/blob/wazi-main/zcodescan/rules.yaml.
Note: VS Code multi-root workspaces are supported. Programs are scanned using the rules file located in the same workspace.
Modify rule severities or disable rules in your rules file:
- Set
severity: OFFto disable a rule - Set
severity: BLOCKER,HIGH,MEDIUM,LOW, orINFOto adjust severity levels - Use the
statementsproperty to enable/disable specific rule behaviors
Multi-Root Workspaces
VS Code multi-root workspaces are supported. Programs are scanned using the rules file and ZAPP profile located in the workspace. The priority of the rules is defined by the order of the folders contained in the multi-root workspace configuration. The first folder has the highest priority.
Editing Rules Files in VS Code
VS Code helps you edit rules files by providing code completion and documentation hovers for the YAML content. This requires you to install the Red Hat YAML VS Code extension and configure the schema file for rules files.
Setup Instructions
Install the YAML Language Support by Red Hat plugin to enable YAML syntax highlighting and schema validation in VS Code.
Click the gear icon ⚙️ in the Sidebar of the editor and select Settings.
Search for
Yaml: Schemasand click Edit in settings.json to open the "settings.json" file.Add the ZCodeScan rules schema to your YAML schemas configuration:
"yaml.schemas": { "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IBM/zopeneditor-about/refs/heads/main/zcodescan/zcodescan-rules-1.2.0.json": ["*rules.yaml"], "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IBM/zopeneditor-about/refs/heads/main/zcodescan/zcodescan-rules-domains-1.2.0.json": ["*domains.yaml"] }If you are working in an air gap configuration and cannot access the internet, ask your administrator to download the schema file and provide it locally. Use a local file URL instead:
"yaml.schemas": { "file:///path/to/zcodescan-rules-1.2.0.json": ["*rules.yaml"], "file:///path/to/zcodescan-rules-domains-1.2.0.json": ["*domains.yaml"] }After you configure the YAML VS Code extension with the schema, you open your rules file and test code completion by adding a file pattern to the schema. Here are some suggested file patterns you can use:
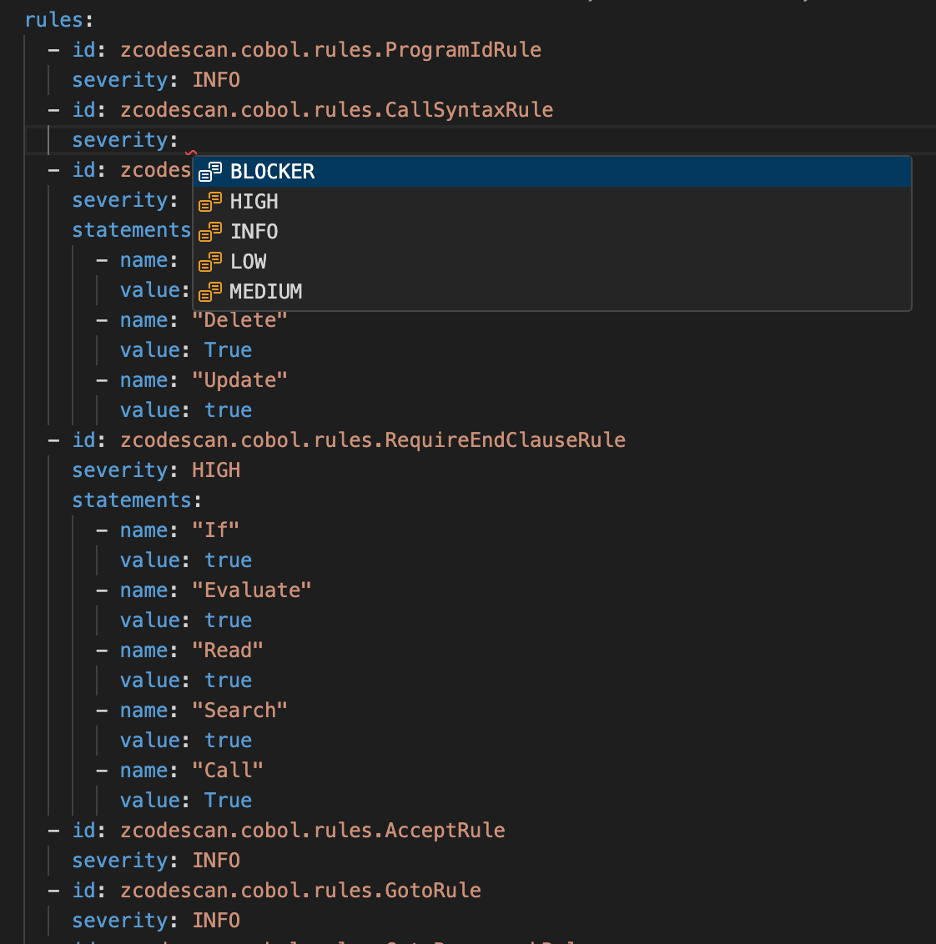
You can now see the schema validation active in configuration files. Use the autocomplete feature by pressing CTRL+Space to display options based on the current index context, or type a keyword and press TAB.